APIs
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are a set of rules and protocols that enable different software applications to communicate and interact with each other. Softyflow provides a powerful API builder that allows you to create custom APIs for integration and data exchange between different platforms, services, and systems.
Creating an API
Softyflow provides an intuitive interface for creating APIs. To create a new API, access the API section located on the left-hand side of the builder interface and provide a name for your API.
The API creation interface allows you to quickly set up new APIs by providing a unique name and initial configuration settings.
Development Modes
Softyflow offers two development approaches for building APIs:
- Native Code: Write JavaScript code directly for custom logic
- Pre-defined Actions: Use visual workflow builder with pre-configured actions
To switch between development modes, click the toggle switch button located at the upper-middle position of the interface.
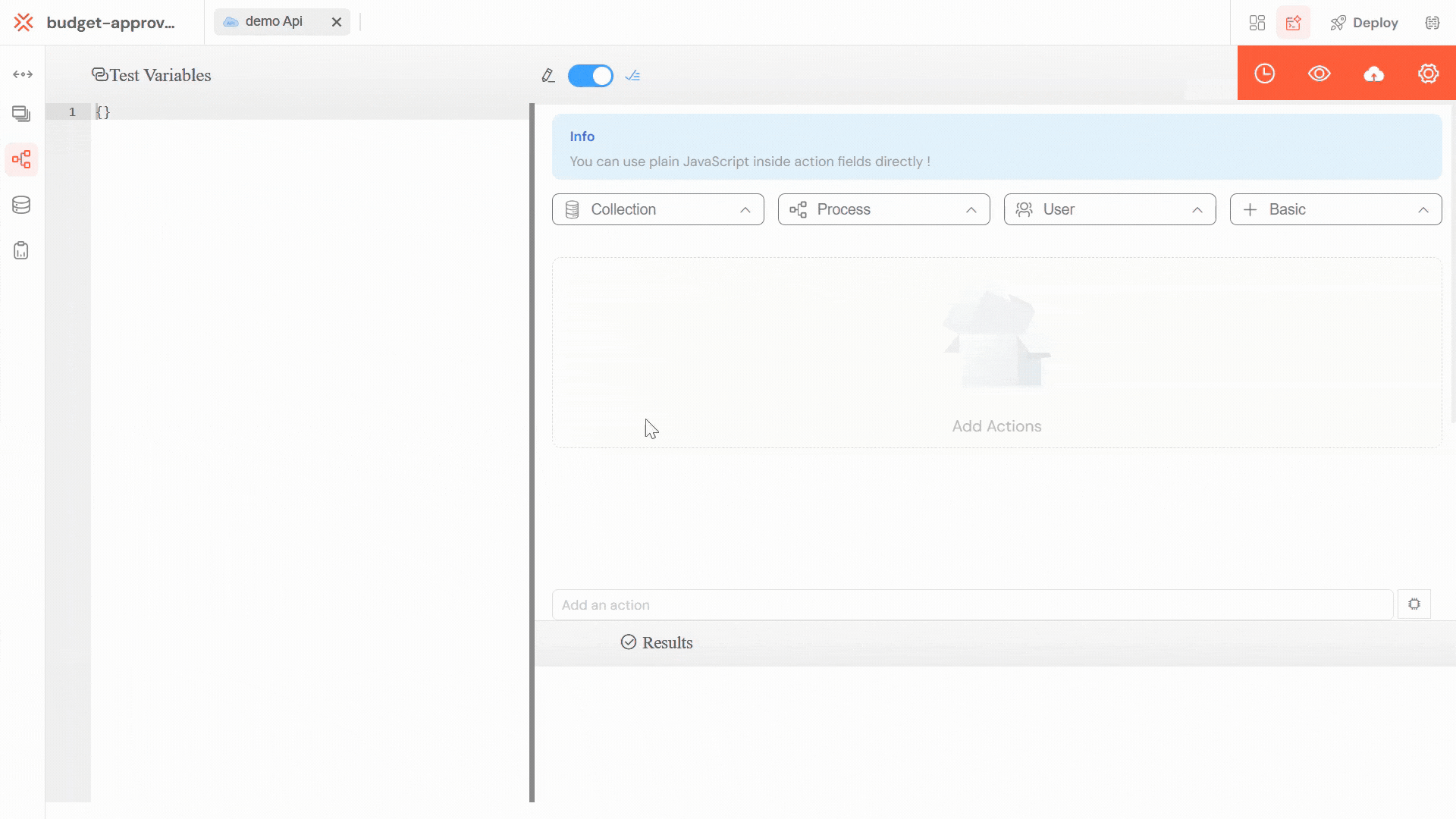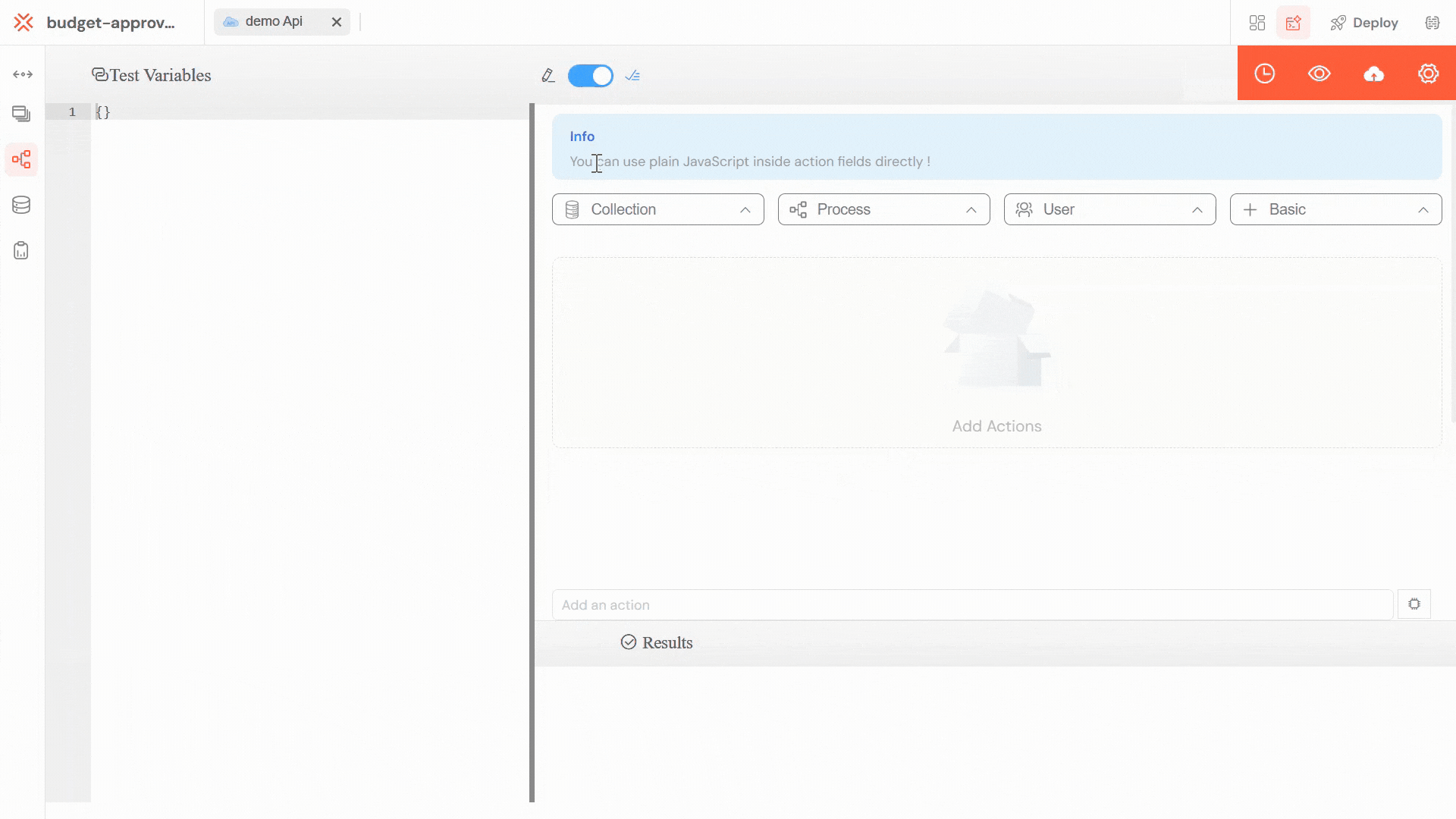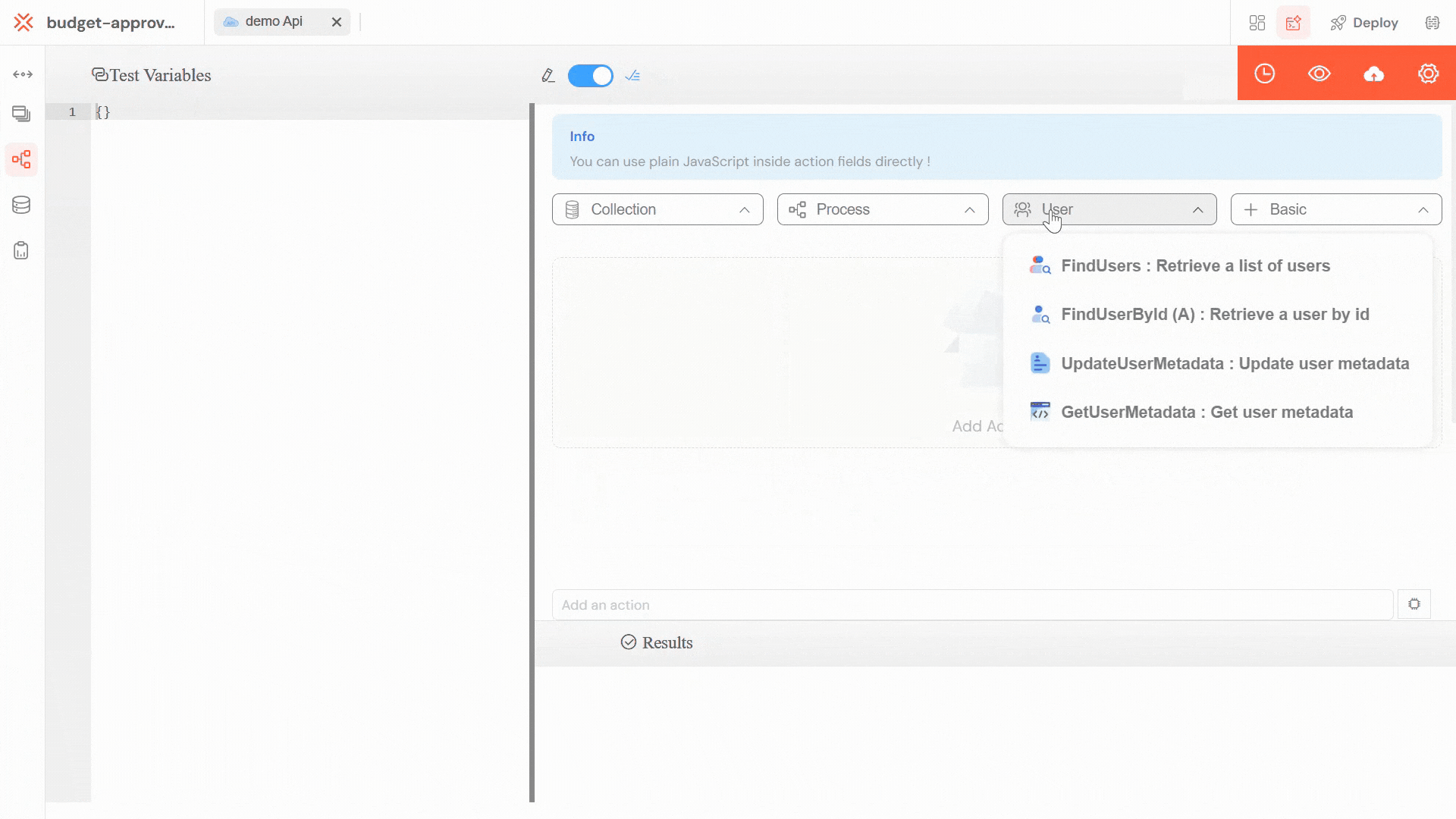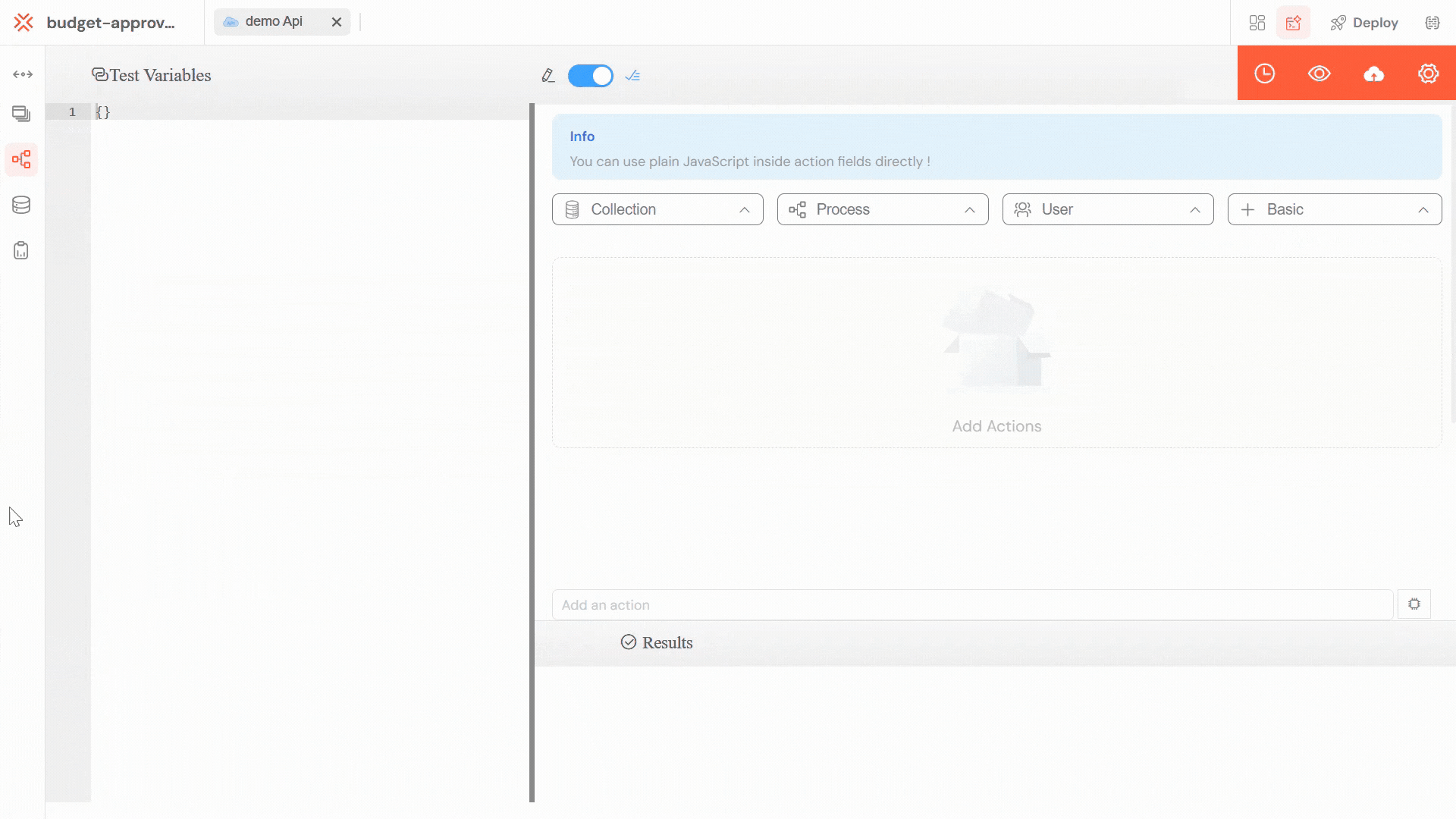
Available System Variables
Softyflow provides several system variables that are automatically available during API development:
| Variable | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
SF_body | Object | Contains the request body data sent to the API |
SF_headers | Object | Contains the HTTP headers from the API request |
SF_query | Object | Contains query parameters from the API URL |
SF_mode | String | Execution mode: "test", "uat", or "prod" |
SF_initiator | Object | Contains information about the user who invoked the API |
Configuring an API
To access API configuration settings, click the settings icon button to open the configuration panel. This panel provides comprehensive control over your API's properties and permissions.
The configuration panel allows you to manage API settings, access rights, and monitor execution logs.
