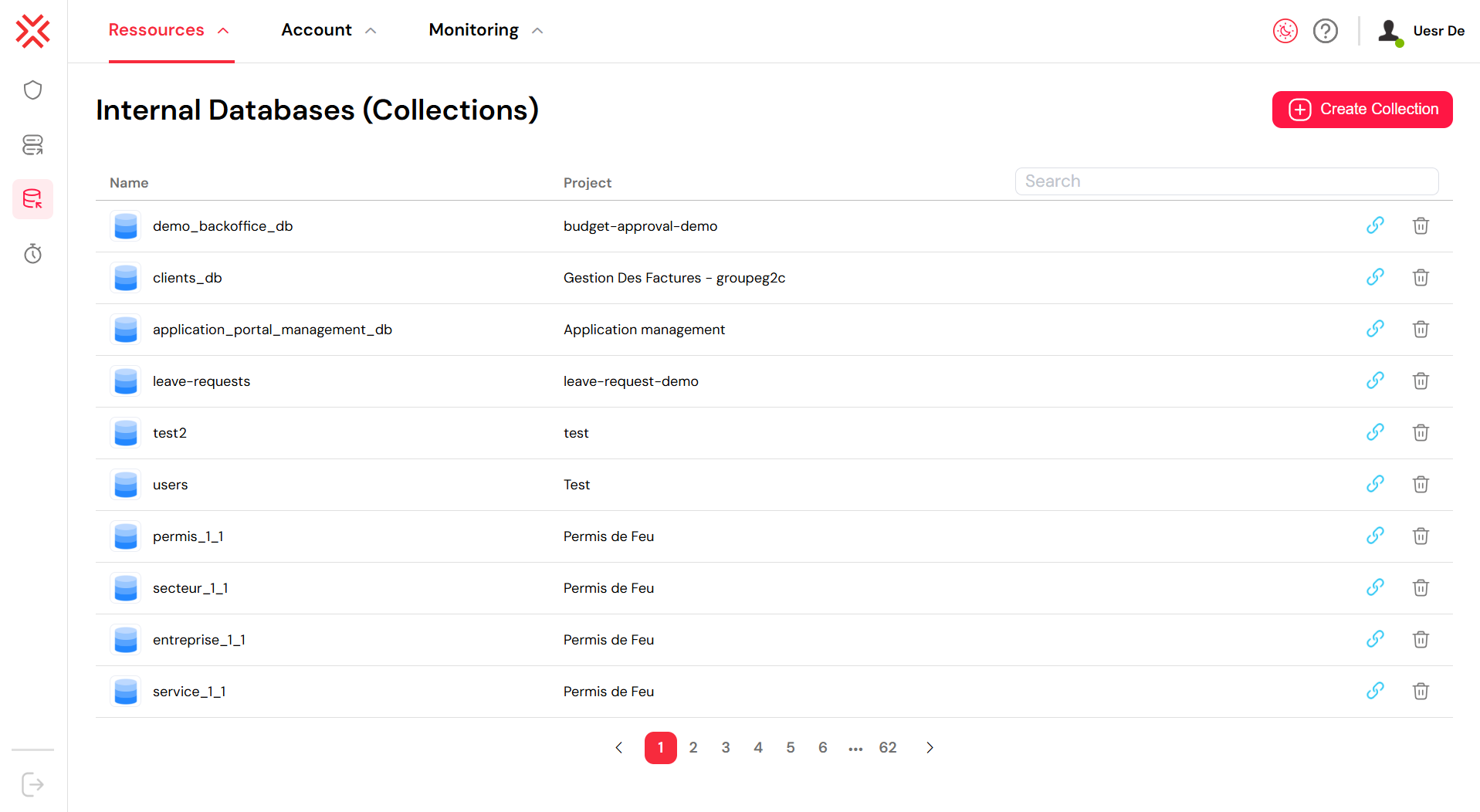
MongoDB Collections
1. Introduction to MongoDB in Softyflow
In the Softyflow ecosystem, Collections are built upon MongoDB, a powerful, cross-platform, document-oriented database. MongoDB is renowned for its high performance, high availability, and easy scalability, making it an ideal choice for managing your application's data. It operates on the concept of collections and documents, which offers a flexible and scalable alternative to traditional relational databases (RDBMS).
1.1. Understanding the Core Concepts
To effectively use Collections in Softyflow, it's important to grasp the fundamental structure of MongoDB.
