Instances Monitoring
The Run section is the central hub for overseeing and managing all process instances across your various environments, such as Testing, User Acceptance Testing (UAT), and Production. It offers a powerful suite of tools for real-time monitoring of execution statuses, in-depth debugging of issues, and complete control over the instance lifecycle.
This comprehensive monitoring system is fully integrated with other critical administrative functions, including user management, role management, mail notifications, and system logs. This synergy provides a holistic view of your operational landscape, ensuring complete oversight and control.
To access this feature, navigate to Monitoring > Run from the main top-level navigation menu.
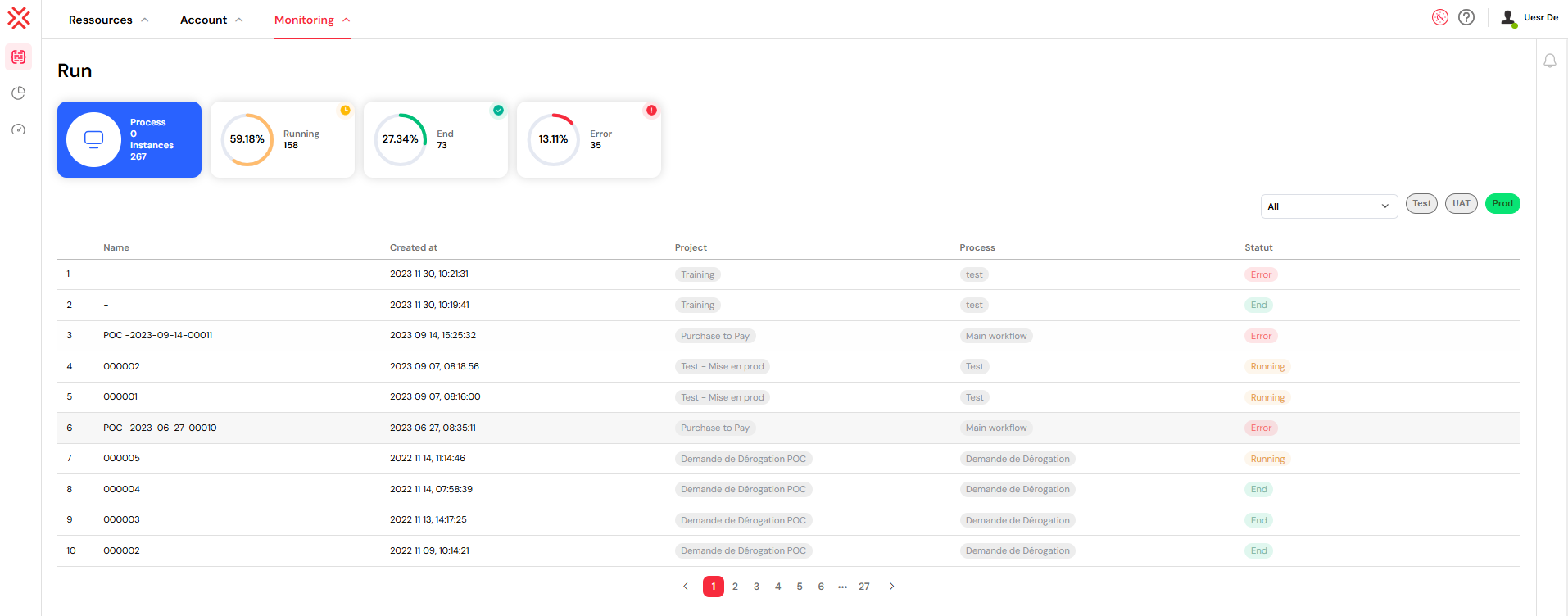
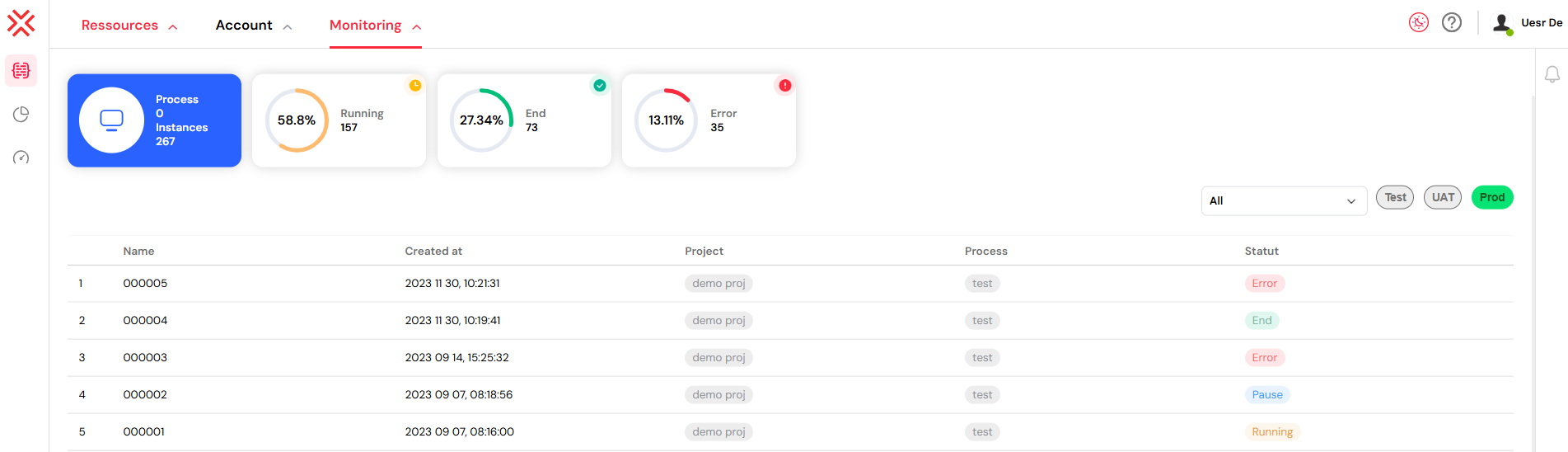
1. Instance Monitoring Dashboard
The main dashboard provides at-a-glance insights into your process execution health.
1.1. Statistics Overview
The dashboard prominently displays key statistics to help you quickly assess system activity:
- Process & Instance Counts: Displays the total number of unique processes that have been deployed and the total number of instances that have been launched from them.
- Status Distribution: A visual breakdown of all instances categorized by their current status. Each status is clearly marked and color-coded for immediate identification:
- Running: Instances that are currently active and executing their defined steps.
- End: Instances that have successfully completed their entire lifecycle.
- Error: Instances that have encountered a failure and require administrative attention.
Each status card presents both the absolute number of instances and their percentage relative to the total, accompanied by progress indicators for a clear visual representation.
1.2. Interactive Filtering
The status cards also serve as interactive filters. Clicking on any status card (e.g., "Error") will instantly filter the instance list below to display only the instances matching that status, allowing for quick navigation and issue resolution.
2. Instance List & Filtering
Below the dashboard, a detailed list of all process instances is displayed, equipped with powerful filtering and navigation capabilities.
2.1. Filter Controls
A set of dedicated controls allows you to refine the instance list based on specific criteria:
- Status Filter: A dropdown menu lets you filter by status, including
All,Running,End, andError. - Environment Filter: Switch between your
Test,UAT, andProdenvironments using clearly labeled, color-coded buttons. These colors correspond to your organization's deployment strategy, ensuring you always know which environment you are viewing:- Test: Marked with a yellow indicator.
- UAT: Marked with a blue indicator.
- Prod: Marked with a green indicator.
2.2. Instance Table
The instance table provides detailed information about each process instance in a clear, organized manner. Each row corresponds to a single instance and displays the following columns:
- Index: A sequential number for easy reference.
- Name: The unique identifier for the instance.
- Created At: The exact date and time the instance was launched.
- Project: The associated project, displayed with a color-coded tag for quick identification.
- Process: The name of the process from which the instance was created, also tagged for clarity.
- Status: The current execution status, with color-coding that matches the dashboard widgets.
2.3. Navigation Actions
The instance table is not just for viewing; it's interactive. Clicking on different parts of a row triggers specific actions:
- Project Column: Clicking on the project name opens the project builder for that specific project in a new browser tab.
- Process Column: Clicking on the process name opens the process builder, loading the specific process diagram for review or editing.
- Other Columns: Clicking anywhere else on the row opens the detailed Instance Details interface for that instance, where you can perform advanced management tasks.
3. Error Notification Configuration
Configure automated alerts for process failures to ensure that your team is immediately notified of any issues. This proactive approach allows for rapid response and resolution, minimizing downtime and maintaining system reliability. The notification system integrates seamlessly with your existing mail management and various collaboration platforms.