Configuration Options
General Settings
During the API configuration process, administrators can:
- API Name: Modify the API's identifier
- Access Rights: Define who can invoke the API
- Select specific user groups
- Set as public for unrestricted access
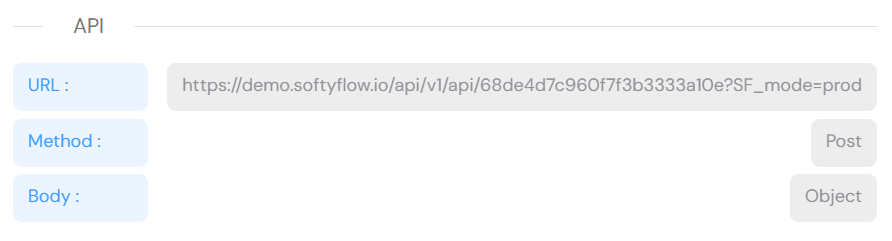
API Information
The configuration panel displays essential API details:
Endpoint Information:
- URL: The complete endpoint URL where the API is accessible
- Method: HTTP method used (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE)
- Body: Expected payload structure and data format
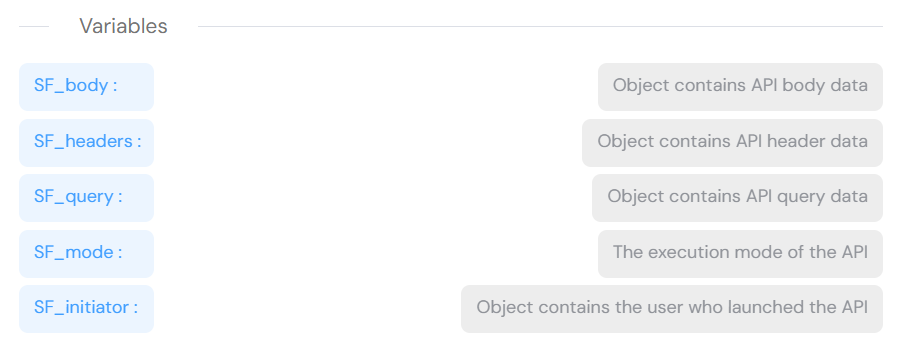
System Variables:
- SF_body: Request body payload
- SF_headers: Request headers
- SF_query: URL query parameters
- SF_mode: Current execution environment
- SF_initiator: User who invoked the API
Execution Logs
The logs section captures detailed execution information:
- User: Identity of the user who invoked the API
- Launch Date: Timestamp of the API call
- Result: Execution outcome and response data
- Details: Click the eye icon to view complete execution details

Logs provide valuable insights for debugging, monitoring API usage, and tracking performance.
Testing and Running APIs