1.1.1. Databases
A Database acts as a physical container for your collections. Each database has its own set of files on the file system, and a single MongoDB server can manage multiple databases.
1.1.2. Collections
A Collection is a grouping of MongoDB documents, analogous to a table in a relational database. It exists within a single database and does not enforce a rigid schema. This means documents within the same collection can have different fields, though they typically serve a similar or related purpose.
1.1.3. Documents
A Document is a set of key-value pairs where all the data is stored. Documents feature a dynamic schema, which allows for significant flexibility. Documents in the same collection don't need to share the same structure, and common fields can hold different types of data.
1.1.3.1. Sample Document Structure
Here is an example of what a MongoDB document looks like. This structure allows for complex and nested data.
{
"_id": "ObjectId(\"7df78ad8902c\")",
"title": "MongoDB Overview",
"description": "MongoDB is a NoSQL database",
"by": "Tutorials Point",
"tags": ["mongodb", "database", "NoSQL"],
"likes": 100,
"comments": [
{
"user": "user1",
"message": "My first comment",
"dateCreated": "new Date(\"2011-01-20T02:15:00Z\")",
"like": 0
},
{
"user": "user2",
"message": "My second comment",
"dateCreated": "new Date(\"2011-01-25T07:45:00Z\")",
"like": 5
}
]
}
The _id field is a 12-byte hexadecimal number that ensures every document is unique. You can provide your own _id when inserting a document. If you don't, MongoDB will automatically generate a unique ID.
1.2. External MongoDB Resources
For more in-depth information about MongoDB's capabilities, you can refer to the official documentation:
- Query and Projection Operators: These operators allow you to locate data and modify how it is presented.
- Update Operators: These operators enable you to modify data or add new data to your database.
- Aggregation Pipeline Stages: Learn about the stages available in the Aggregation Pipeline.
- Aggregation Pipeline Operators: Explore the operators used to define and manipulate documents in pipeline stages.
2. Working with Collections in Softyflow
Softyflow simplifies the process of creating and managing MongoDB collections directly from the studio.
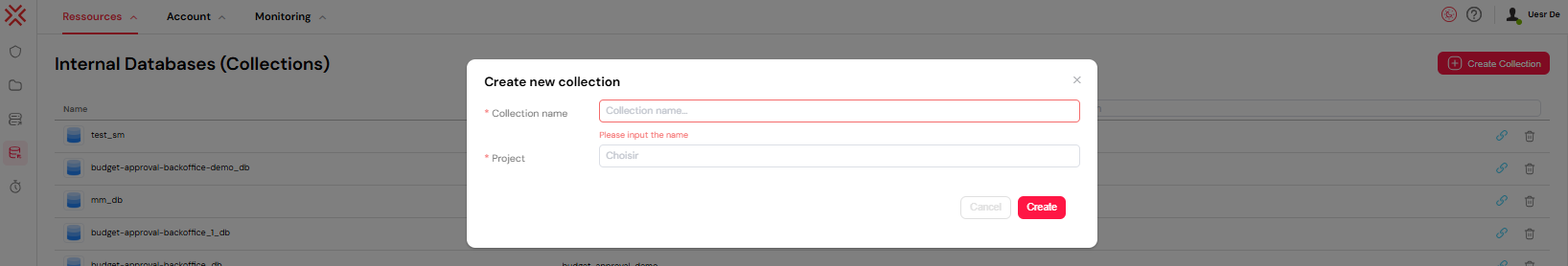
2.1. Creating a New Collection
To get started, navigate to the Collection tab in your Softyflow project and provide a name for your new collection.
