Logs
The Logs section offers administrators a powerful tool for comprehensive visibility into all platform activities. It serves as a centralized audit trail, capturing everything from user actions to system events, which is essential for security analysis, debugging, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
1. Logs Dashboard
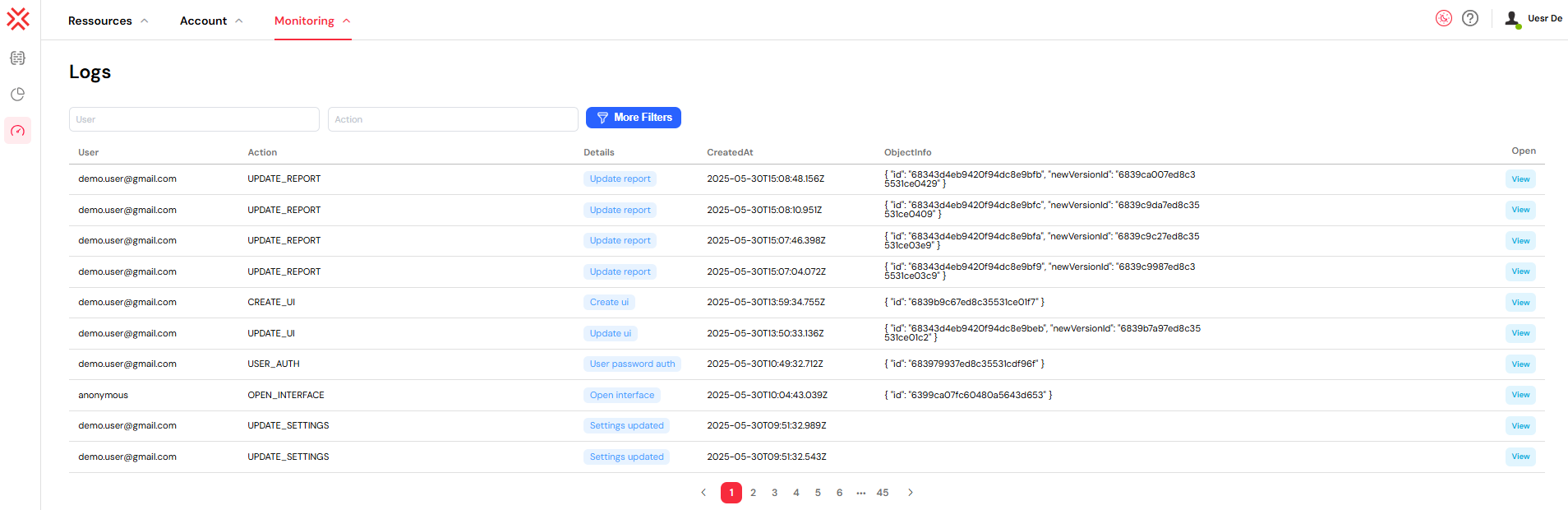
The main logs interface presents a real-time, structured feed of all platform activities. This table-based view allows administrators to efficiently track user behavior, monitor system events, and review operational changes across the entire Softyflow environment.
Understanding Log Entries
Each entry in the log provides detailed information about a specific event. The structure is designed for clarity and quick analysis:
- User: The email address of the user who performed the action, providing clear accountability.
- Action: A specific code representing the type of operation, such as
USER_AUTH,ADD_USERS_TO_GROUP, orUPDATE_INSTANCE. - Details: A brief, human-readable description or categorization of the action.
- CreatedAt: The precise timestamp indicating when the action occurred.
- ObjectInfo: A JSON object containing structured data and metadata related to the event, useful for in-depth analysis and debugging.
- Open: An interactive button that provides a direct link to the relevant resource, allowing for quick navigation and context-aware investigation.
2. Filtering and Searching Logs
The logs interface includes powerful filtering capabilities to help you quickly locate specific events or analyze trends.
2.1. Basic Filtering
- User Filter: Search for all activities performed by a specific user. This field supports autocomplete for user email addresses, making it easy to select the correct user.
- Action Filter: Isolate events by their action type. You can enter keywords to find specific actions (e.g.,
DELETE).
2.2. Advanced Filtering
For more granular searches, click "More Filters" to reveal additional options:
- Details Filter: Search for keywords within the action's description.
- Date Range Selector: Constrain your search to a specific timeframe by selecting a start and end date from the calendar view.