3.1. Setup Process
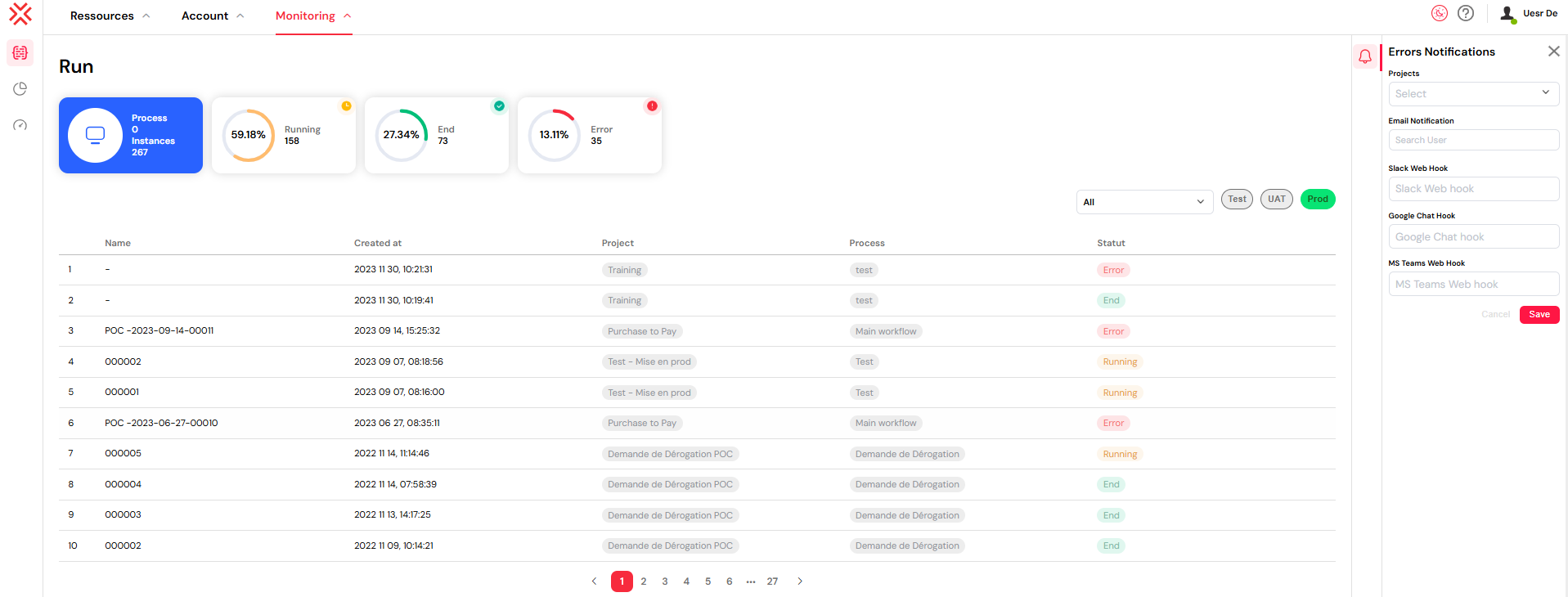
- Click the notification icon located in the right panel of the Run dashboard.
- In the configuration modal, set up your desired notification channels:
- Projects: Select the specific projects you wish to monitor for errors.
- Email Notification: Add recipient email addresses. These notifications will be sent using your configured mail providers.
- Slack Web Hook: Integrate with Slack by providing a webhook URL.
- Google Chat Hook: Connect to Google Chat spaces using a webhook URL.
- MS Teams Web Hook: Send alerts to Microsoft Teams channels via a webhook URL.
3.2. Benefits
- Stay Informed: Receive immediate alerts for recurrent or critical process failures.
- Reduce Response Time: Enable your team to address critical issues faster, reducing their impact on business operations.
- Customize Alerts: Tailor the scope of notifications on a per-project basis to ensure the right people are alerted for the right systems.
3.3. Setting Up Webhook Integrations
Webhooks are a simple and effective way to send automated messages from Softyflow to your team's collaboration tools. Below are detailed instructions for setting up webhooks for Slack, Google Chat, and Microsoft Teams.
3.3.1. Slack Webhook Setup
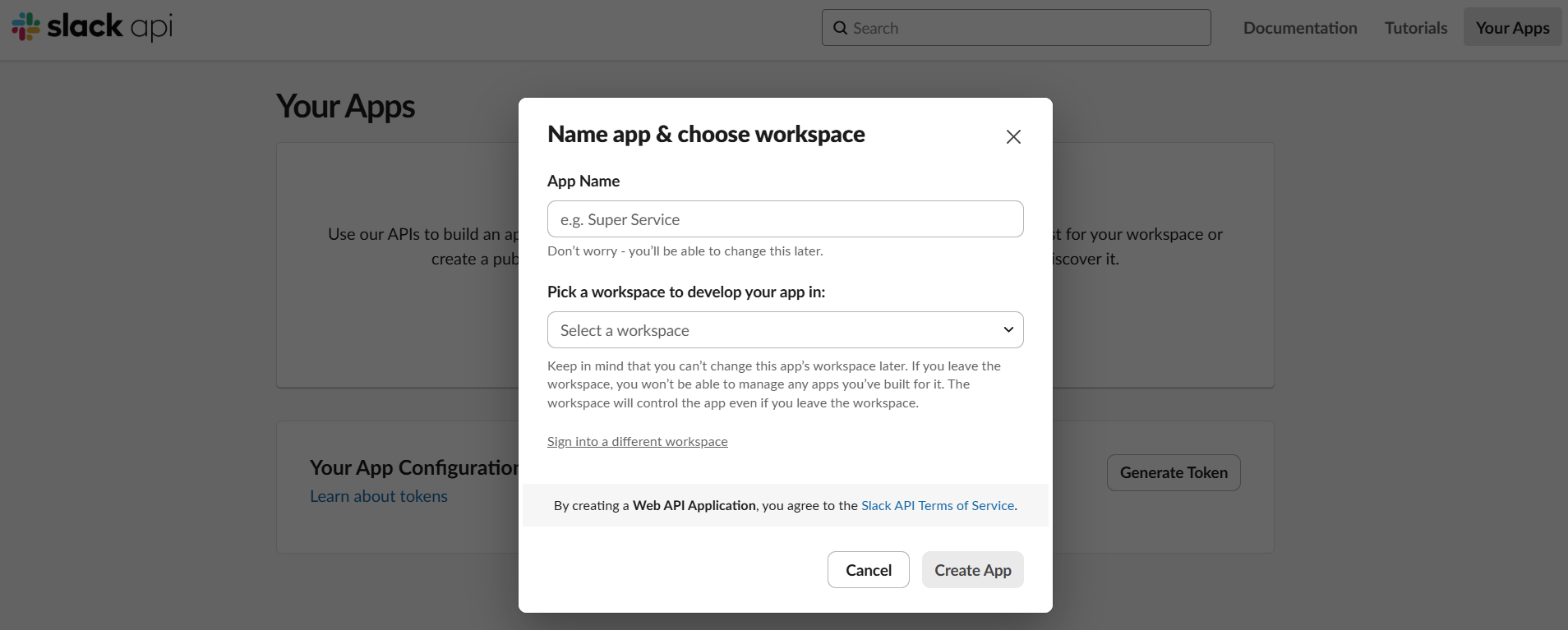
- Create a Slack App:
- Navigate to the Slack API website.
- Click "Create New App" and choose to create it "From scratch".
- Provide an app name (e.g., "Softyflow Notifications") and select your desired Slack workspace.
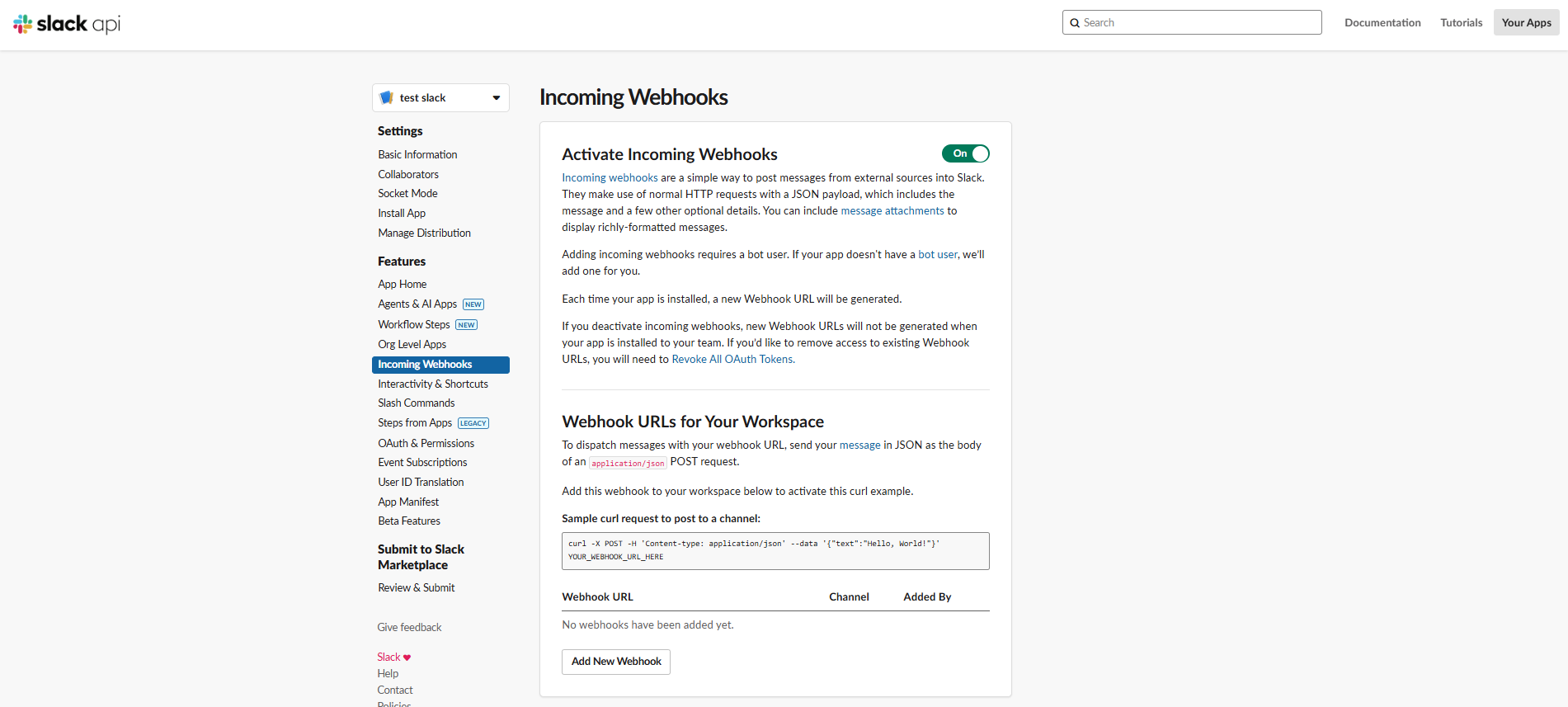
- Enable Incoming Webhooks:
- From your new app's settings page, navigate to the "Incoming Webhooks" feature.
- Toggle the "Activate Incoming Webhooks" switch to On.
- Click "Add New Webhook to Workspace".
- Authorize and Configure Channel:
- Select the specific Slack channel where the notifications should be posted.