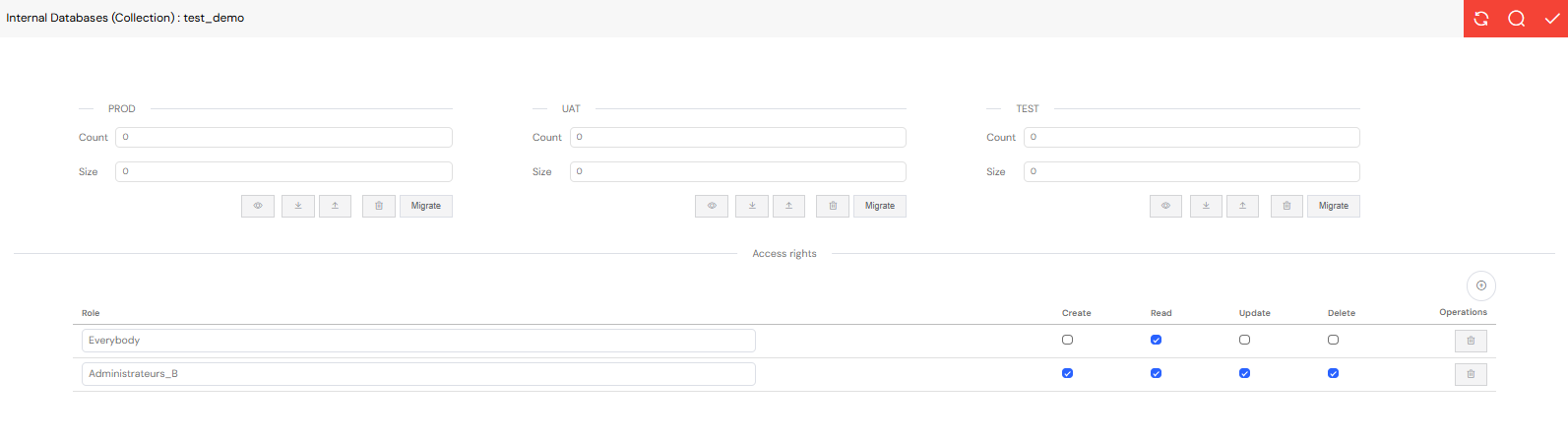
2.2. Performing CRUD Operations
CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations in MongoDB are performed on a single collection at a time. Softyflow provides a user-friendly interface and SDK methods to handle these operations.
2.2.1. Create (Insert) Operations
Insert operations in MongoDB are atomic at the single-document level. Softyflow supports the standard MongoDB insert methods.
- InsertOne in Softyflow: You can insert a single document into your collection from a user form or a process. This is typically done by configuring an action. For processes, you first need to create an input/output variable and then select the appropriate action. More details can be found in the Web Interface Actions documentation.
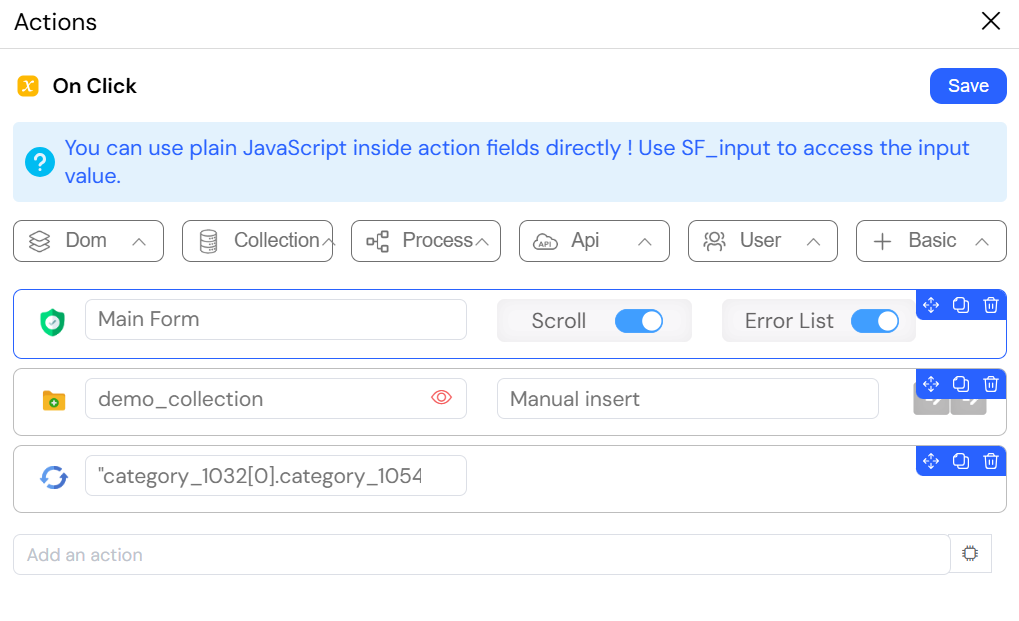
Example: Submitting a Form to a Collection
The following image shows a multi-step action triggered on a form. First, validateForm ensures all data is valid. Then, InsertOne saves the form data as a new document in the collection. Finally, refreshwidget updates the UI to display the new entry.
- InsertMany in Softyflow: To insert multiple documents at once, you can use a script. This is detailed in the Web Modeler SDK documentation for insertMany.