Testing an API
Softyflow provides built-in testing capabilities during the development phase. You can define test variables and validate API behavior before deployment.
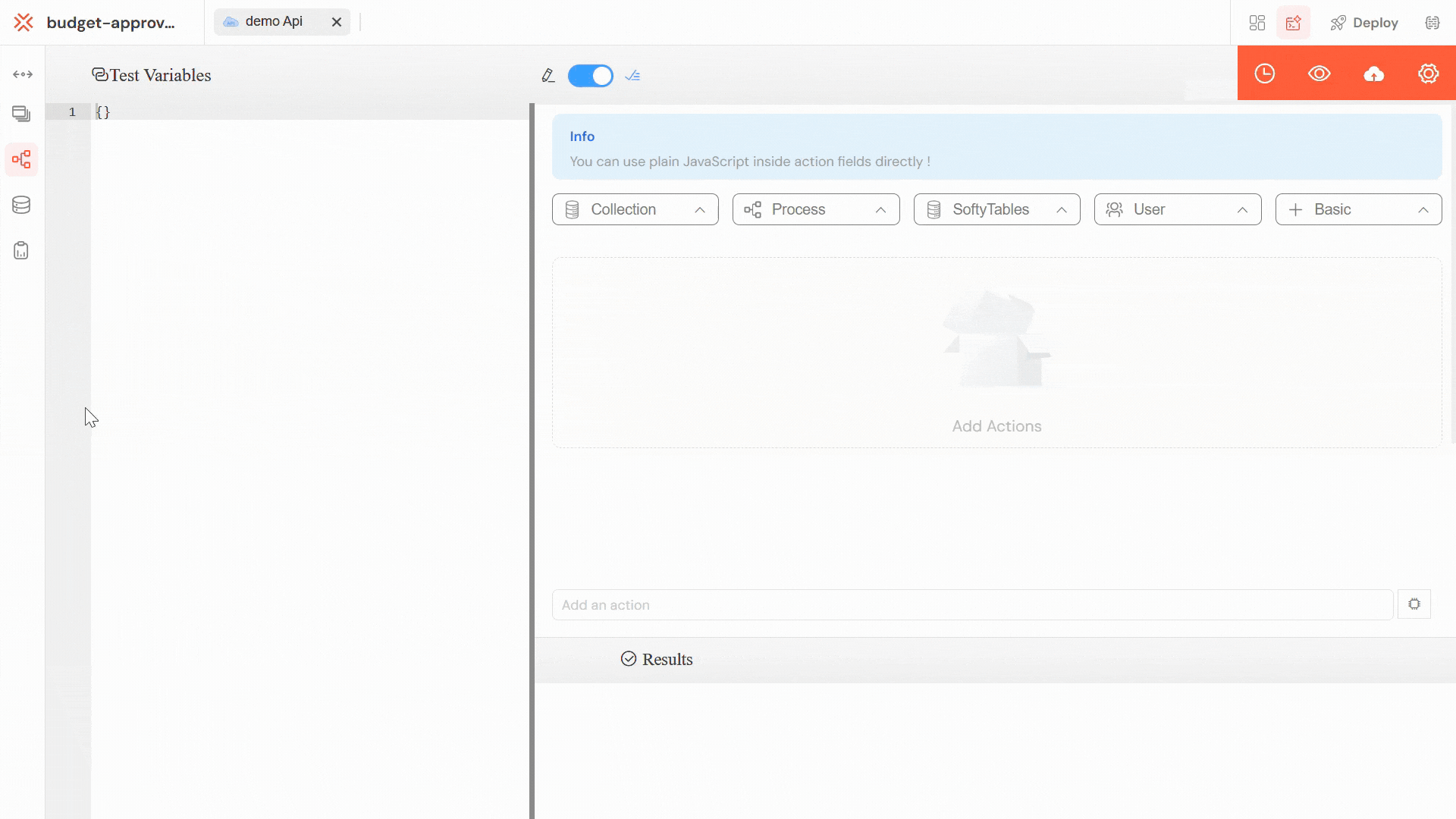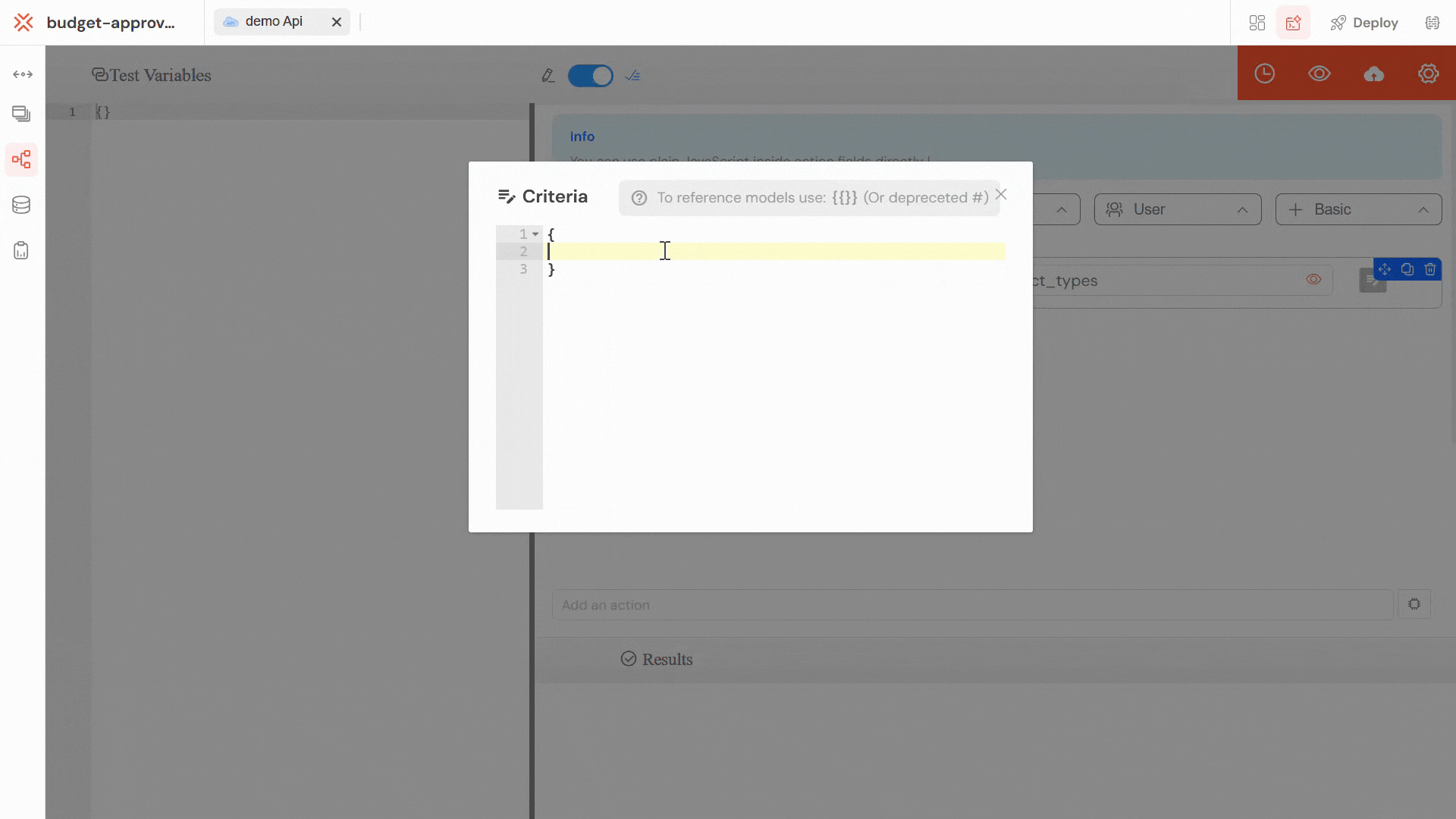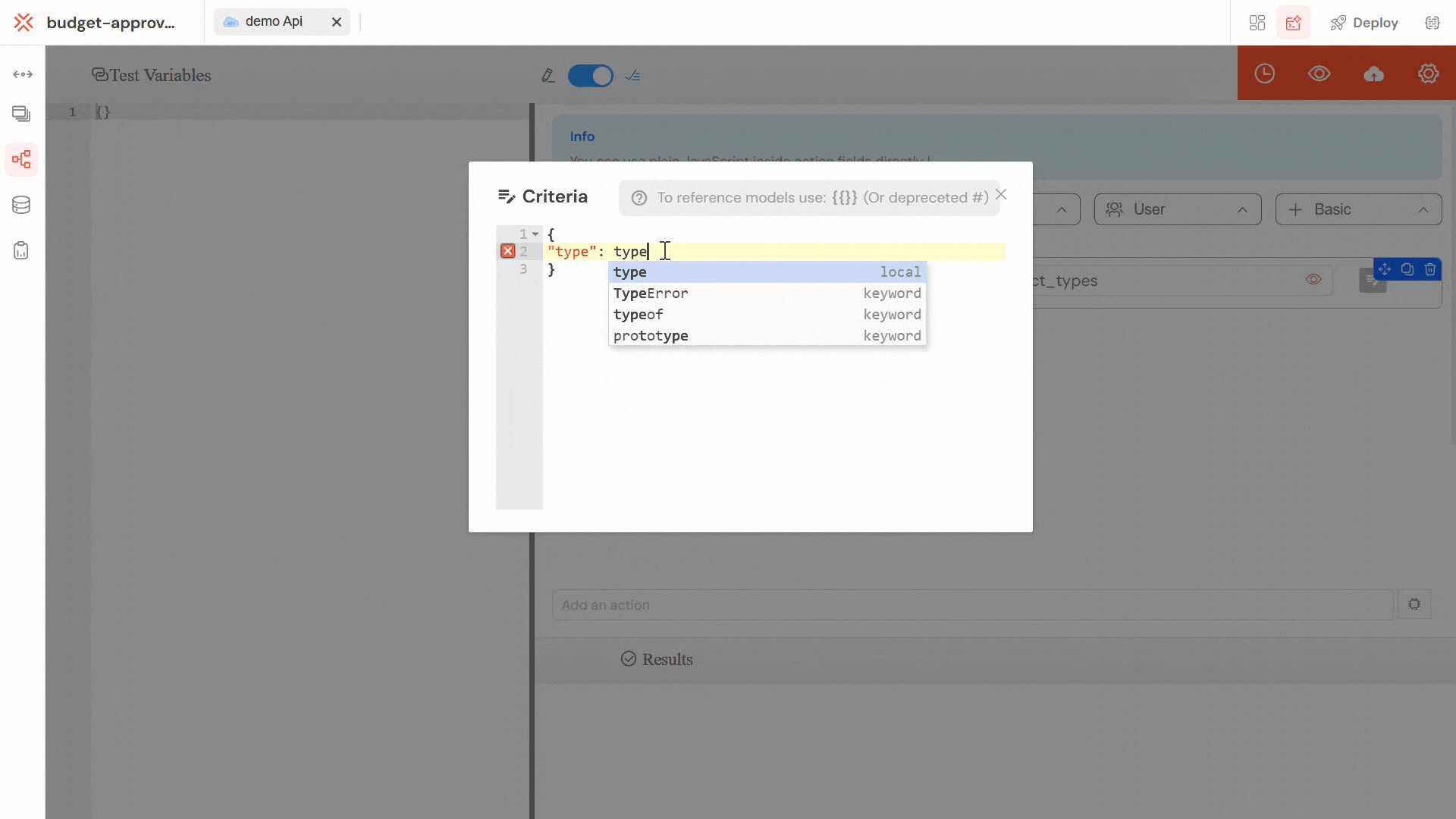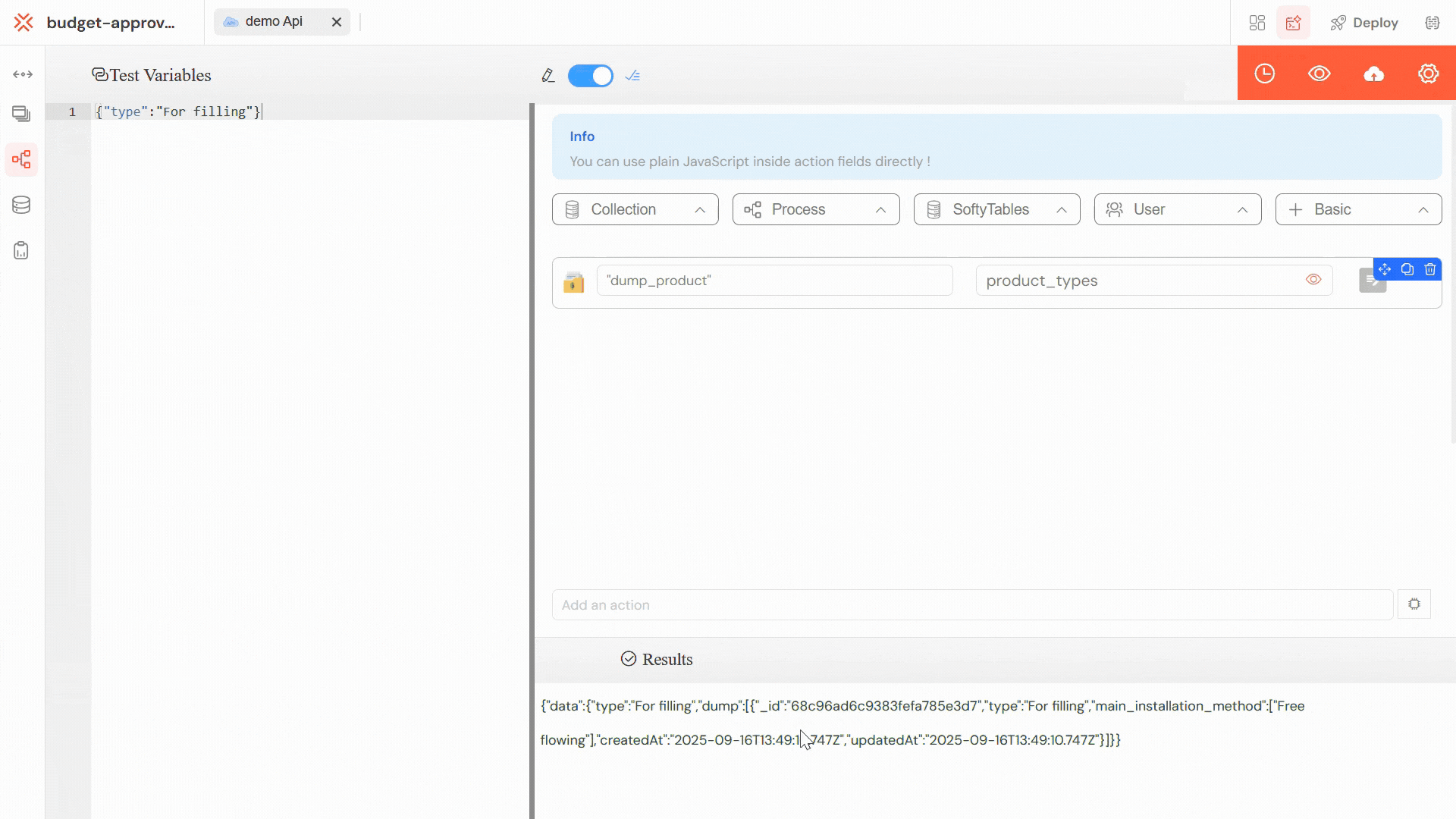
Define test variables in JSON format to simulate real API requests. This allows you to validate your API logic with different input scenarios.
Running Tests
Click the eye button to execute the API test. The results will be displayed in the output section below.