- Click "Allow" to grant the necessary permissions and authorize the webhook.
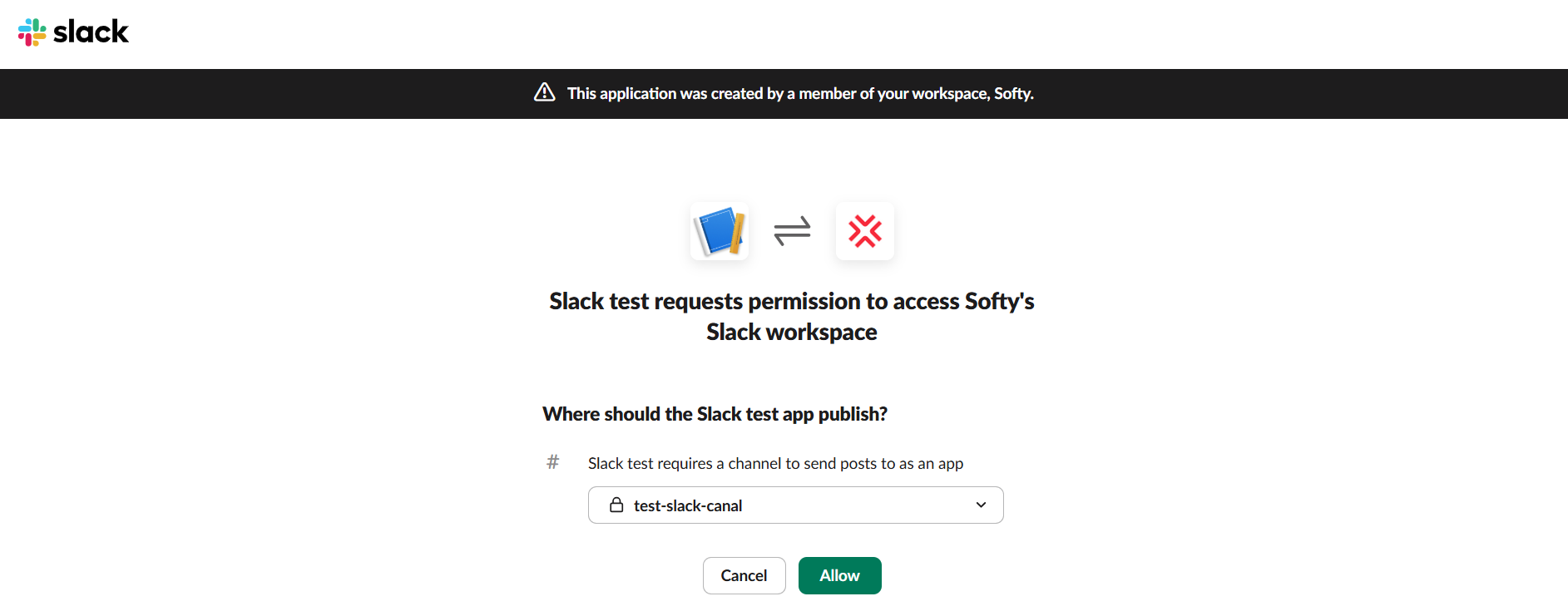
- Copy the Webhook URL:
- Once authorized, Slack will generate a unique webhook URL. Copy this URL to your clipboard. It will follow a format similar to
https://hooks.slack.com/services/T00000000/B00000000/XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX.
- Once authorized, Slack will generate a unique webhook URL. Copy this URL to your clipboard. It will follow a format similar to
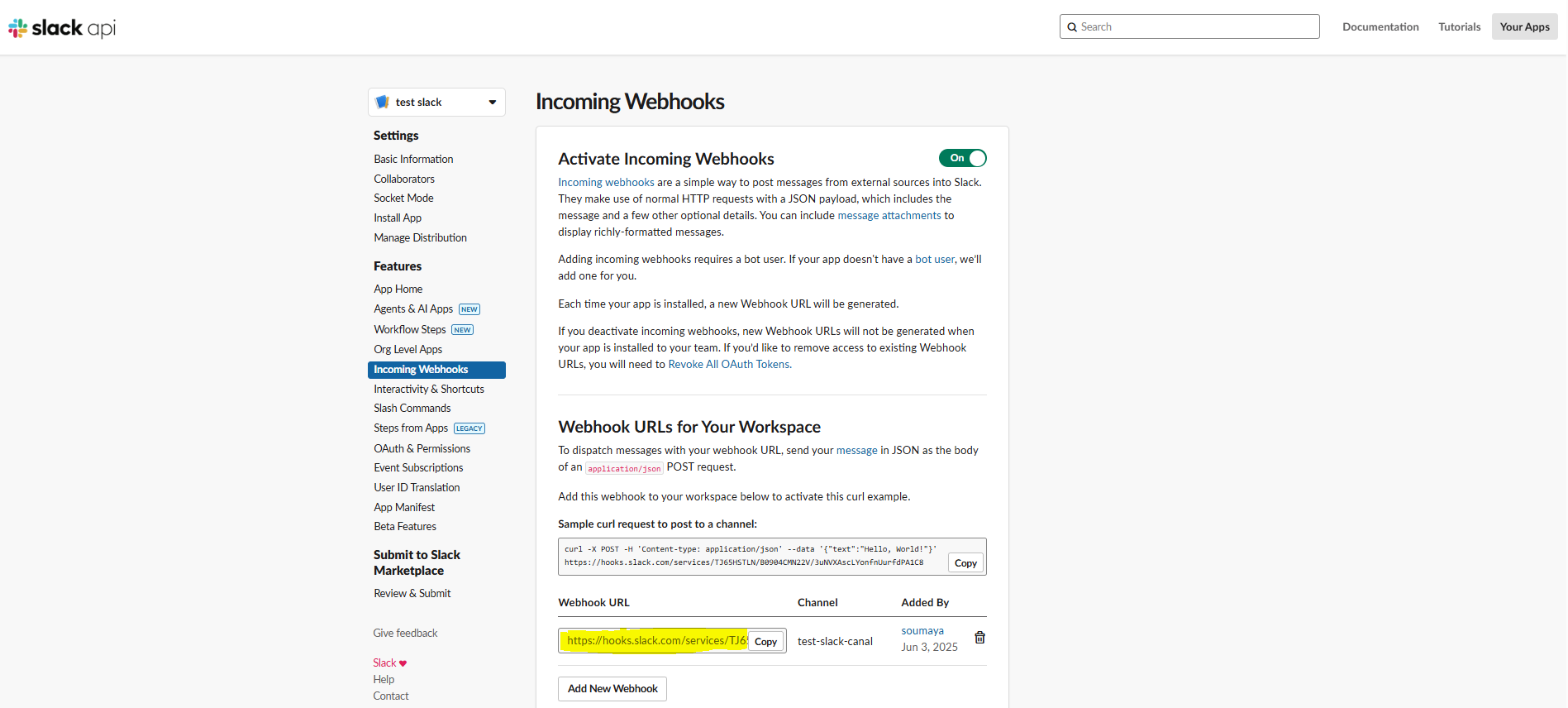
- Finally, paste this URL into the "Slack Web Hook" field in the Softyflow notification settings.
Example Slack Webhook URL format:
https://hooks.slack.com/services/T1234567890/B1234567890/abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwx
3.3.2. Google Chat Webhook Setup
- Open Google Chat:
- Navigate to the Google Chat space where you want to receive notifications.
- If you don't have a suitable space, you can create one by clicking "+ Create space".
- Configure Webhooks for the Space:
- In your selected chat space, click on the space name at the top to open the menu.
- Select "Apps & integrations" from the dropdown list.
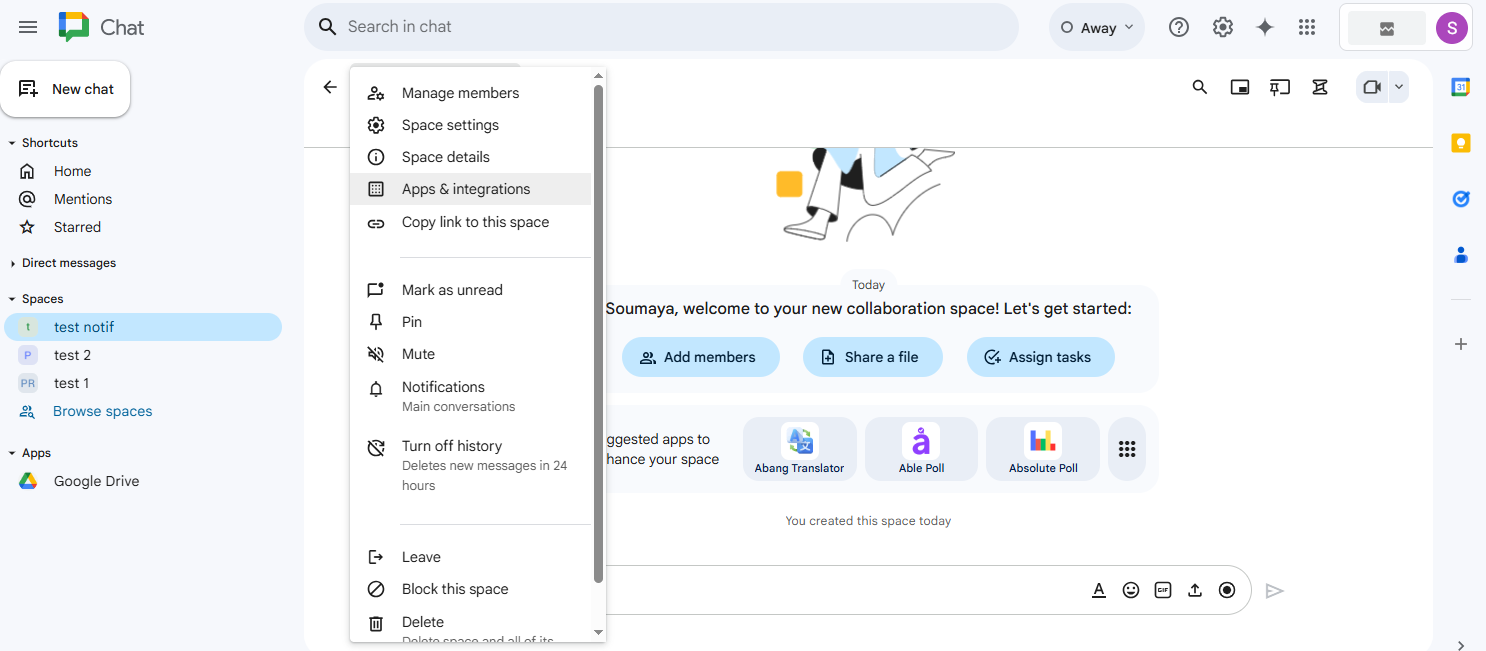
- Click on the "Add webhooks" button to proceed.