2.2.2. Read (Find) Operations
Read operations allow you to retrieve documents using specific query filters. You can learn more about query filters from the MongoDB documentation.
Find in Softyflow: To retrieve multiple documents, you can use the
findaction. This is available in both user forms and processes.FindOne in Softyflow: To retrieve a single document, use the
findOneaction. This is also available in both user forms and processes.
Example: Loading Data into a Form
This image shows an action that finds a document in a collection and uses its data to populate the fields of a form.
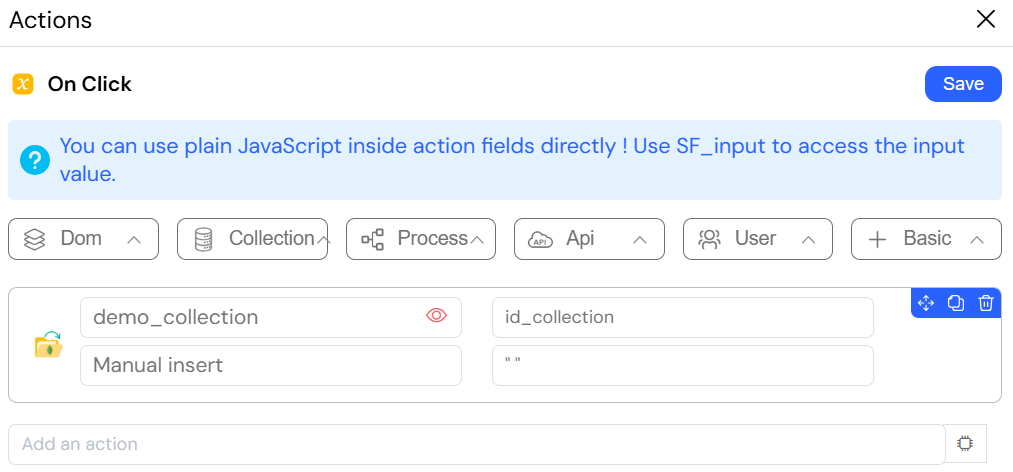
2.2.3. Update Operations
Update operations modify existing documents in a collection and are atomic at the document level. Be cautious, as updates are permanent.
Example: Updating a Document from a Form
The image below illustrates an action configured to update a document in a collection by referencing its unique _id.
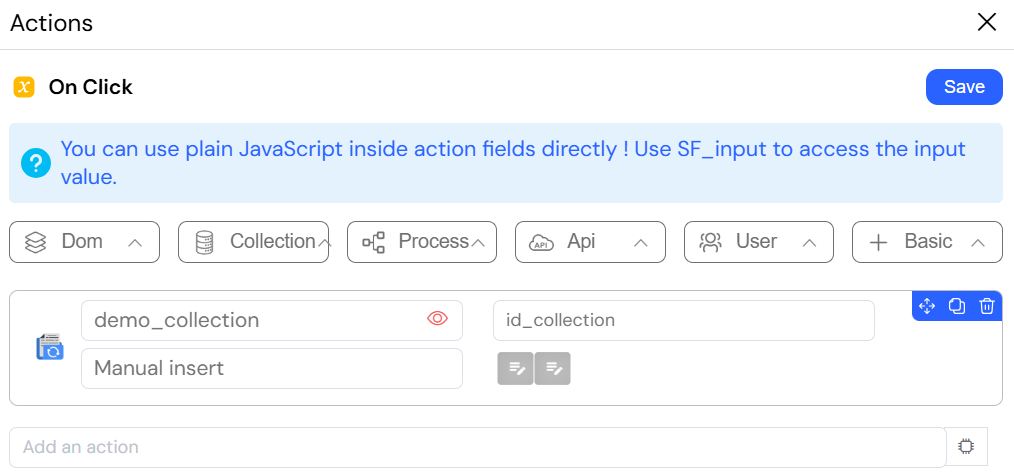
UpdateMany in Softyflow: For updating multiple documents, a script is required. Refer to the Web Modeler SDK
updatemethod for guidance.ReplaceOne: This operation replaces an entire document, except for the
_idfield.
2.2.4. Delete Operations
Delete operations are used to remove documents from a collection and are also atomic at the document level. Like updates, deletions are permanent.
DeleteOne in Softyflow: You can delete a single document using an action in a user form or process.
DeleteMany in Softyflow: To delete multiple documents, you will need to use a script. The Web Modeler SDK
deletemethod provides the necessary functionality.