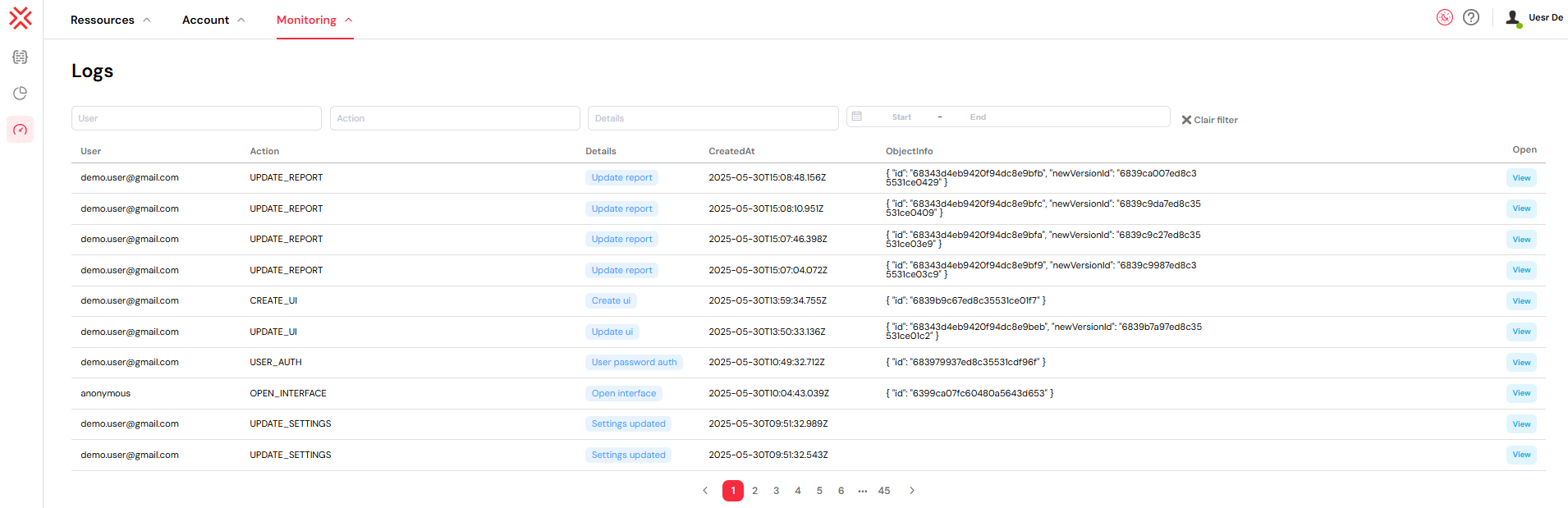
Filter Management
- To clear all active filters and reset the log view, simply click the "X" button.
- Filters are applied dynamically as you type or select options, providing real-time feedback.
- You can combine multiple filters (e.g., a specific user and a date range) to perform highly targeted searches.
3. Interactive Log Features
3.1. Context-Aware Navigation
The "View" button in each log entry is a smart link that directs you to the most relevant part of the platform:
USER_AUTH: Opens the corresponding user's profile page.ADD_USERS_TO_GROUP/REMOVE_USERS_FROM_GROUP: Navigates directly to the associated role management page.UPDATE_INSTANCE: Links to the specific instance configuration page for that process.OPEN_INTERFACE: Takes you to the specific web interface that was accessed.PROCESS_EXECUTION: Provides a link to the relevant process design or runtime monitoring view.
3.2. Pagination Controls
- Use the pagination controls at the bottom of the table to navigate through large volumes of log data.
- The number of entries displayed per page is configurable (defaulting to 10), allowing you to adjust the view to your preference.
- The total page count updates automatically based on your filter criteria.
4. Practical Use Cases for Log Analysis
4.1. Security and Auditing
Logs are a cornerstone of a robust security posture. Use them to:
- Monitor Authentication Events: Track all user login attempts, successes, and failures.
- Audit Permission Changes: Review any modifications to roles and permissions.
- Detect Anomalies: Identify unusual access patterns or suspicious activities that may indicate a security threat.
- Track Configuration Changes: Maintain a record of all changes to critical platform settings.
4.2. System Debugging and Troubleshooting
Quickly diagnose and resolve system issues by investigating:
- Process Execution Flow: Trace the lifecycle of process instances to identify bottlenecks or errors.