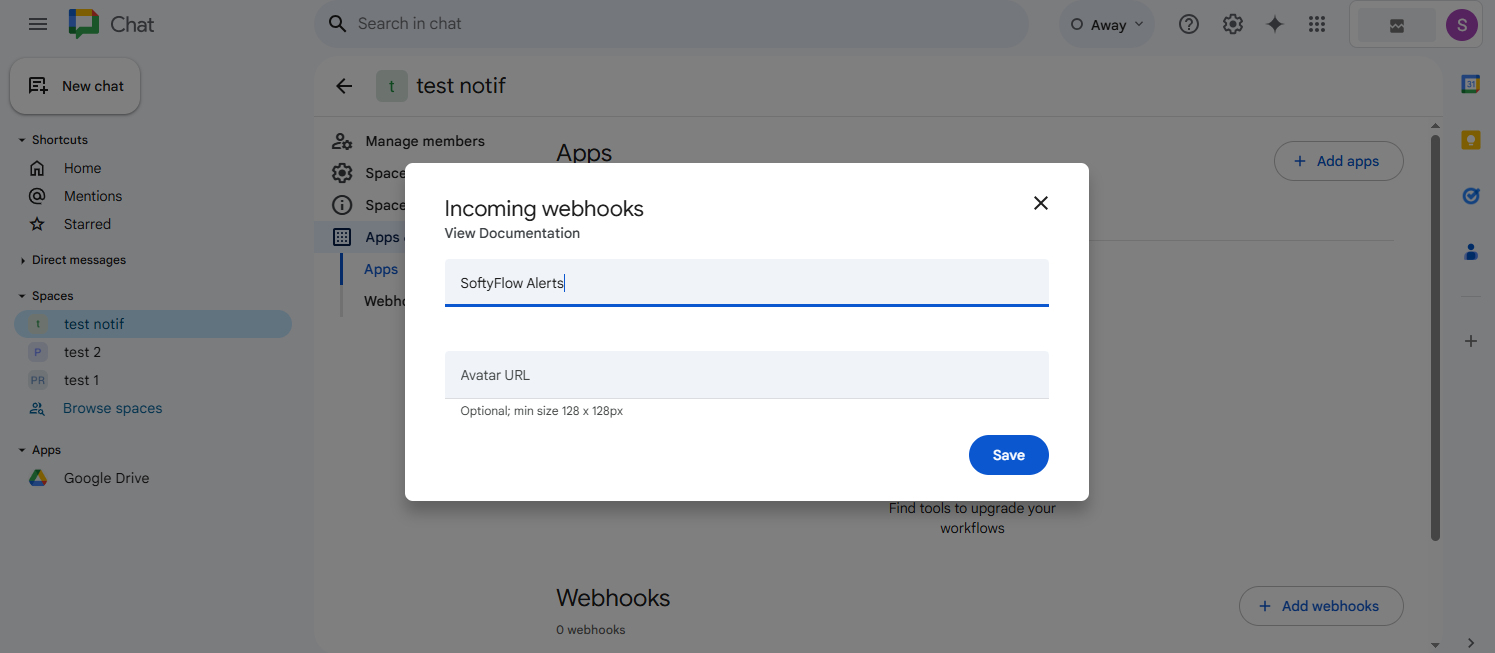
- Create the Webhook:
- Enter a descriptive name for the webhook (e.g., "Softyflow Alerts").
- You can optionally add an avatar URL to customize the appearance of messages sent by the webhook.
- Click "Save".
- Copy the Webhook URL:
- Google Chat will generate a unique webhook URL. Copy this URL. The format will be similar to
https://chat.googleapis.com/v1/spaces/XXXXXXX/messages?key=YYYYYYY&token=ZZZZZZZ.
- Google Chat will generate a unique webhook URL. Copy this URL. The format will be similar to
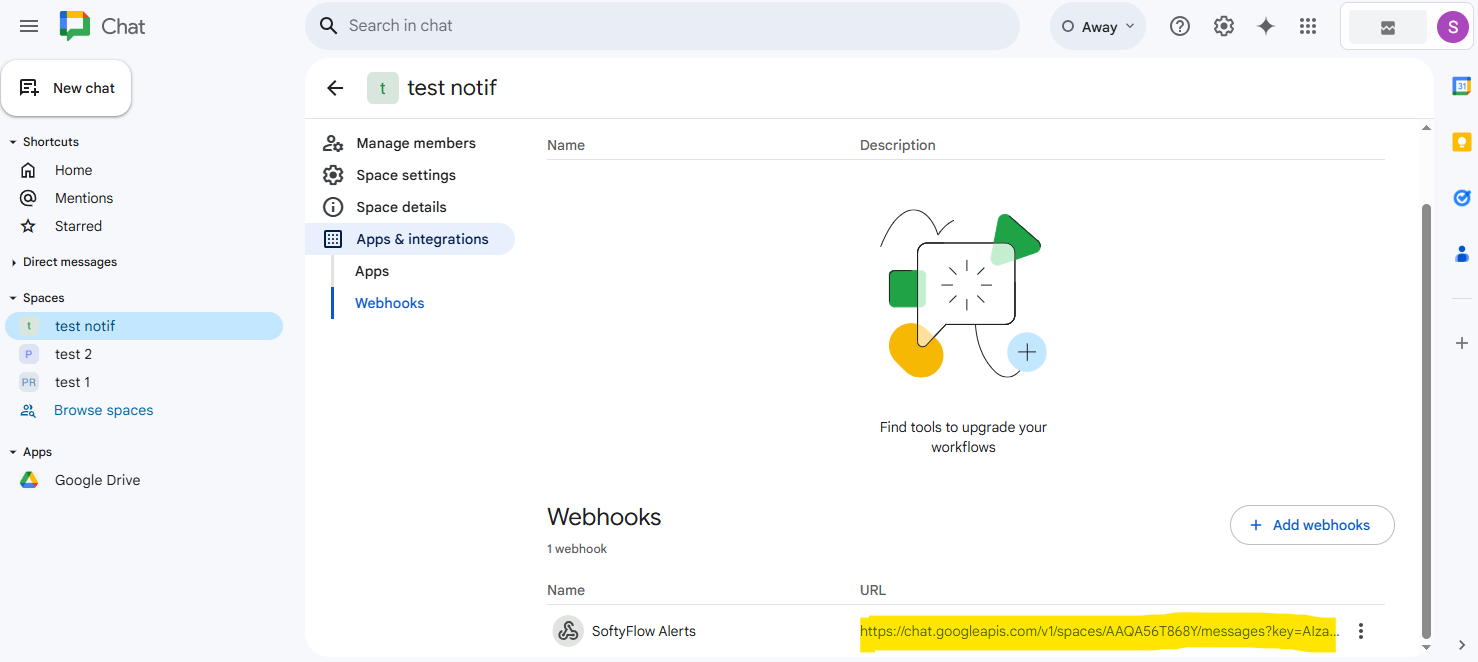
- Paste this URL into the "Google Chat Hook" field in Softyflow's notification settings.
Example Google Chat Webhook URL format:
https://chat.googleapis.com/v1/spaces/AAAABbbbCCCc/messages?key=AIzaSyDdI0hCZtE6vySjMm-WEfRq3CPzqKqqsHI&token=abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz123456789
3.3.3. Microsoft Teams Webhook Setup
- Navigate to your Teams Channel:
- Open Microsoft Teams and go to the channel where you want to receive notifications.
- If you don't have a specific channel for alerts, you can create a new one or use a general-purpose channel.
