Radio Widget Documentation
Overview
The Radio widget allows users to select a single option from a predefined list of choices. It renders as a group of radio buttons where only one option can be selected at a time.
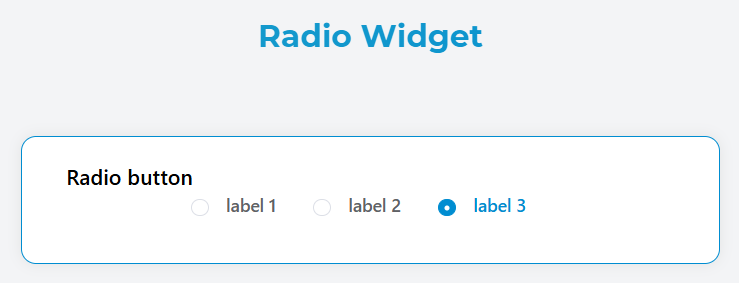
Basic Configuration
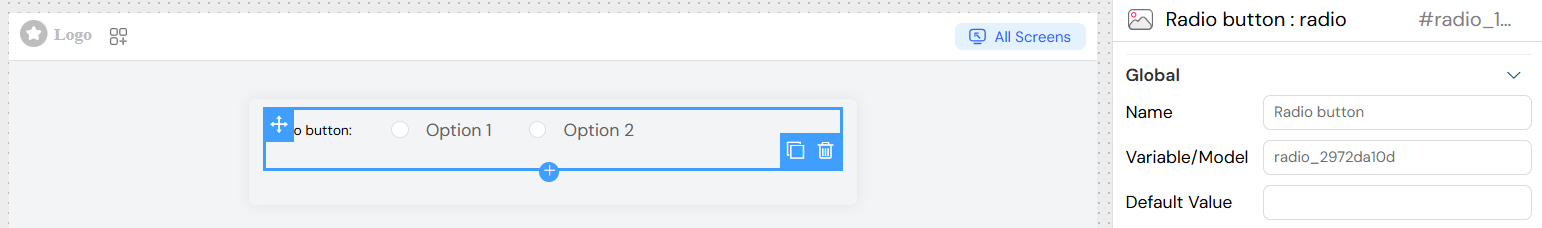
Global Settings
Name
- Field: Name
- Description: The display label for the radio group
- Required: Yes
- Example: "Select Priority Level"
Variable/Model
- Field: Variable/Model
- Description: The data model property that stores the selected value
- Required: Yes
- Format: Must be a valid variable name
- Example:
priority_level
Default Value
- Field: Default Value
- Description: The initial selected value when the form loads
- Required: No
- Type: String
- Example: "medium"
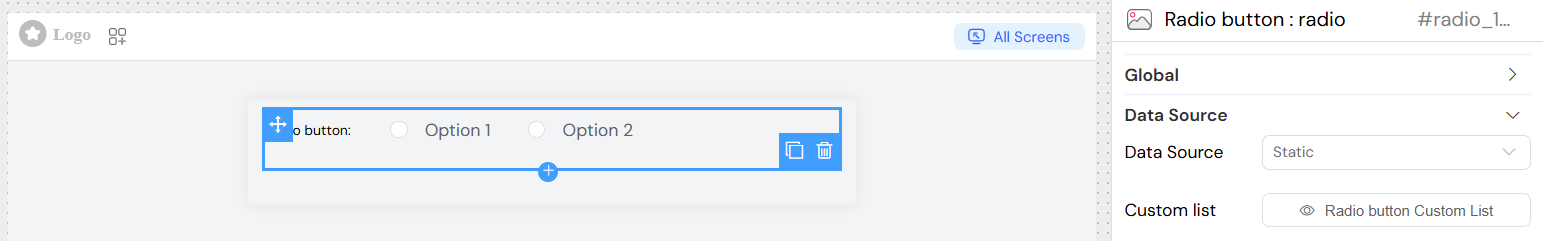
Data Source Configuration