- Interface Performance: Correlate web interface access logs with performance reports.
- Integration Failures: Monitor logs for errors related to external API calls.
- Database Operations: Analyze database interaction logs to troubleshoot data-related issues.
4.3. Compliance and Reporting
Generate detailed reports to meet regulatory and business requirements:
- User Activity Reports: Create comprehensive activity reports for specific users or time periods.
- Change Management Documentation: Use logs as an official record of system changes for audits.
- Data Governance: Maintain a complete audit trail to ensure data governance policies are being followed.
5. Log Categories and Action Types
Logs are categorized by the area of the platform they relate to. Below are common action types you will encounter.
5.1. User Management Actions
USER_AUTH: Successful and failed user login attempts.CREATE_USER,UPDATE_USER,DELETE_USER: User account lifecycle events.BLOCK_USER/UNBLOCK_USER: Changes to a user's account status.
5.2. Role and Permission Actions
ADD_USERS_TO_GROUP/REMOVE_USERS_FROM_GROUP: Modifications to role memberships.CREATE_ROLE,UPDATE_ROLE,DELETE_ROLE: Role definition and lifecycle events.
5.3. Process and Instance Actions
START_PROCESS: Initiation of a new process instance.UPDATE_INSTANCE,END_INSTANCE: Modifications or termination of a running process.VALIDATE_TASK,UPDATE_TASK: User interactions with tasks within a process.
5.4. System Configuration Actions
UPDATE_SETTINGS: Changes to global platform settings.UPDATE_MAIL_PROVIDER: Modifications to the email service configuration.UPDATE_AUTH_SETTINGS: Adjustments to the authentication provider.
6. Best Practices for Effective Log Management
6.1. Search and Analysis Strategies
- Start with a Timeframe: Always use the date filter to narrow your search. This significantly improves performance.
- Combine Filters: For precise results, combine multiple criteria, such as a user, an action type, and a date range.
- Focus on a User: To investigate an individual's activity, filter by their email first.
6.2. Proactive Monitoring Routines
- Daily Checks: Briefly review logs daily to spot any immediate anomalies or critical errors.
- Weekly Analysis: Generate weekly summaries to identify trends in user activity or system performance.
- Alert Integration: Complement logging with the real-time alerts for critical events.
6.3. Performance and Data Retention
- Limit Broad Searches: Avoid overly broad searches on large datasets. Always apply specific filters first.
- Export for Offline Analysis: For complex investigations, export filtered log data to CSV or other formats.
- Define an Archive Strategy: Implement a log archiving and rotation policy to manage long-term storage and maintain system performance.
7. Integration with Other Features
7.1. Development Integration
Logs provide insights for development activities:
- Project Setup: Track project creation and configuration changes
- Web Interface Design: Monitor interface usage and identify popular features
- Process Design: Analyze process execution patterns and optimization opportunities.
- Database Integration: Track database operations and performance issues.
- Integration: Monitor external API calls and integration health.
- Test & Deploy: Track deployment activities and environment changes.
7.2. Administration Integration
Logs support comprehensive platform administration:
- User Management: Track user account changes and access patterns.
- Role Management: Monitor role assignments and permission changes.
- Authentication: Track login attempts and security events.
- Settings: Monitor platform configuration changes.
- Mail Management: Track email operations and delivery issues.
- Run Management: Deep dive into process execution details.
8. Compliance & Security
Use logs for security and compliance requirements:
- Regulatory Compliance: Meet audit requirements with comprehensive activity tracking.
- Security Monitoring: Identify potential security threats and unusual access patterns.
- Change Management: Document all system changes for governance purposes.
- Access Reviews: Regular review of user access and activity patterns.
Next Steps
Continue building your monitoring and security infrastructure:
Enhanced Monitoring:
- Run & Instance Management - Detailed process instance management and control.
- Settings - Configure logging preferences and retention policies.
- Mail Management - Set up email notifications for critical log events.
Security & Administration:
- User Management - Manage users based on activity patterns from logs.
- Role Management - Adjust permissions based on access pattern analysis.
- Authentication - Strengthen security based on authentication log analysis.
- Home Redirection - Configure personalized experiences based on usage patterns.
Development Optimization:
- Project Setup - Optimize project configurations based on usage data.
- Web Interface Design - Improve interfaces based on usage analytics.
- Process Design - Optimize processes based on execution patterns.
- Monitor & Run - Implement comprehensive runtime monitoring.