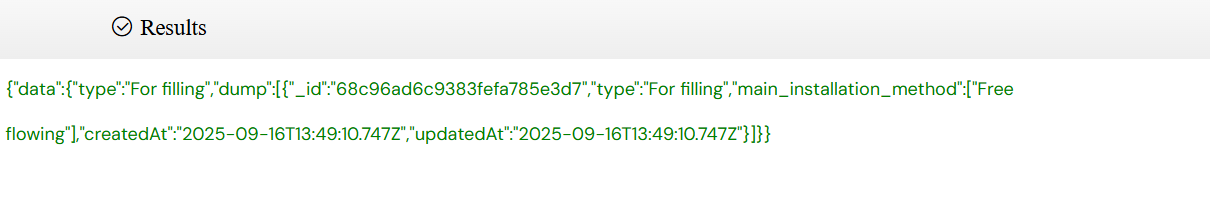
The results panel shows the API response, execution time, and any errors or warnings encountered during testing.
Invoking APIs
Softyflow provides two methods for invoking APIs:
Method 1: Using the InvokeApi Action
The InvokeApi action provides a visual, no-code approach to calling APIs from within your processes or workflows.
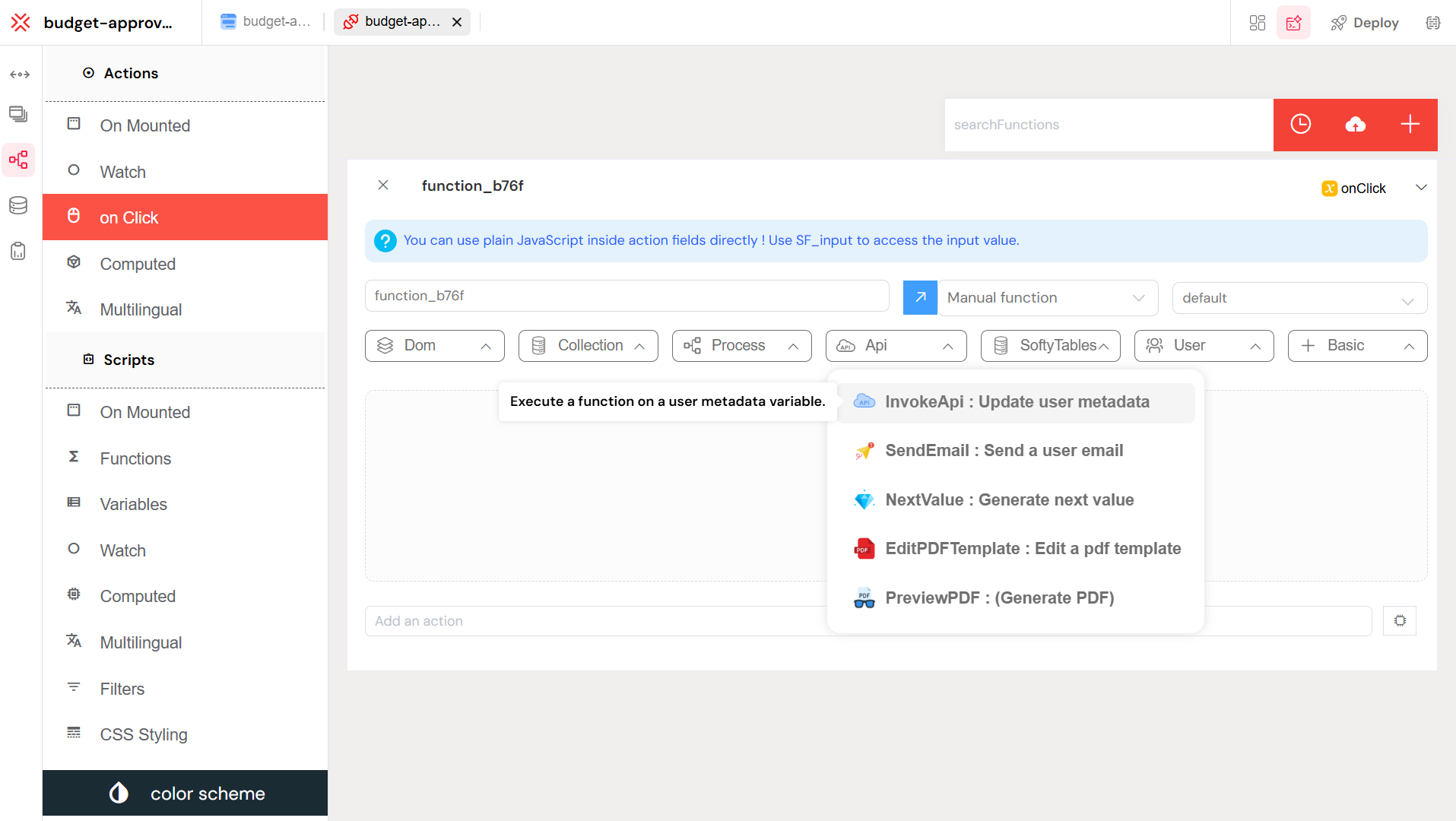
Select the InvokeApi action from the actions palette to begin configuring your API call.
