Timer Widget
Overview
The Timer widget provides a comprehensive time tracking solution that can count up or count down from a specified duration. It displays time in HH:MM:SS format and includes functionality for starting, stopping, and tracking both active running time and break time periods.
Configuration Options
Basic Configuration
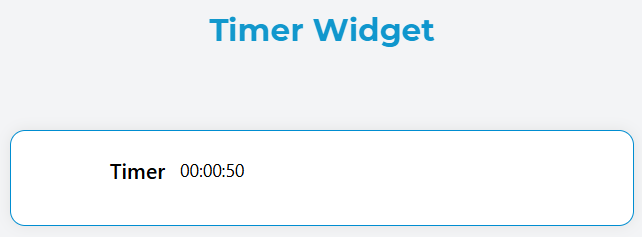
Widget Identity
- Name: Display name for the widget
- Variable/Model: The data model name that stores the timer values
Timer Settings
Count Type
Choose how the timer should behave:
Up: Timer counts upward from 00:00:00
- Displays
(+)prefix when exceeding the set duration - Useful for tracking elapsed time with optional time limits
- Displays
Down: Timer counts downward from the set duration
- Displays
(-)prefix when going below zero - Useful for countdown timers and deadline tracking
- Displays
Duration
- Input: Number of seconds for the timer duration
- Purpose:
- For count-up mode: Sets the target/limit time
- For count-down mode: Sets the starting countdown value
- Format: Enter value in seconds (e.g., 3600 for 1 hour)
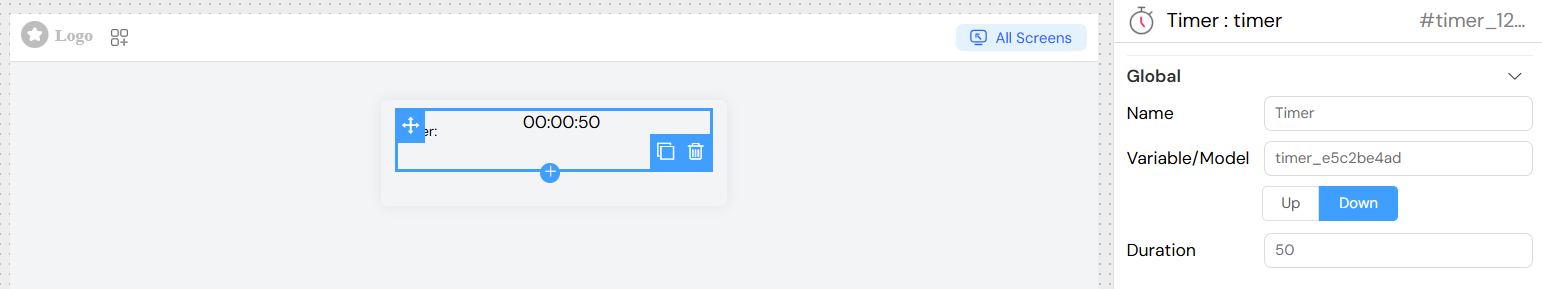
Validation Settings
The timer widget supports comprehensive validation rules across different screens:
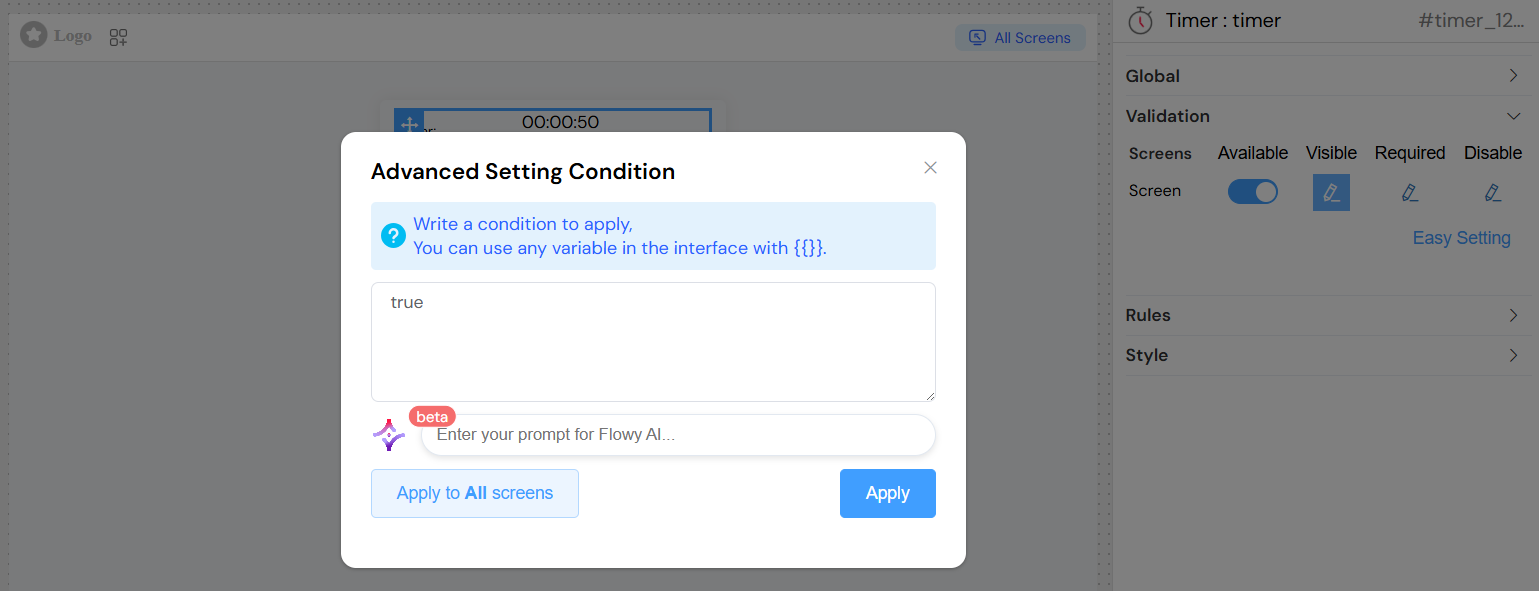
Screen-based Validation
Configure different behaviors for each screen in your application:
- Available: Whether the widget appears on the screen
