File Management in Softyflow
The Files section in Softyflow is a centralized hub for managing all your project-related files. It offers a robust interface to upload, organize, view, and secure your files, ensuring seamless integration with your workflows. This guide provides a detailed walkthrough of its features and best practices.
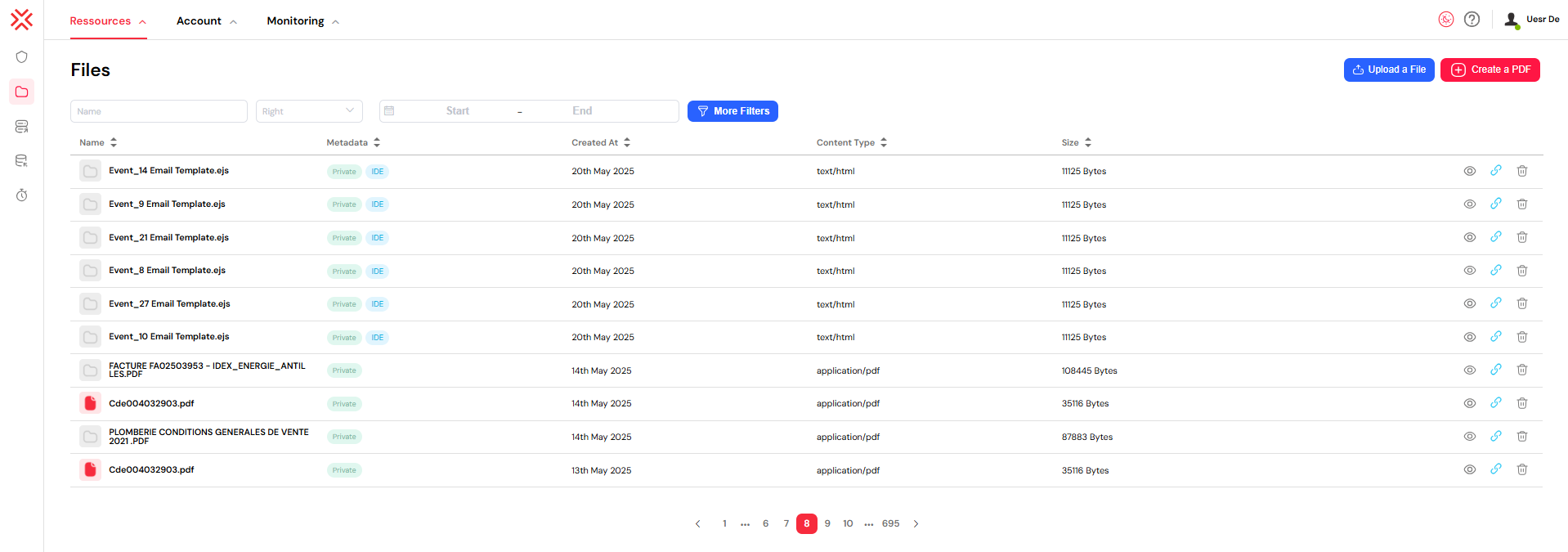
The file management screen provides a comprehensive overview of all uploaded files. The tabular layout is designed for clarity, presenting key information at a glance, including file metadata, creation dates, types, and access permissions.
1. Uploading Files to Your Repository
You can easily add files to your project repository. Softyflow supports various file types and provides options to control their visibility.
1.1. Step-by-Step Upload Process
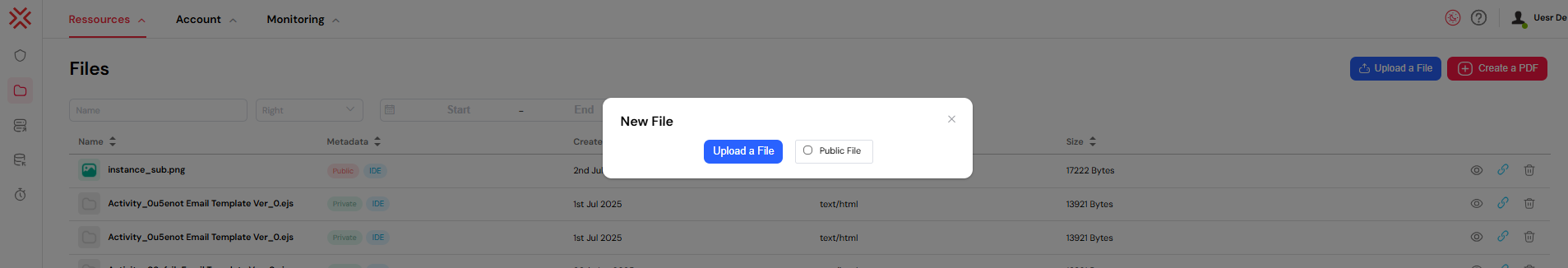
- Click the "Upload a File" button, located in the top-right corner of the interface.
- A dialog box will appear, allowing you to select one or more files from your local system.
- Before uploading, you must choose a visibility setting for your files:
- Public: The file will be accessible via a public URL, which can be shared with anyone.