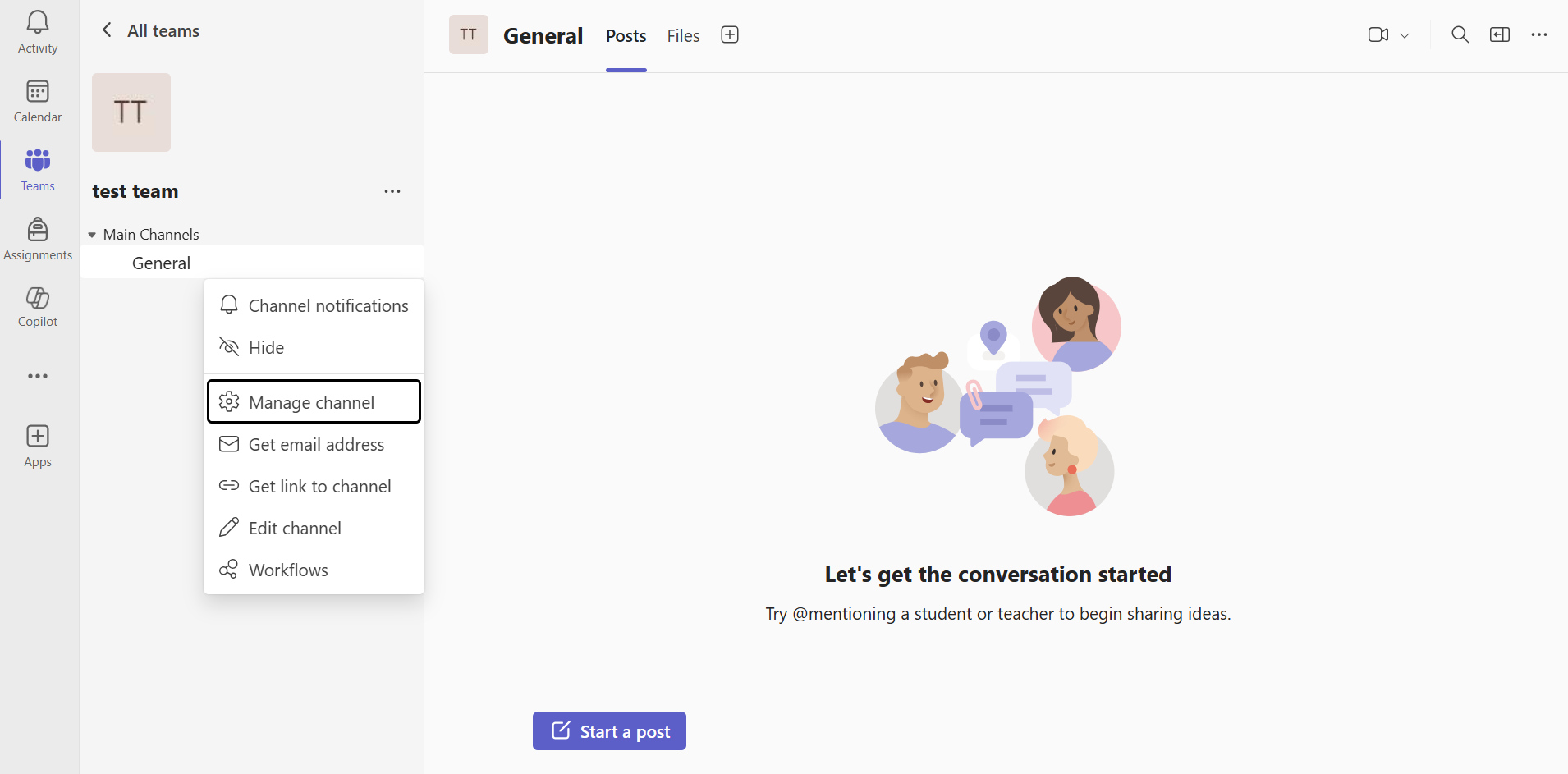
- Add the Incoming Webhook Connector:
- Click on the "..." (more options) menu next to your channel's name.
- Select "Connectors" from the menu.
- In the connectors gallery, search for "Incoming Webhook" and click the "Configure" button next to it.
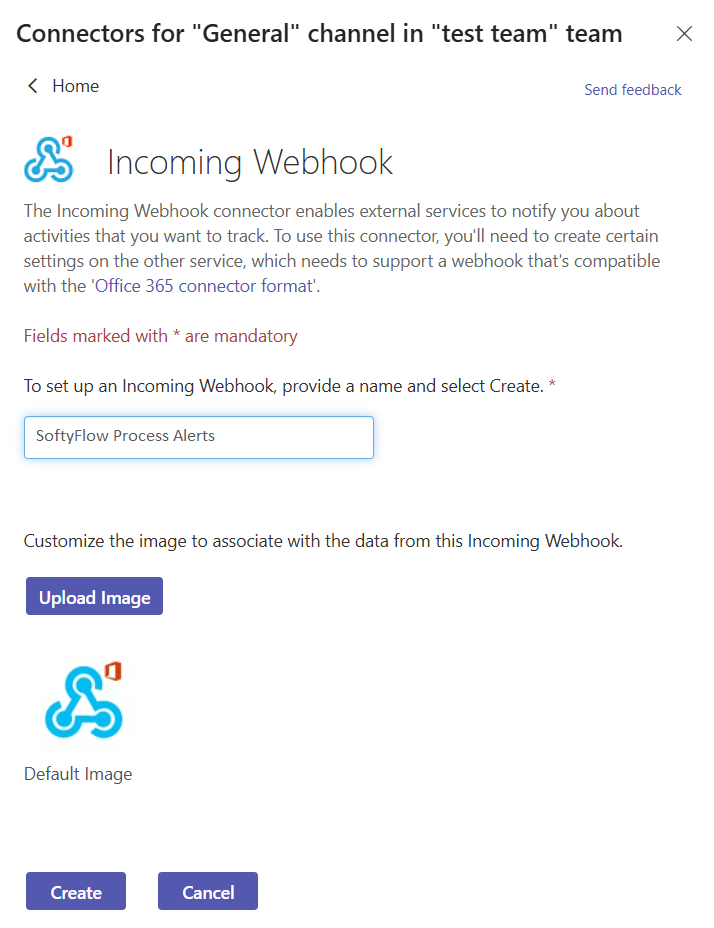
- Configure the Webhook:
- Provide a name for your webhook (e.g., "Softyflow Process Alerts").
- You can also upload a custom image to serve as the avatar for notifications from this webhook.
- Click "Create".
- Copy the Webhook URL:
- Teams will generate a unique webhook URL. Copy this URL. It will have a format like
https://[tenant].webhook.office.com/webhookb2/[GUID]@[GUID]/IncomingWebhook/[GUID]/[GUID].
- Teams will generate a unique webhook URL. Copy this URL. It will have a format like
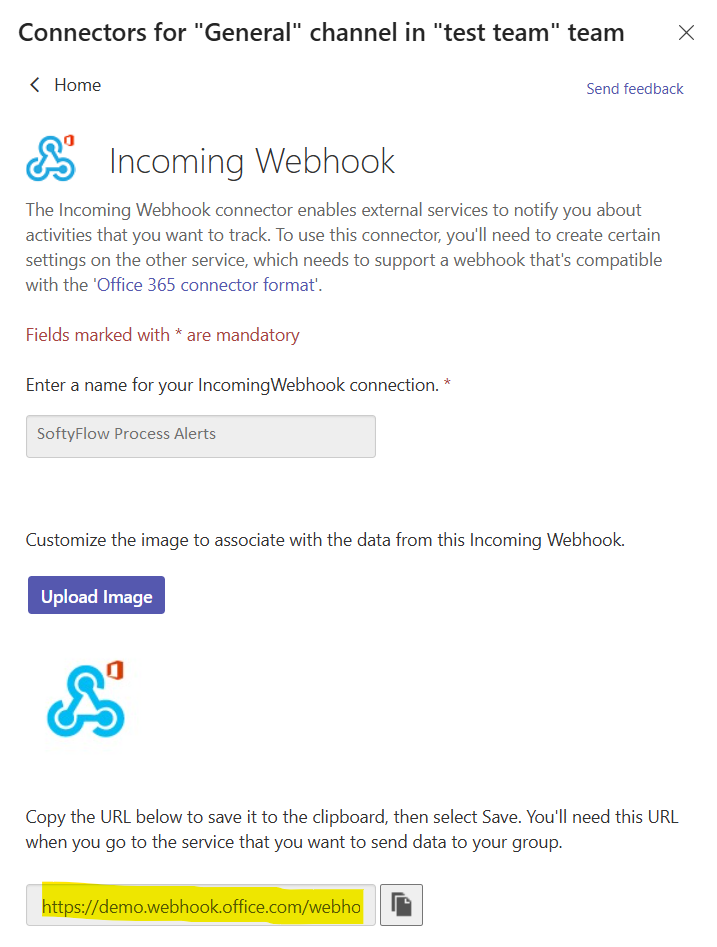
- Click "Done" to close the configuration window.
- Paste the copied URL into the "MS Teams Web Hook" field in the Softyflow notification settings.
Example MS Teams Webhook URL format:
https://yourtenant.webhook.office.com/webhookb2/12345678-1234-1234-1234-123456789012@12345678-1234-1234-1234-123456789012/IncomingWebhook/abcdefgh12345678/87654321-4321-4321-4321-210987654321
3.4. Webhook Security Best Practices
- URL Protection: Treat your webhook URLs as sensitive information. Do not expose them in public repositories or client-side code.
- Regular Rotation: For enhanced security, consider periodically regenerating your webhook URLs and updating them in Softyflow.
- Team Access: Limit access to webhook configuration settings to authorized team members only.
- Testing: Always test your webhook configurations in a non-production environment before deploying them to your live production systems.
3.5. Notification Message Format
Softyflow sends well-structured, informative notifications to your configured webhooks. Each message typically includes:
- Instance Name: The identifier of the failed process instance.
- Error Type: A classification of the error that occurred.
- Timestamp: The exact time when the error was logged.
- Project Information: Details of the associated project.
- Direct Links: A hyperlink to the instance details view in Softyflow for immediate troubleshooting.
3.6. Troubleshooting Webhook Issues
If you are not receiving notifications as expected, consider the following common issues:
Common Issues:
- Invalid URL: Ensure the webhook URL was copied and pasted correctly, without any extra characters or missing parts.
- Expired Webhooks: Some platforms may disable or expire webhooks after a period of inactivity.
- Permission Issues: Verify that the app or connector associated with the webhook has the necessary permissions to post messages to the designated channel or space.
- Network Restrictions: Check for any firewall rules or network policies within your organization that might be blocking outbound HTTPS requests from Softyflow to the webhook provider.
Testing Webhooks:
- Save your webhook configuration in Softyflow.
- Either manually trigger an error in a test process or wait for a natural error to occur.
- Check the configured channel or space for the notification message.
- If no message appears, double-check the webhook URL, review the permissions, and consult the logs of your webhook provider if available.
4. Performance and Scalability
Softyflow is designed to handle a large volume of process instances and data with high performance. The platform incorporates several key features to ensure a smooth and responsive user experience, even when working with extensive datasets.
4.1. Efficient Data Loading and Timeout Management
Loading and displaying thousands of process instances can be resource-intensive. To prevent browser freezing and ensure a fluid interface, Softyflow includes:
- Progressive Loading: Instead of loading all data at once, the system loads data in manageable chunks as you scroll or navigate through pages.
- Asynchronous Operations: Many operations, such as filtering and searching, are performed asynchronously in the background to keep the UI responsive.
- Automatic Timeout Detection: If a data query takes too long to execute, the system will detect the delay and offer you the option to "Load Anyway." This gives you control over long-running operations, allowing you to choose whether to wait for the comprehensive data or to refine your filters for a faster response.