- Visible: Whether the widget is visible (supports dynamic conditions)
- Required: Whether interaction with the timer is mandatory
- Disable: Whether the timer controls are disabled

Advanced Validation
- Dynamic Conditions: Use JavaScript expressions with model variables
- Example:
{{userRole}} === 'admin'to show timer only for admin users
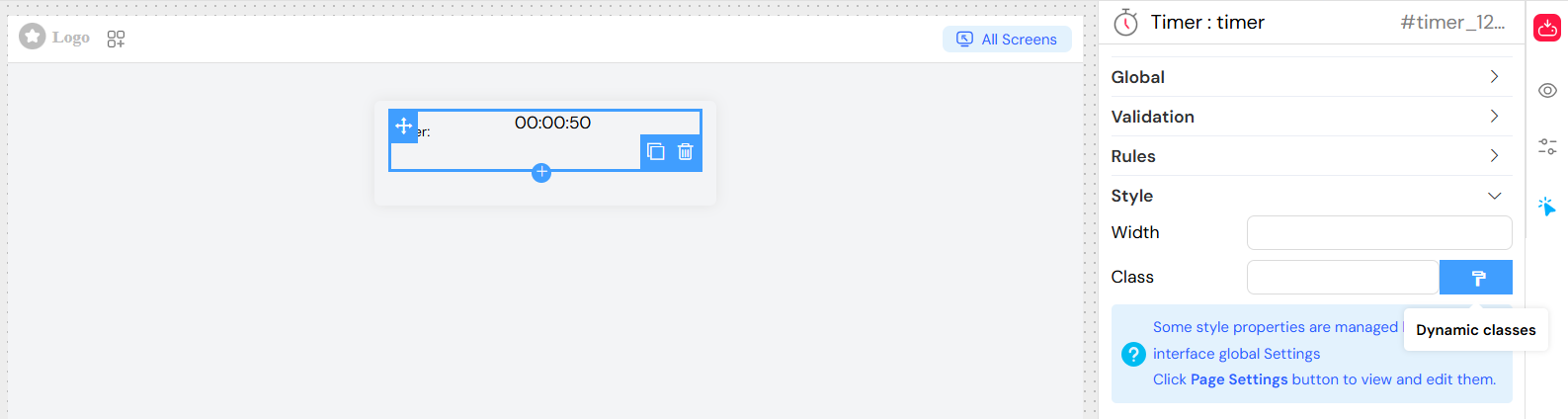
Styling Options
Layout
- Width: Set custom width for the timer display
- Class Names: Add custom CSS classes for styling
- Dynamic Classes: JavaScript expressions for conditional styling
Appearance
- Placeholder: Not applicable for timer widget
- Border: Enable/disable border around the timer
- Inline Layout: Display timer inline with other elements
Rules and Validation
Custom Validation Rules
Add validation rules to ensure proper timer usage:
- Required: Make timer interaction mandatory
- Custom Rules: JavaScript-based validation functions
- Error Messages: Custom error messages for validation failures
Usage Instructions
Basic Setup
- Add Timer Widget: Drag the Timer widget to your interface
- Set Model Name: Choose a unique variable name (e.g.,
workTimer) - Configure Count Type: Select "Up" or "Down" based on your needs
- Set Duration: Enter the duration in seconds
Count-Up Timer Example
Configuration:
- Count Type: Up
- Duration: 3600 (1 hour)
- Model:
workSession
Behavior:
- Starts at 00:00:00
- Counts upward: 00:00:01, 00:00:02, etc.