The radio widget supports multiple data sources for populating the available options:
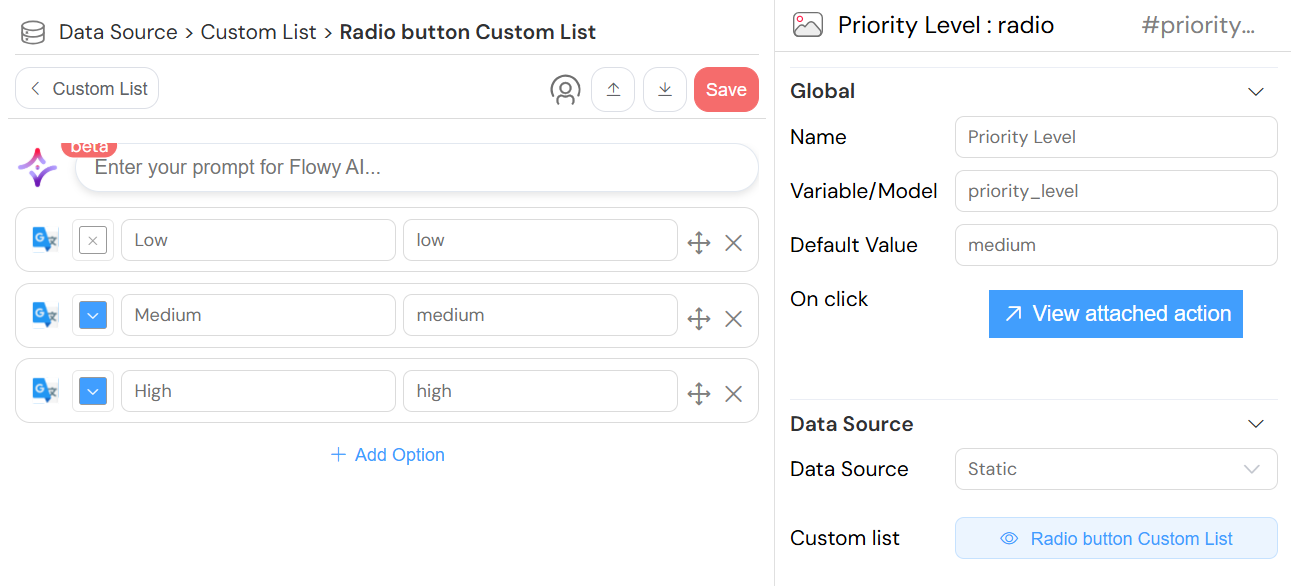
Static Data
- Source: Custom Lists
- Description: Use predefined static lists
- Configuration:
- Select an existing custom list
- Create a new custom list if none exists
- Data Format: Each item requires
labelandvalueproperties
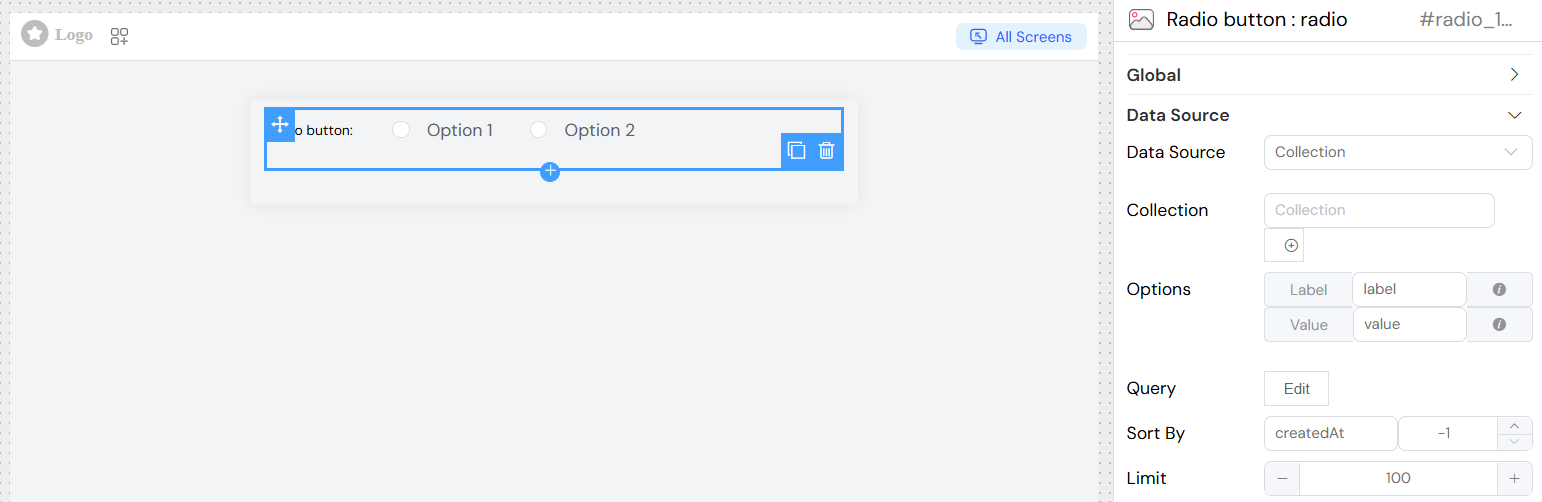
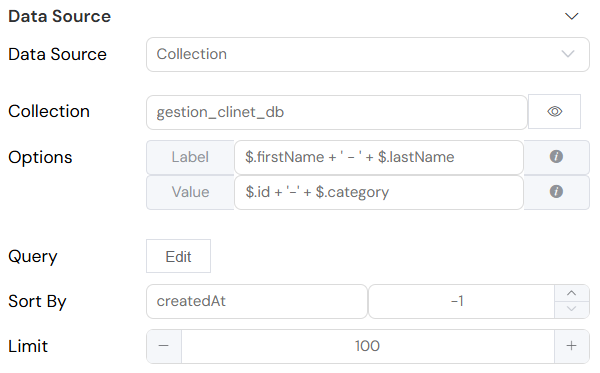
Collection Data
- Source: Database Collections
- Description: Dynamically load options from a collection
- Configuration:
- Select target collection
- Configure label and value mappings
- Set up optional query filters
- Define sort order and limits
Report Data
- Source: Reports
- Description: Use report results as data source
- Configuration:
- Select target report
- Map result columns to label/value
- Configure aggregation if needed