- Private: The file will only be accessible to authenticated users with the appropriate permissions.
- Click the final "Upload" button to add the files to your repository.
1.2. Supported File Types
Softyflow recognizes and visually distinguishes various file types to help you identify them quickly. Each type is represented by a unique, color-coded icon:
- CSS files (
.css): Blue icon. Used for styling web interfaces. - PDF files (
.pdf): Red icon. Used for documents and report templates. - JavaScript files (
.js): Yellow icon. Used for client-side or server-side scripting. - Images (
.png,.jpeg,.tif,.gif): Green icon. - Generic files: Grey icon. Represents all other file types not listed above.
2. Understanding the File Information Table
The file list is organized into several columns, each providing specific information about the files.
2.1. Name
This column displays the filename along with its corresponding type icon. Clicking on a filename will open it in a previewer or editor, depending on the file type.
2.2. Metadata
This column provides crucial tags that describe the file's status and origin:
- Visibility Tags:
Public(Red Tag): Indicates the file is publicly accessible.Private(Green Tag): Indicates the file is restricted to authorized users.
- Source Tags:
IDE(Blue Tag): The file was created or modified within the Softyflow Integrated Development Environment (IDE).User(Blue Tag): The file was uploaded directly by a user.
- Storage Tags:
S3(Yellow Tag): The file is stored in an Amazon S3 bucket, indicating cloud-based storage.
2.3. Other Columns
- Created At: Shows the exact date and time the file was uploaded, formatted for readability.
- Content Type: Displays the file's MIME type (e.g.,
application/pdf), which helps in identifying the file's format. - Size: Shows the file size in bytes, which is useful for storage management and monitoring.
3. Performing File Operations
You can perform several actions on each file directly from the list.
3.1. View
Click the View button (eye icon) to open a preview of the file. PDF templates have a dedicated preview mode, while other file types will typically open in a new browser tab for viewing or downloading.
3.2. Copy URL
Click the Copy button (clipboard icon) to copy the file's direct URL to your clipboard. A success notification will confirm the action. This is useful for sharing links or embedding files in other applications.
3.3. Delete
Click the Delete button (trash icon) to permanently remove a file. A confirmation dialog will appear to prevent accidental deletions.
4. Filtering and Searching for Files
Efficiently locate files using a powerful set of filtering and search tools.
4.1. Basic Filters
You can quickly narrow down the file list using the primary filter fields:
- Name: Search for files by their filename.
- Visibility: Filter the list to show only
PublicorPrivatefiles. - Date Range: Use the date picker to find files created within a specific time period.

4.2. Advanced Filters
For more specific searches, click the "More Filters" button to reveal additional options:
- Content Type: Filter files by their specific MIME type (e.g.,
image/png). - You can clear all active filters at once by clicking the "Clear filter" button.

5. Navigating and Sorting the File List
5.1. Pagination
When dealing with a large number of files, the pagination controls at the bottom of the list allow you to navigate through different pages. You can also configure the number of items displayed per page (default is 10).
5.2. Sorting
You can sort the file list by clicking on the column headers. A second click will reverse the sort order (ascending/descending). Sorting is available for the following columns:
- Name
- Created At
- Content Type
- Size
- Metadata
6. Handling of Special File Types
6.1. PDF Templates
Files with a .PDFtemplate extension are treated as dynamic templates. These can be used to generate PDFs with variable data. A dedicated "Create a PDF" button and a special preview mode are available for these files.
6.2. IDE Files vs. User Files
Softyflow distinguishes between files originating from the IDE and those uploaded by users. This distinction can affect how files are handled and processed within the system.
7. Access Control and File URLs
7.1. Public Files
- Public files are accessible via a direct URL in the format:
/uploads/{fileId}/name/{filename}. - These URLs can be shared freely, as they do not require authentication.
7.2. Private Files
- Access to private files is restricted and requires user authentication.
- The system enforces permissions to ensure that only authorized users can view or download these files.
8. Best Practices for File Management
8.1. Organization
- Use Descriptive Names: Employ clear and consistent filenames for easy identification.
- Set Visibility Correctly: Always set the appropriate
PublicorPrivatevisibility based on the sensitivity of the content. - Regularly Clean Up: Periodically review and remove outdated or unused files to keep your repository organized.
8.2. Storage and Security
- Monitor File Sizes: Keep an eye on storage usage to avoid exceeding limits.
- Audit Public Files: Regularly check publicly accessible files to ensure they do not contain sensitive information.
- Use Private by Default: When in doubt, mark files as
Privateto maintain security.
9. Troubleshooting Common Issues
9.1. Upload Failures
- File Size: Ensure the file size does not exceed the system's maximum upload limit.
- File Type: Verify that the file type is supported.
- Network Issues: A stable internet connection is crucial, especially for large uploads.
9.2. Access Denied
- Visibility: Double-check if the file is set to
Privatewhen you expect it to be public. - Permissions: For private files, confirm that the user has the necessary permissions to access them.
- URL Errors: Ensure you are using the correct and complete URL for the file.