4.2. Real-time Updates
The Run & Instance Management interface provides real-time feedback on the state of your processes:
- Status Synchronization: The status of instances is updated in real-time across all views, from the main dashboard to the detailed instance list.
- Activity Highlighting: As a process executes, the visual BPMN diagram is updated instantly to highlight the current state of each activity.
- Log Streaming: For active monitoring, the audit logs can stream new entries as they are generated, providing a live look into instance activity.
5. Instance Details Management
Clicking on any instance in the list opens the Instance Details view, which provides a comprehensive suite of tools for in-depth analysis and management. This view is organized into several tabs, each focusing on a specific aspect of the process instance.
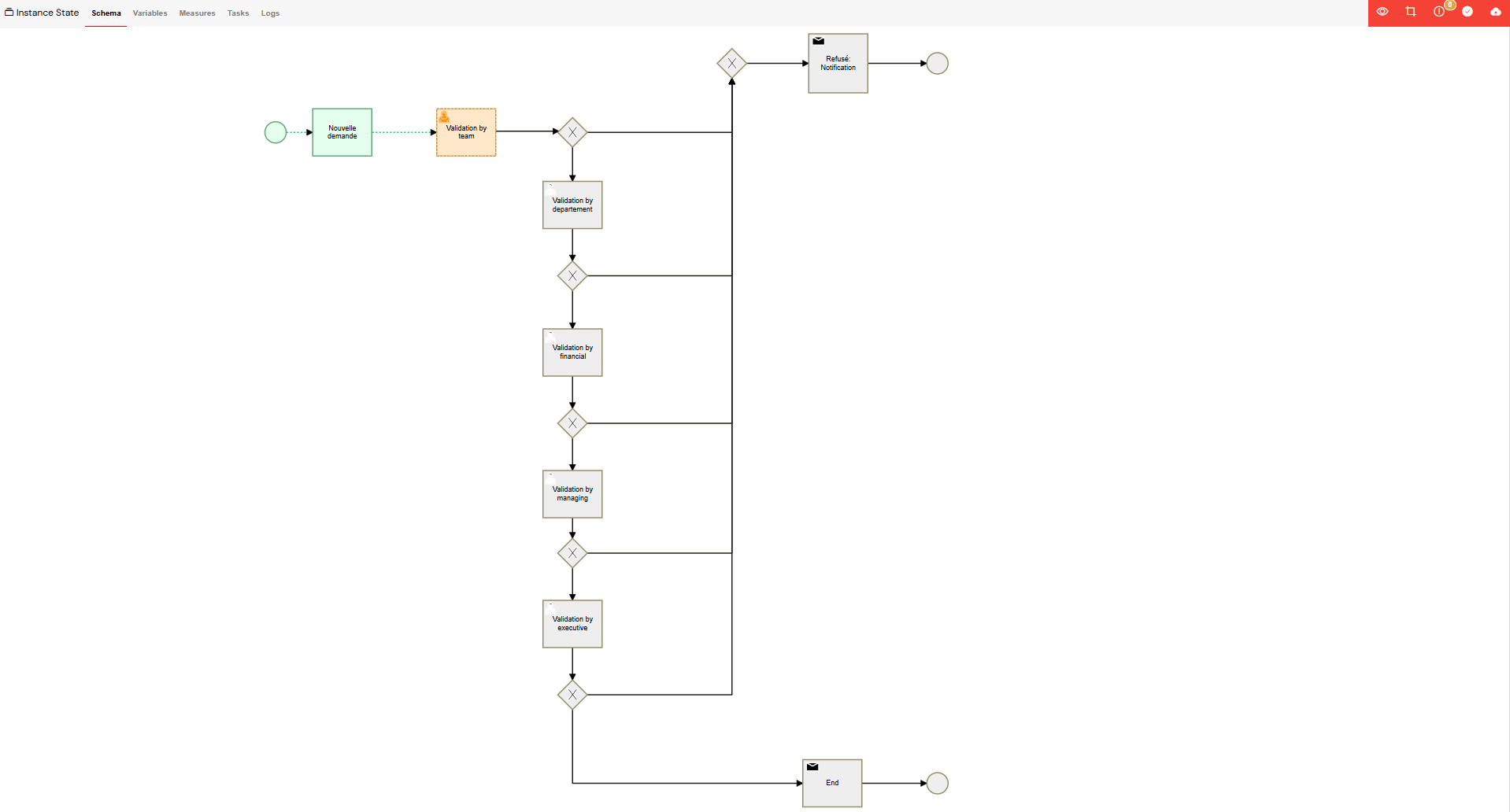
5.1. Schema View - Process Visualization
This view provides a real-time, visual representation of the process instance's execution path on an interactive BPMN diagram.
Visual Process Tracking
The diagram dynamically highlights the status of each activity, providing an intuitive overview of the process flow:
- Running: The current activity is outlined in orange with an animated dashed border.
- Completed: Successfully executed activities are highlighted in green.
- Error: Activities that have failed are highlighted in red, often with an error icon.
- Default: Inactive or pending activities retain their standard gray appearance.
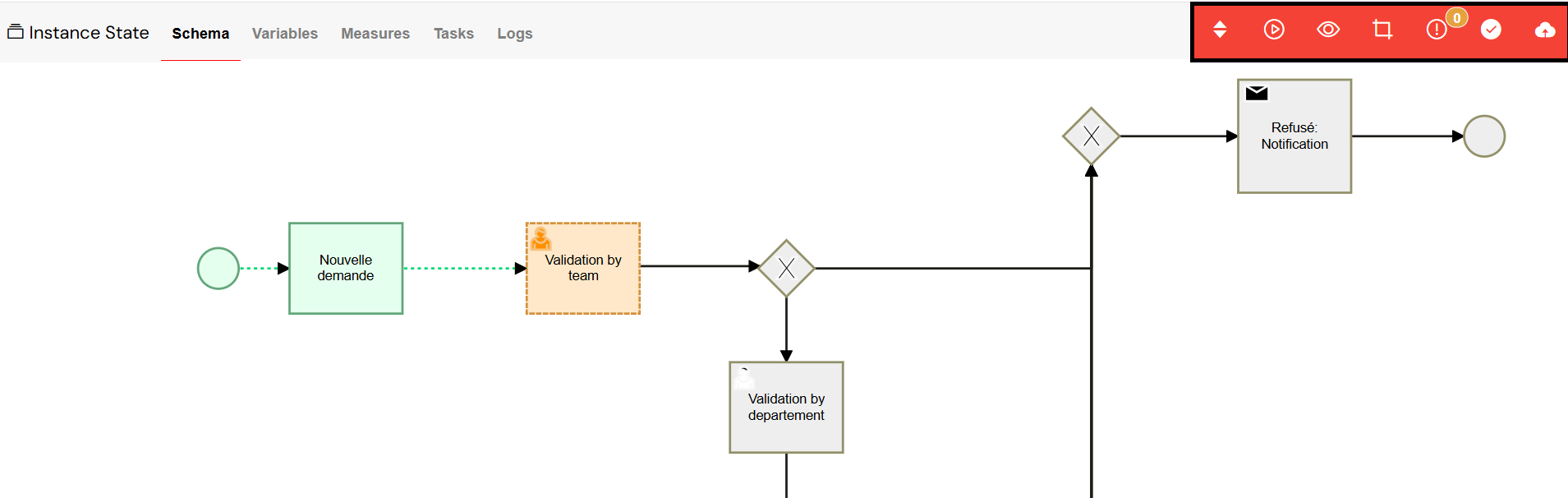
Instance Lifecycle Controls
A toolbar at the top of the view provides powerful controls for managing the instance's lifecycle:
- Switch Version: Update the running instance to a different version of the process.
- Revive: Resume a paused or failed instance from a specific activity.
- View Instance: Open the associated web interface for this instance, if applicable.
- Edit Process: Navigate directly to the process builder for the underlying process definition.
- Errors: Display a detailed log of any errors that have occurred in the instance.
- End Instance: Manually terminate the instance's execution. This is an irreversible action that affects all related tasks.
- Save: Persist any changes made to the instance's state.
Activity Management
You can interact directly with the elements on the BPMN diagram:
- Click any BPMN element to view its detailed properties and status.
- Dynamically add new activities to a running instance if required.
- Manually edit the status and properties of an activity for debugging or recovery purposes.
- Manage variables within the different branches of a parallel gateway.
5.2. Variables Management
The Variables tab allows you to inspect and manipulate all the data associated with the process instance.
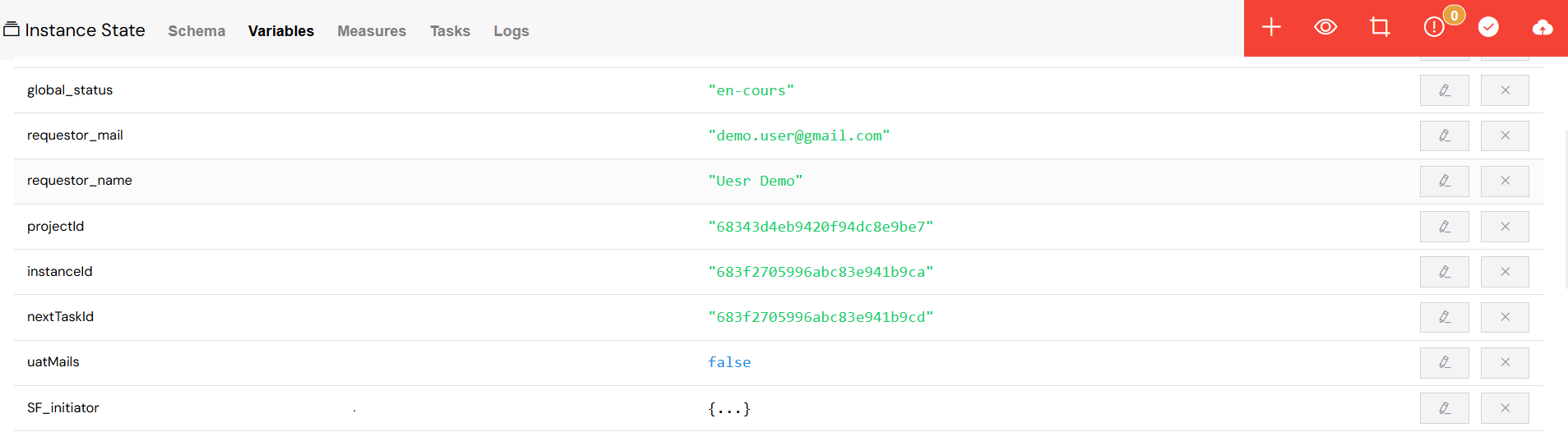
Variable Operations
- View: See a complete list of all process variables and their current values.