SQL/External Database
- Source: External Database Connection
- Description: Query external databases for options
- Configuration:
- Select database connection
- Write SQL query
- Map result columns
](/img/04_ressources/project/web-interface/widgets/radioDataSourceEDS.png)
Props Configuration
For dynamic data sources (Collection, Report, SQL):
Label Property
- Field: Label
- Description: Field name or expression for display text
- Static Usage:
firstName - Dynamic Usage:
$.firstName + ' - ' + $.lastName
Value Property
- Field: Value
- Description: Field name or expression for stored value
- Static Usage:
id - Dynamic Usage:
$.id + '-' + $.category
Query Configuration
For collection and report data sources:
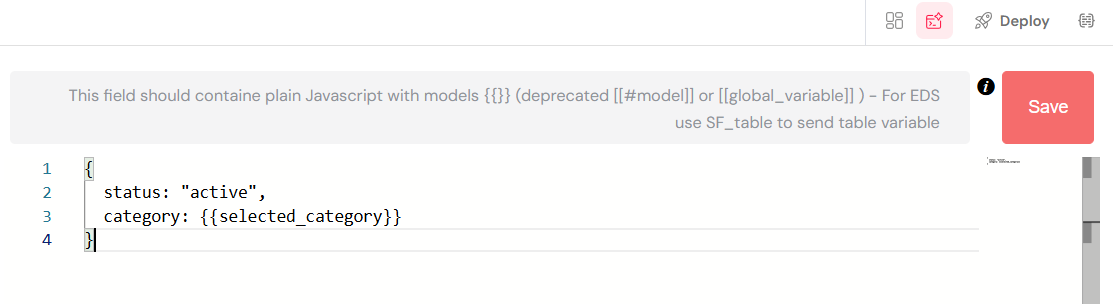
Basic Query
- Purpose: Filter and customize data retrieval
- Language: JavaScript with model references