- Shows "(+) 01:00:01" when exceeding 1 hour
Count-Down Timer Example
Configuration:
- Count Type: Down
- Duration: 1800 (30 minutes)
- Model:
breakTimer
Behavior:
- Starts at 00:30:00
- Counts downward: 00:29:59, 00:29:58, etc.
- Shows "(-) 00:00:01" when going below zero
Timer Controls
The timer widget provides the following methods that can be called programmatically:
- startTimer(): Begins or resumes the timer
- stopTimer(): Pauses the timer and begins break time tracking
Data Model
Generated Variables
When you create a timer with model name timerName, the system automatically creates:
Primary Variables
timerName: Formatted time string (HH:MM:SS format)timerName_runTime: Total running time in secondstimerName_breakTime: Total break time in seconds
Usage in Other Components
Access timer data in other widgets or actions:
// Get formatted time
let currentTime = {{timerName}};
// Get raw running time in seconds
let runSeconds = {{timerName_runTime}};
// Calculate net working time (run time minus breaks)
let netTime = {{timerName_runTime}} - {{timerName_breakTime}};
Advanced Features
Break Time Management
The timer automatically tracks break periods:
- When
stopTimer()is called, break time tracking begins - Break time continues until
startTimer()is called again - Both run time and break time increment during break periods
Time Calculation Logic
Count-Up Mode
time = runTime - breakTime;
if (duration && time > duration) {
prefix = "(+) ";
}
Count-Down Mode
time = duration - (runTime - breakTime);
if (time < 0) {
time = Math.abs(time);
prefix = "(-) ";
}
Integration with Forms
The timer integrates seamlessly with form validation:
- Can be marked as required field
- Supports form submission with timer data
- Validates timer state before form processing
Event Handling
onClick Events
Configure actions to trigger when the timer display is clicked:
- Navigate to detailed time tracking page
- Show timer statistics
- Export time data
Form Integration
The timer automatically updates form data when:
- Timer starts or stops
- Time values change
- Form is submitted
Best Practices
Performance Optimization
- Use appropriate duration values (avoid extremely large numbers)
- Consider impact of multiple timers on page performance
- Implement proper cleanup when timers are not needed
User Experience
- Provide clear visual indicators for timer state
- Use appropriate count type for the use case
- Include instructions for users on how to operate the timer
Data Management
- Regularly save timer data to prevent loss
- Consider server-side synchronization for important timing data
- Implement backup mechanisms for critical time tracking
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Timer Not Starting
- Check if widget is enabled and visible
- Verify JavaScript console for errors
- Ensure proper model name configuration
Incorrect Time Display
- Verify duration is set in seconds
- Check count type matches intended behavior
- Validate time calculation logic
Performance Issues
- Limit number of active timers per page
- Check for memory leaks in interval management
- Monitor browser performance with developer tools
Browser Compatibility
- Supports all modern browsers
- Uses standard JavaScript timing functions
- Responsive design works on mobile devices
Technical Implementation
Dependencies
- Vue.js framework
- Element UI components
- Standard JavaScript timing functions
Browser Requirements
- Modern browser with JavaScript enabled
- Support for setInterval/clearInterval functions
- CSS3 support for styling
Security Considerations
- Timer data should be validated on server side
- Consider rate limiting for timer operations
- Implement proper session management for persistent timers