Configuration Steps:
- Select API: Choose the API you want to invoke from the dropdown
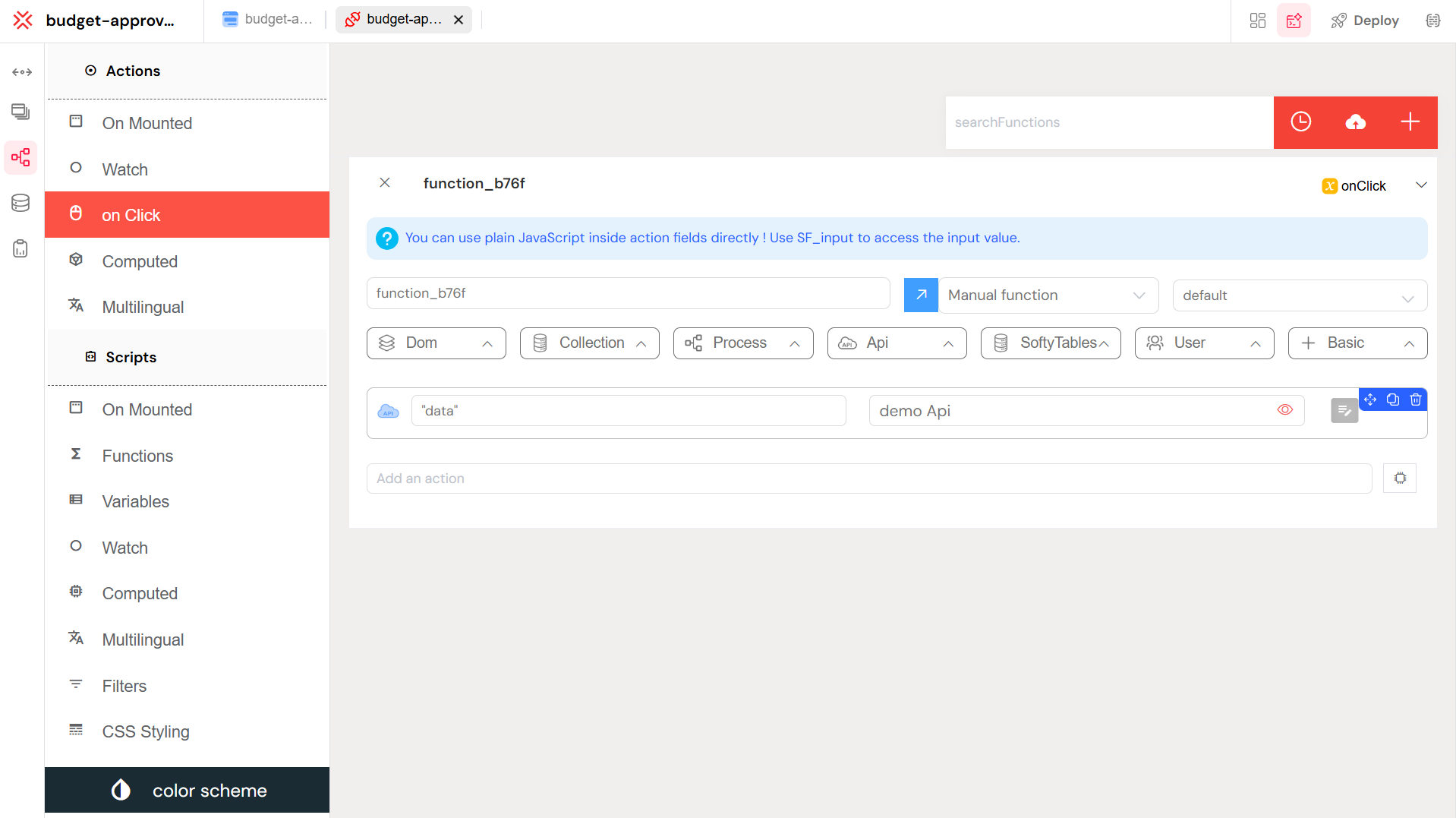
Variable Name: Specify the variable name where the API response will be stored
Request Body (optional): Add body data for POST/PUT requests

The body editor allows you to define the payload in JSON format, with support for dynamic variables.
Method 2: Using Axios (Code-Based Approach)
For advanced use cases or external integrations, you can invoke Softyflow APIs using standard HTTP clients like Axios.
Example Implementation:
// Define request body
let body = {
email: "client1@gmail.com",
userId: 12345,
};
// Construct API URL with mode parameter
let apiUrl =
"https://softydev.softyflow.io/api/v1/api/6491696d1ef51ed2f7044b79?SF_mode=prod";
// Available modes: test, uat, prod
// Make POST request
let result = await axios.post(apiUrl, body);
// Access response data
console.log(result.data);
Key Considerations:
- Mode Parameter: Always specify
SF_modein the URL (test, uat, or prod) - Authentication: Include authentication headers if required
- Error Handling: Implement try-catch blocks for robust error handling
- Response Format: API responses are typically JSON formatted
Advanced Example with Headers:
try {
let body = {
email: "user@example.com",
action: "getData",
};
let config = {
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
Authorization: "Bearer YOUR_TOKEN",
},
};
let apiUrl =
"https://your-instance.softyflow.io/api/v1/api/YOUR_API_ID?SF_mode=prod";
let response = await axios.post(apiUrl, body, config);
// Process response
return response.data;
} catch (error) {
console.error("API call failed:", error);
throw error;
}
Best Practices
API Design
- Clear Naming: Use descriptive names that indicate the API's purpose
- Consistent Structure: Maintain uniform request/response formats
- Version Control: Consider API versioning for future changes
- Documentation: Document expected inputs, outputs, and error codes
Security
- Access Control: Restrict API access to authorized users/groups
- Input Validation: Always validate incoming data
- Error Messages: Avoid exposing sensitive system information
- Rate Limiting: Implement throttling for production APIs
Testing
- Test All Modes: Validate behavior in test, UAT, and production modes
- Edge Cases: Test with various input scenarios
- Error Conditions: Verify proper error handling
- Performance: Monitor response times and optimize as needed
Monitoring
- Review Logs: Regularly check execution logs for errors
- Usage Patterns: Monitor which APIs are called most frequently
- Performance Metrics: Track response times and success rates
- Alert Systems: Set up notifications for critical failures
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
API Not Responding
Problem: API calls return no response or timeout
Solutions:
- Verify the API URL is correct
- Check if the API is enabled in the specified mode
- Ensure network connectivity to Softyflow instance
- Review execution logs for error details
Authentication Errors
Problem: "Unauthorized" or "Forbidden" responses
Solutions:
- Verify user has proper access rights
- Check if API is set to public if needed
- Confirm authentication headers are correct
- Review role assignments in configuration
Incorrect Data Format
Problem: API receives or returns unexpected data
Solutions:
- Validate request body matches expected schema
- Check SF_body, SF_query variable usage
- Review API logic for proper data transformation
- Test with sample data in test mode
Performance Issues
Problem: Slow API response times
Solutions:
- Optimize database queries within API logic
- Reduce unnecessary data processing
- Consider caching frequently accessed data
- Monitor and limit concurrent executions
For additional support, consult the execution logs and review the API configuration settings.