- Variables: Use
{{variable_name}}for dynamic values - Example:
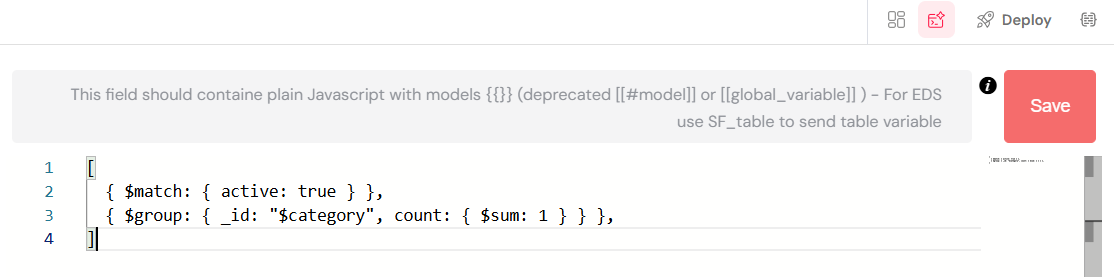
Aggregation
- Purpose: Perform complex data aggregation
- Toggle: Enable "Is Aggregation" switch
- Example:
Sort Configuration
- Sort By: Field name for sorting
- Direction:
1for ascending-1for descending
Limit
- Purpose: Restrict number of options
- Type: Number
- Default: No limit
Validation
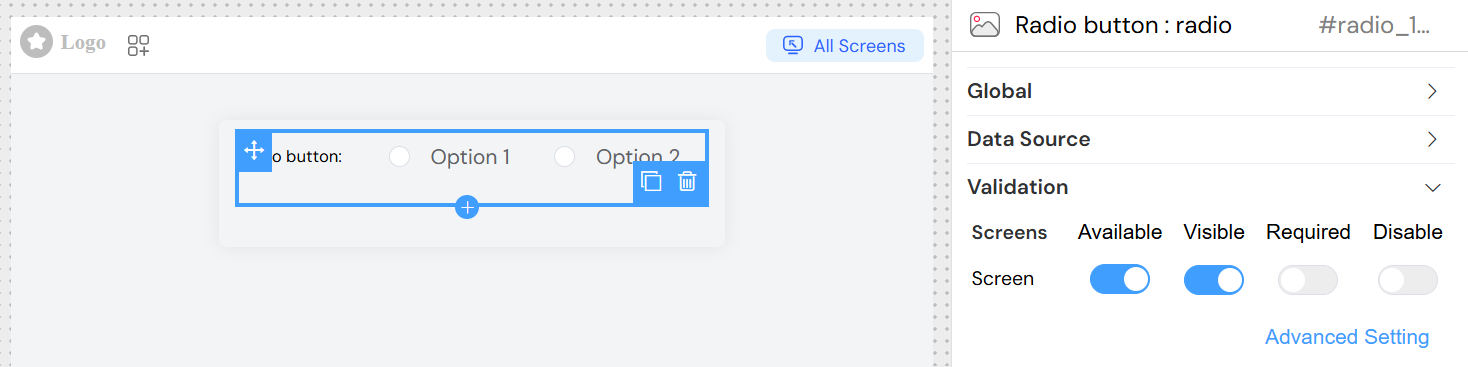
Screen-based Validation
Configure different behaviors across multiple screens:
Available
- Purpose: Control if widget appears on specific screens
- Type: Boolean per screen
- Default: true
Visible
- Purpose: Control widget visibility
- Options:
- Simple: Boolean toggle
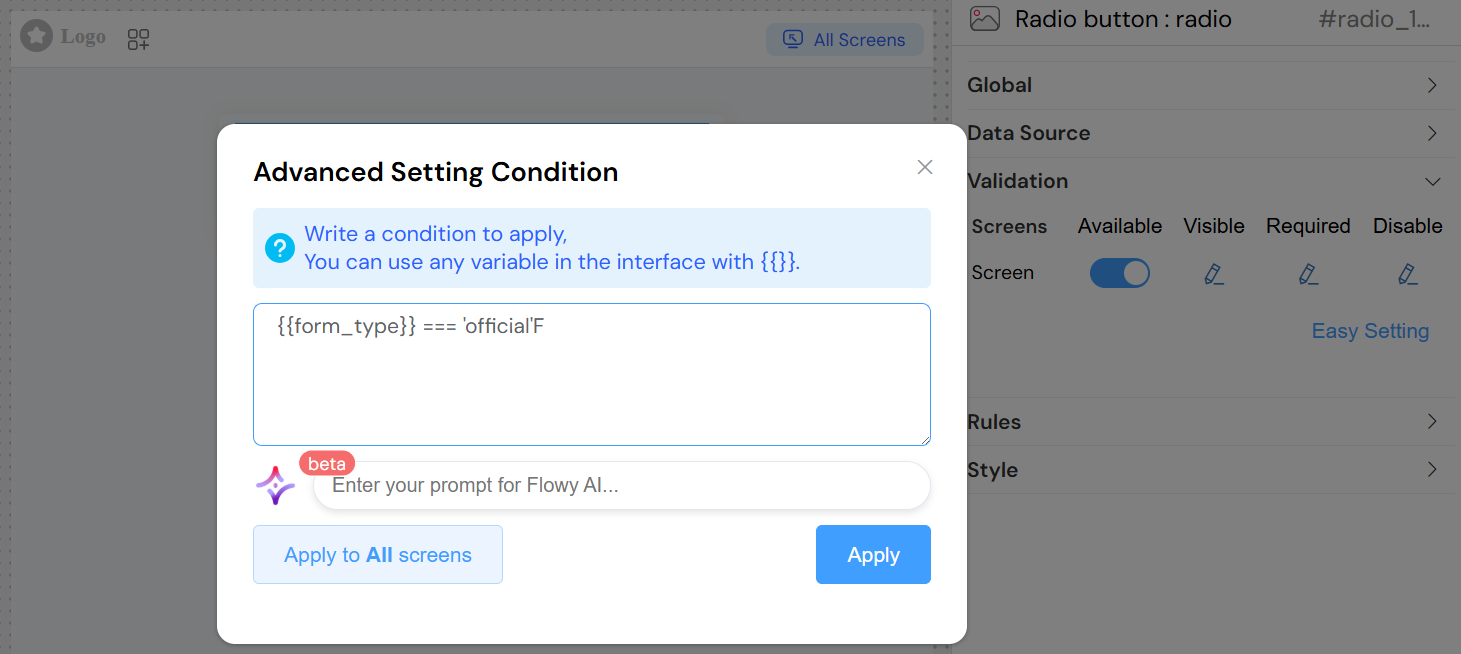
- Advanced: JavaScript condition
Required
- Purpose: Make selection mandatory
- Options:
- Simple: Boolean toggle
- Advanced: JavaScript condition
Disabled
- Purpose: Prevent user interaction
- Options:
- Simple: Boolean toggle
- Advanced: JavaScript condition
Simple Example
Advanced Example
Validation Rules
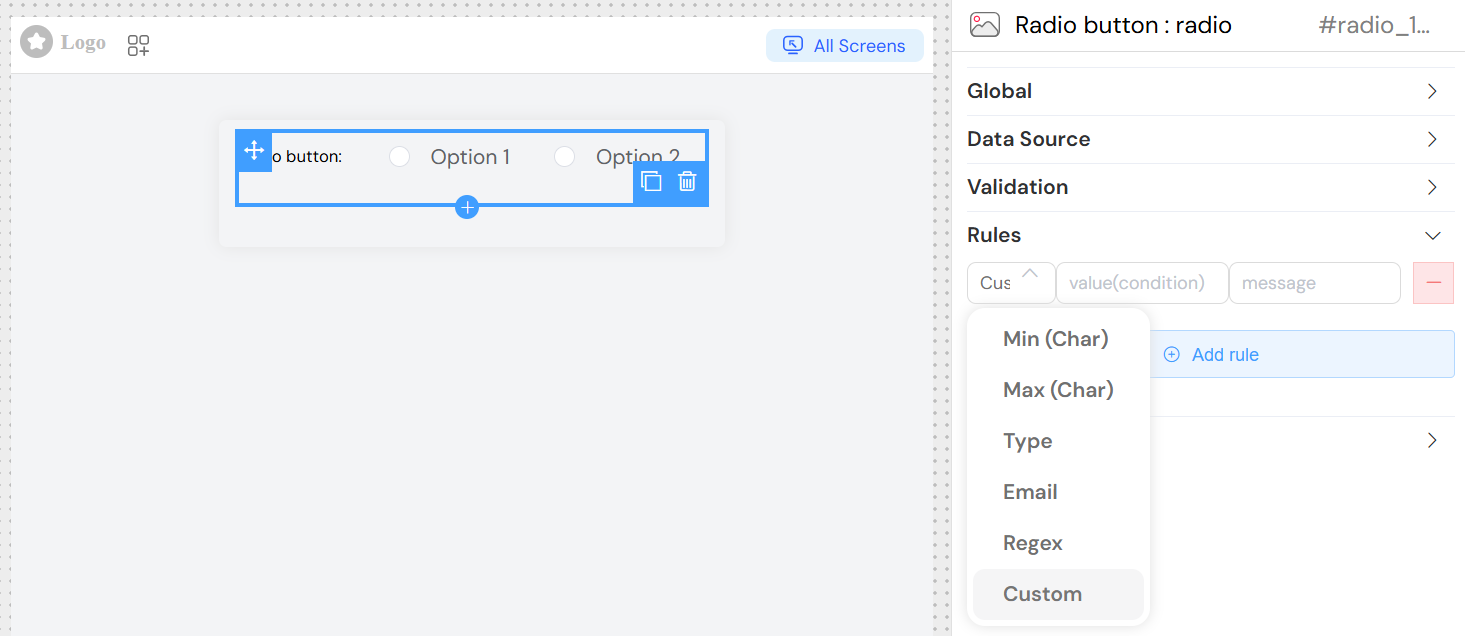
Add custom validation rules:
Rule Types
- Pattern: Regular expression validation
- Custom: JavaScript validation function
- Range: Value range validation
- Required: Built-in required validation
Rule Configuration
- Rule: Select validation type
- Value: Rule parameter or pattern
- Message: Error message to display
Styling and Layout
Layout Options
Display Mode
- Block: Vertical stack (default)
- Inline: Horizontal arrangement
Border
- Purpose: Add borders around radio buttons
- Type: Boolean
- Default: false
Width Configuration
- Field: Width
- Description: CSS width value
- Examples:
100%(full width)300px(fixed width)50vw(viewport-based)
CSS Classes
Static Classes
- Field: Class
- Description: Space-separated CSS class names
- Example: "custom-radio highlight-group"
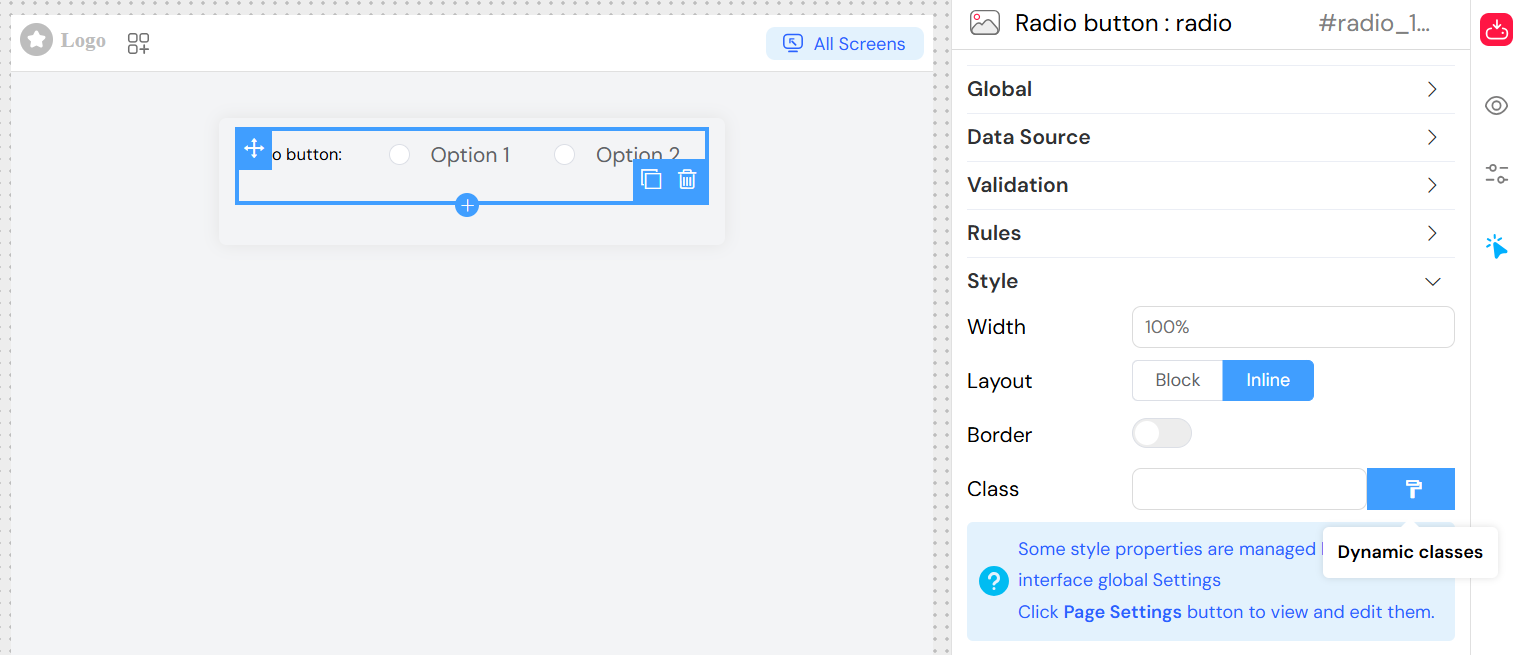
Dynamic Classes
- Purpose: Conditional styling based on data
- Language: JavaScript expressions
- Access: Click "Dynamic classes" button
- Example:
{
'error-state': {{has_errors}},
'required-field': {{is_required}}
}
Events and Interactions
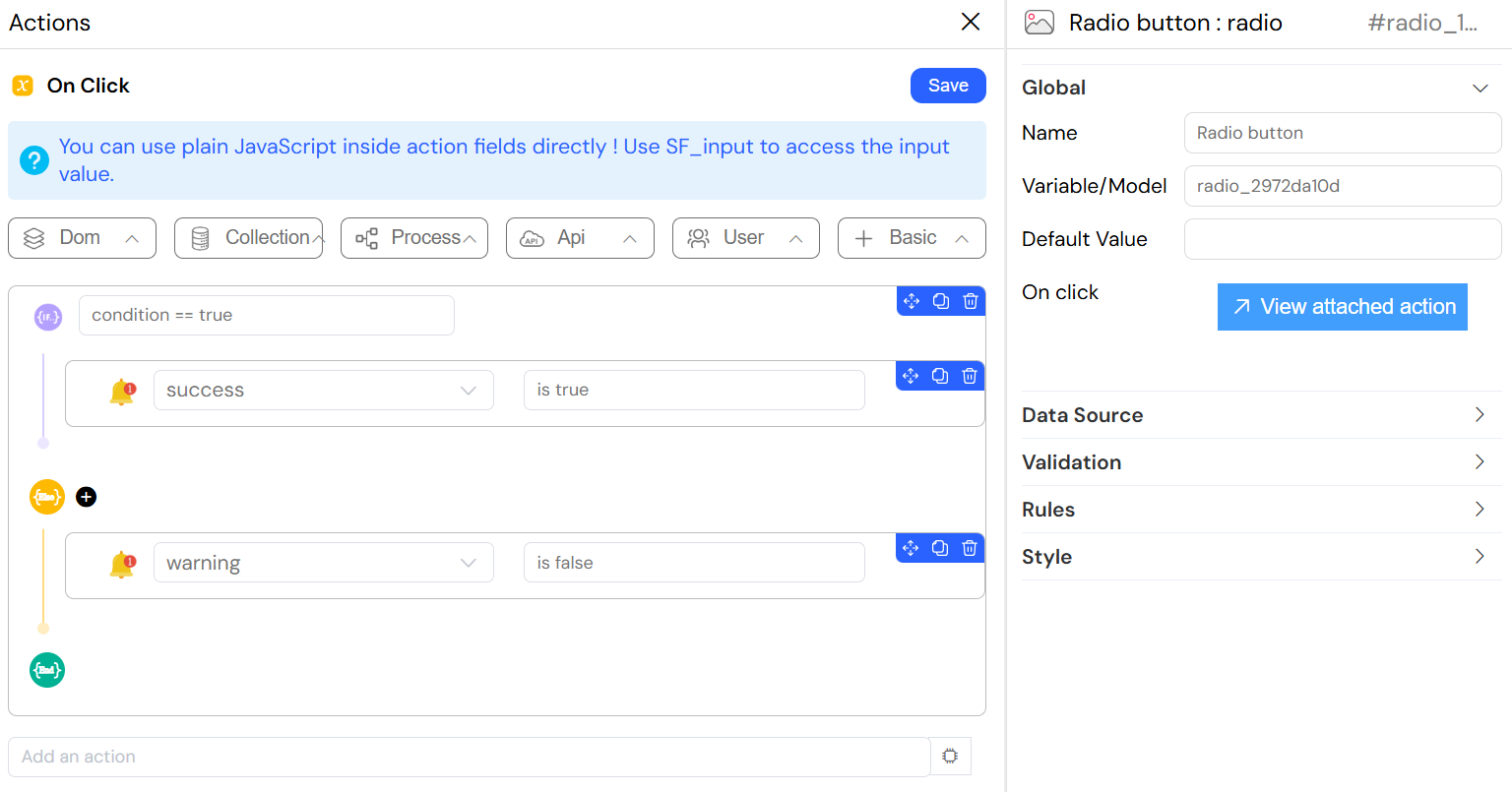
On Click Event
- Trigger: When radio option is selected
- Access Variables:
SF_input.value: Selected valueSF_input.SF_data: Full selected objectSF_input.SF_currentIndex: Loop index (if in repeating context)
Simple Event
- Field: On click
- Type: Function name
- Example:
Working with Actions and SF_input
Attaching Actions to onChange Event
The radio widget's onChange (or onClick) event allows you to execute custom Actions when the user selects an option. This functionality is powerful for:
- Auto-populating form fields with data from the selected option
- Creating dependent field relationships and cascading updates
- Fetching related information from the backoffice database
- Implementing conditional logic based on the selection
How to Attach an Action
- Navigate to the Global section in the radio widget configuration
- Find the On Click or On Change event field
- Write plain JavaScript code directly in the action field
- The code executes automatically whenever the user selects a radio option
Accessing Values with SF_input
The radio widget provides rich data access through the SF_input object. Unlike simple value storage, you get access to both the selected value AND the complete data object from your data source.