- Edit: Modify the value of a variable directly in the interface. For complex objects or arrays, a full JSON editor is provided.
- Add: Create new variables on the fly, specifying their type (e.g., string, number, array, JSON).
- Delete: Remove variables from the instance, with a confirmation step to prevent accidental deletion.
Variable Types Support
The interface provides dedicated editors for different data types:
- String: A simple text input.
- Boolean: A checkbox for true/false values.
- Date: A date and time picker.
- Numeric: A number input field with validation.
- Objects/Arrays: An advanced JSON editor with syntax highlighting and validation.
Variable Categorization
Variables are organized into logical categories for clarity:
- Master Variables: The main variables belonging to the process.
- Branch Variables: Variables that are specific to a particular branch of a parallel gateway.
- Duration Variables: System-generated variables that track timing and performance metrics.
5.3. Measures Management
The Measures tab displays the Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and other measures that have been configured for the process.
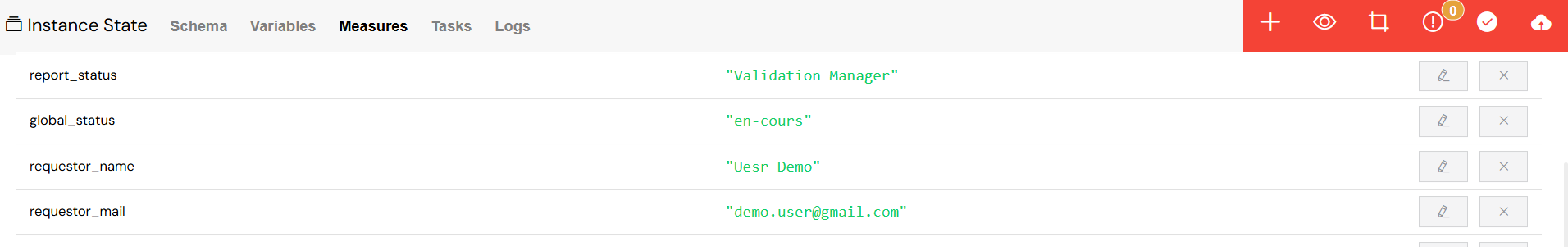
Performance Metrics
- View calculated KPIs as defined in the process design.
- Track metrics related to Service Level Agreement (SLA) compliance and task durations.
- Manually edit measure values to perform "what-if" analysis or to correct data.
- Add new custom measures with specific values if needed.
Operations
- Inline editing is supported for simple measure types.
- A JSON editor is available for more complex measure objects.
- Values are updated in real-time.
5.4. Tasks Management
The Tasks tab provides a complete overview of all user and system tasks associated with the instance.
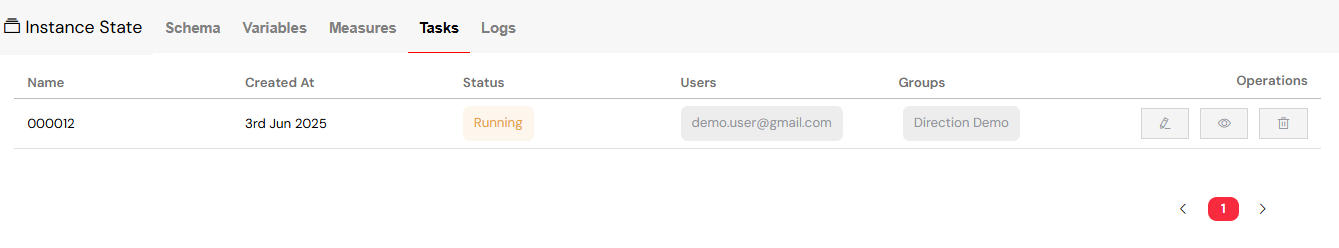
Task Oversight
- Task List: View a comprehensive list of all tasks within the instance.
- Task Properties: For each task, you can see:
Task Operations
- Edit: Modify task assignments, reassigning them to different users or groups.
- View: Open the task's web interface in a new tab.
- Delete: Remove a task, with a confirmation dialog to prevent errors.
- Update Status: Manually change the execution state of a task.
Assignment Management
- A multi-select dropdown with a search function makes it easy to assign tasks to one or more users.
- Assign tasks to entire groups for role-based workflows.
5.5. Sub-processes Management
The Sub-processes tab is where you can track the execution of any child processes that have been spawned by the current instance.
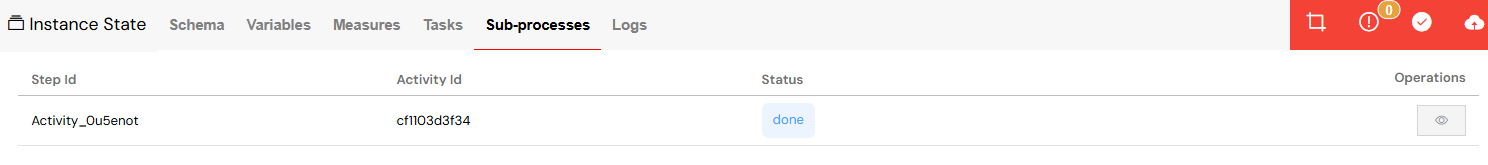
Child Instance Tracking
- View a list of all spawned sub-process instances.
- Monitor the status and health of each sub-process.
- Quickly navigate from the parent instance to any of its child instances for detailed inspection.
Sub-process Information
- See the mapping between the parent process's Step ID and the child's Activity ID.
- The status of the parent process can influence the child process.
- Gain direct access to the full management interface for each child instance.
5.6. Comprehensive Audit Logs
The Logs tab provides a detailed, time-stamped audit trail of every action and event that has occurred within the process instance.
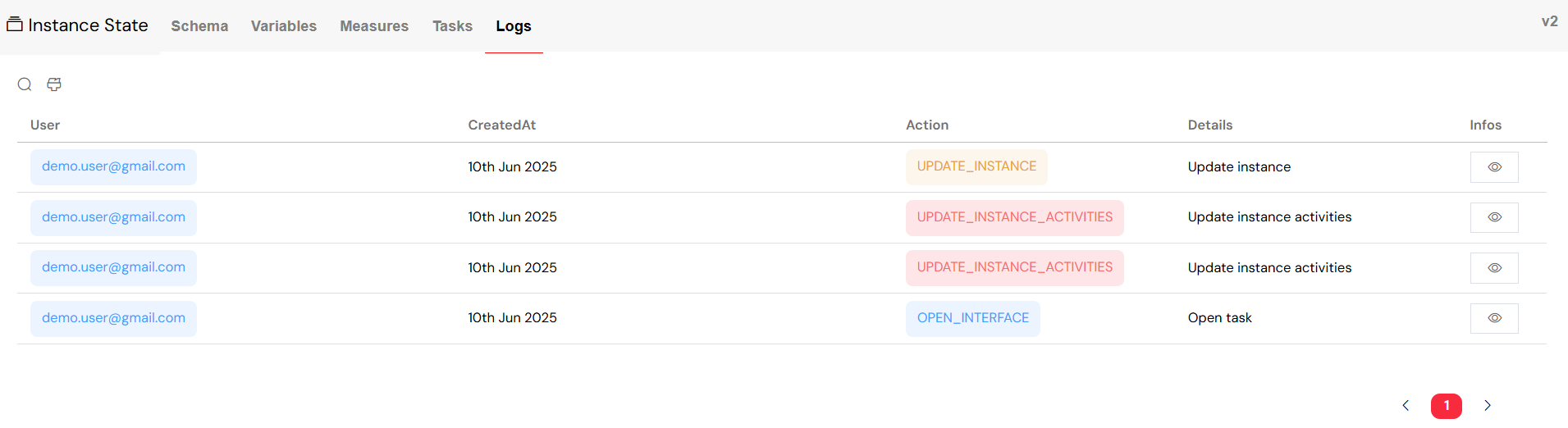
Log Categories
Logs are categorized by the type of action, including:
- Process Actions:
START_PROCESS,RESUME_INSTANCE. - Instance Updates:
UPDATE_INSTANCE,UPDATE_INSTANCE_MEASURES,UPDATE_INSTANCE_ACTIVITIES. - Task Operations:
VALIDATE_TASK,UPDATE_TASK,DELETE_TASK. - Interface Access: Tracking when users
OPEN_INTERFACE.
Log Features
- Advanced Filtering:
- Filter logs by the user who performed the action.
- Select a specific date range.
- Filter by the type of action.
- Perform a full-text search within the log details.
- Detailed Information: Each log entry can be expanded to show the full object information, providing complete context for the event.
- Pagination: Efficiently navigate through large sets of log data.
Log Analysis
The audit logs are invaluable for:
- Tracking user activity and ensuring compliance.
- Analyzing event sequences for debugging.
- Identifying performance patterns and bottlenecks.
- Providing a full, auditable history of the instance for troubleshooting and reporting.
6. Advanced Instance Operations
Beyond basic monitoring, Softyflow provides advanced capabilities for managing the entire lifecycle of a process instance, including versioning and error recovery.
6.1. Version Management
You can dynamically manage the version of the process that an instance is running on.
- Current Version Display: The system clearly displays the current version of the process that the instance is based on.
- Version Switching: You can update a running instance to a newer process version. This is particularly useful for applying bug fixes or process improvements to long-running instances without having to terminate them.
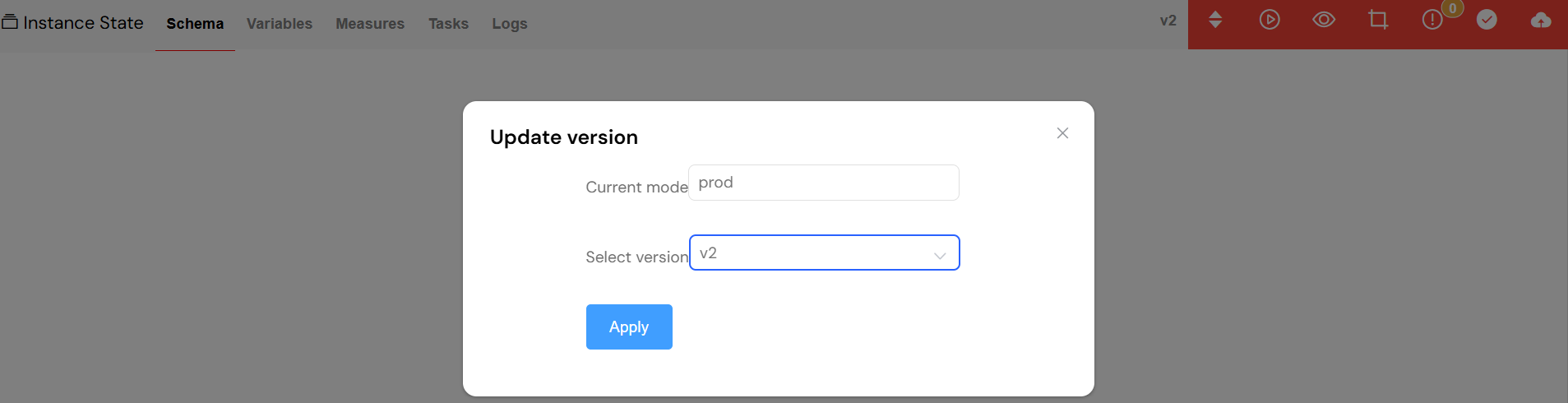
- Version History: You have access to a complete history of all available versions for each environment, allowing you to choose the appropriate version for an update.
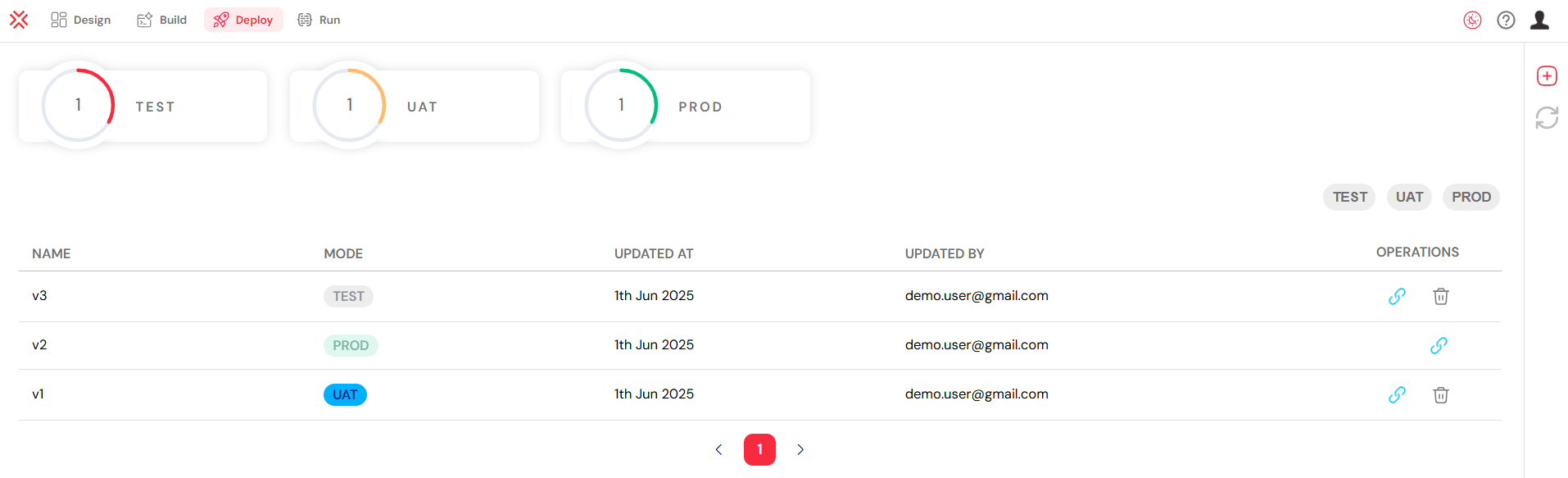
6.2. Error Handling & Recovery
When an instance fails, Softyflow provides the tools needed to diagnose and recover from the error.
- Error Visualization: Failed activities are clearly highlighted in red on the process diagram.
- Error Details: A dedicated error panel provides comprehensive details about the failure, often including stack traces and error messages.
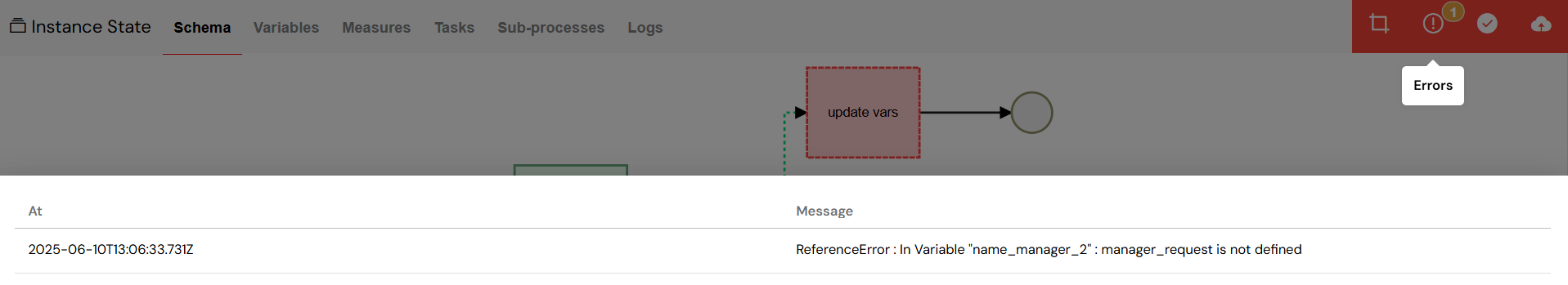
- Recovery Options: You have multiple paths to resolve instance issues, such as modifying variables, updating the process version, or manually advancing the process.
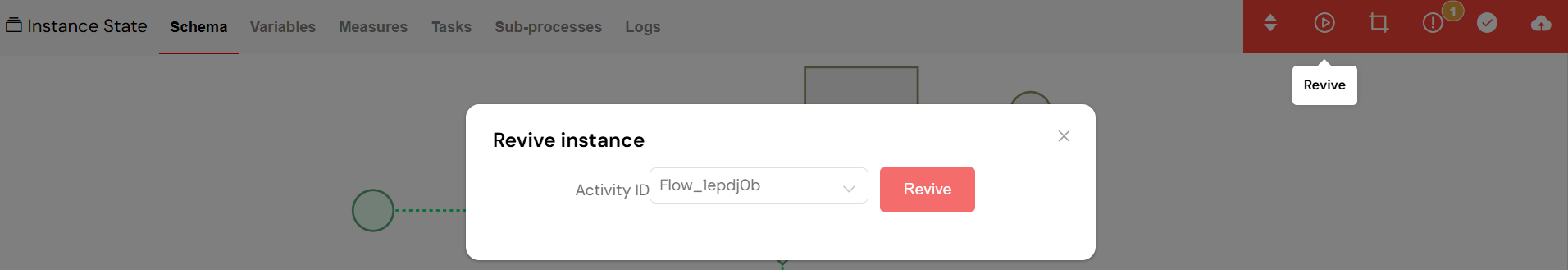
- Manual Intervention: For stuck processes, you can manually intervene to "revive" the process from a specific step, allowing it to continue execution.
6.3. Activity Flow Control
You have granular control over the flow of activities within a running instance:
- Manual Activity Addition: If necessary, you can add a missing activity to a running process.
- Parallel Gateway Handling: The system correctly manages variables in different branches of a parallel gateway.
- Flow Resumption: You can resume a process from any specific activity.
- Status Override: For recovery scenarios, you can manually override the status of an activity.
7. Instance Lifecycle States
The state of a process instance is always clearly indicated by its status, both in the instance list and in the detailed view.
| Status | Description | Visual Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Running | The process is actively executing steps, or is waiting for user tasks, conditions, or scheduled timers. | Orange |
| End | The instance has successfully executed all of its activities and has completed its lifecycle. | Green |
| Error | The instance has encountered an error and is in a failed state, requiring intervention. | Red |
| Pause | The execution of the instance has been paused, typically while waiting for external input or manual reactivation. | Blue |
By mastering the tools and features within the Run & Instance Management section, you can ensure that your automated processes run smoothly, efficiently, and reliably, forming the backbone of your organization's digital operations.
Next Steps
With a solid understanding of instance management, you can now explore related areas to further optimize your process operations:
Advanced Monitoring:
- Instances Monitoring: Dive into high-level monitoring with automated alerting capabilities.
- System Logs: Explore comprehensive audit trails for system-wide analysis.
- Settings: Configure global monitoring preferences and performance thresholds.
- Mail Management: Set up sophisticated automated notifications for your processes.
Administration Optimization:
- User Management: Optimize user and group assignments based on process execution data.
- Role Management: Refine role-based permissions based on real-world process usage.
- Authentication: Ensure that your process management environment is secure.
- Home Redirection: Create customized landing pages for different user roles to guide them to their relevant processes.
Development Enhancement:
- Project Setup: Fine-tune your project configurations based on execution data.
- Web Interface Design: Improve your user interfaces based on how they are used within your processes.
- Process Design: Optimize your process models based on execution analytics and performance data.
- Database Integration: Refine your database interactions based on process performance.
- Integration: Enhance your external system integrations based on execution patterns.
- Monitor & Run: Coordinate your development and operational monitoring strategies for a holistic view.