SF_input Structure for Radio Widget
{
value: /* The selected value based on your "Value Property" configuration */,
SF_data: /* Complete JSON object of the selected item */,
SF_currentIndex: /* Loop index if widget is inside a loop */
}
Understanding SF_input Properties
| Property | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| value | The selected value from your "Value Property" configuration | 'option1', 'high_priority', 'DEPT001' |
| SF_data | Complete JSON object of the selected radio option | {id: 'opt1', name: 'Option 1', details: {...}} |
| SF_currentIndex | Current iteration index if the widget is in a loop | 0, 1, 2, ... |
Practical Examples
Example 1: Access Selected Value
// Get the selected value
console.log(SF_input.value);
// Output: 'high'
// Store the selected value
model.selected_priority = SF_input.value;
// Use value in conditional logic
if (SF_input.value === 'urgent') {
model.requires_immediate_action = true;
}
Example 2: Access Complete JSON Object (SF_data)
The most powerful feature - accessing the full data object with all its properties:
// Access the complete data object
console.log(SF_input.SF_data);
// Output: {
// id: 'PRIORITY_HIGH',
// value: 'high',
// label: 'High Priority',
// sla_hours: 4,
// escalation_level: 2,
// notification_required: true,
// color_code: '#FF5733',
// description: 'Requires immediate attention'
// }
// Access any property from the selected option
model.sla_hours = SF_input.SF_data.sla_hours;
model.escalation_level = SF_input.SF_data.escalation_level;
model.priority_color = SF_input.SF_data.color_code;
model.priority_description = SF_input.SF_data.description;
// Use boolean flags from the data
if (SF_input.SF_data.notification_required) {
model.send_notification = true;
model.notification_type = 'urgent';
}
Example 3: Fill Multiple Fields from Backoffice Data
When you connect a radio widget to a Collection, Report, or SQL data source, each option contains a complete record. Use SF_data to populate related fields:
// When user selects a department from radio options connected to Departments collection
if (SF_input.SF_data) {
const department = SF_input.SF_data;
// Auto-fill department information
model.department_id = department.id;
model.department_name = department.name;
model.department_code = department.code;
model.department_location = department.location;
// Fill management information
model.department_head = department.manager_name;
model.department_head_email = department.manager_email;
model.department_head_phone = department.manager_phone;
// Fill budget information
model.department_budget = department.annual_budget;
model.budget_spent = department.budget_utilized;
model.budget_remaining = department.annual_budget - department.budget_utilized;
// Fill operational details
model.employee_count = department.total_employees;
model.office_location = department.office?.building + ', Floor ' + department.office?.floor;
model.cost_center = department.cost_center_code;
// Set conditional fields
if (department.requires_approval) {
model.approval_required = true;
model.approver_id = department.approval_authority;
}
}
Best Practices
Always Validate SF_data: Check if SF_data exists before accessing its properties
if (SF_input.SF_data) {
// Your code here
}Use Optional Chaining: For nested properties, use optional chaining to prevent errors
const managerEmail = SF_input.SF_data?.manager?.email || 'Not available';Leverage SF_data for Rich Information: Always use SF_data when you need more than just the value - it gives you access to the complete record from your data source
Clear Dependent Fields: When selection changes, clear fields that depend on the previous selection
// Clear previous data
model.related_field_1 = null;
model.related_field_2 = null;
// Then populate with new data from SF_input.SF_dataHandle Edge Cases: Check for null/undefined values and provide defaults
model.field = SF_input.SF_data?.property || 'default value';Use Descriptive Variable Names: Make your code readable and maintainable
const selectedDepartment = SF_input.SF_data;
const departmentBudget = selectedDepartment.budget;Document Complex Logic: Add comments to explain business rules
// Apply VIP discount if customer lifetime value exceeds threshold
if (SF_input.SF_data.lifetime_value > 10000) {
model.vip_discount = 20;
}Error Handling: Wrap asynchronous operations in try-catch
try {
const data = await SF_executeAction('fetchData', { id: SF_input.value });
// Process data
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error:', error);
model.error_message = 'Failed to fetch data';
}
Best Practices
Data Source Selection
- Static Lists: For fixed, rarely changing options
- Collections: For user-managed data
- Reports: For computed/aggregated options
- SQL: For complex external data
Performance Optimization
- Use limits for large datasets
- Implement proper indexing for sort fields
- Cache static data when possible
- Use aggregation for summary options
User Experience
- Provide clear, descriptive labels
- Use logical ordering (alphabetical, priority-based)
- Set appropriate default values
- Include validation with helpful error messages
Validation Strategy
- Use required validation for critical fields
- Implement conditional validation when needed
- Provide immediate feedback on selection
- Consider cross-field validation rules
Examples
Basic Static Radio Group
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Options Not Loading
- Check data source configuration
- Verify query syntax
- Ensure proper field mappings
- Check network connectivity for external sources
Selection Not Saving
- Verify model variable name
- Check validation rules
- Ensure proper form submission
- Validate data types
Styling Issues
- Check CSS class names
- Verify width/height values
- Review responsive design settings
- Test dynamic class conditions
Event Not Triggering
- Verify function names
- Check JavaScript syntax
- Ensure proper variable access
- Review browser console for errors