Softyflow BPMN Process Components
This guide provides comprehensive documentation for all available BPMN components in Softyflow's Process Modeler and their configuration options.
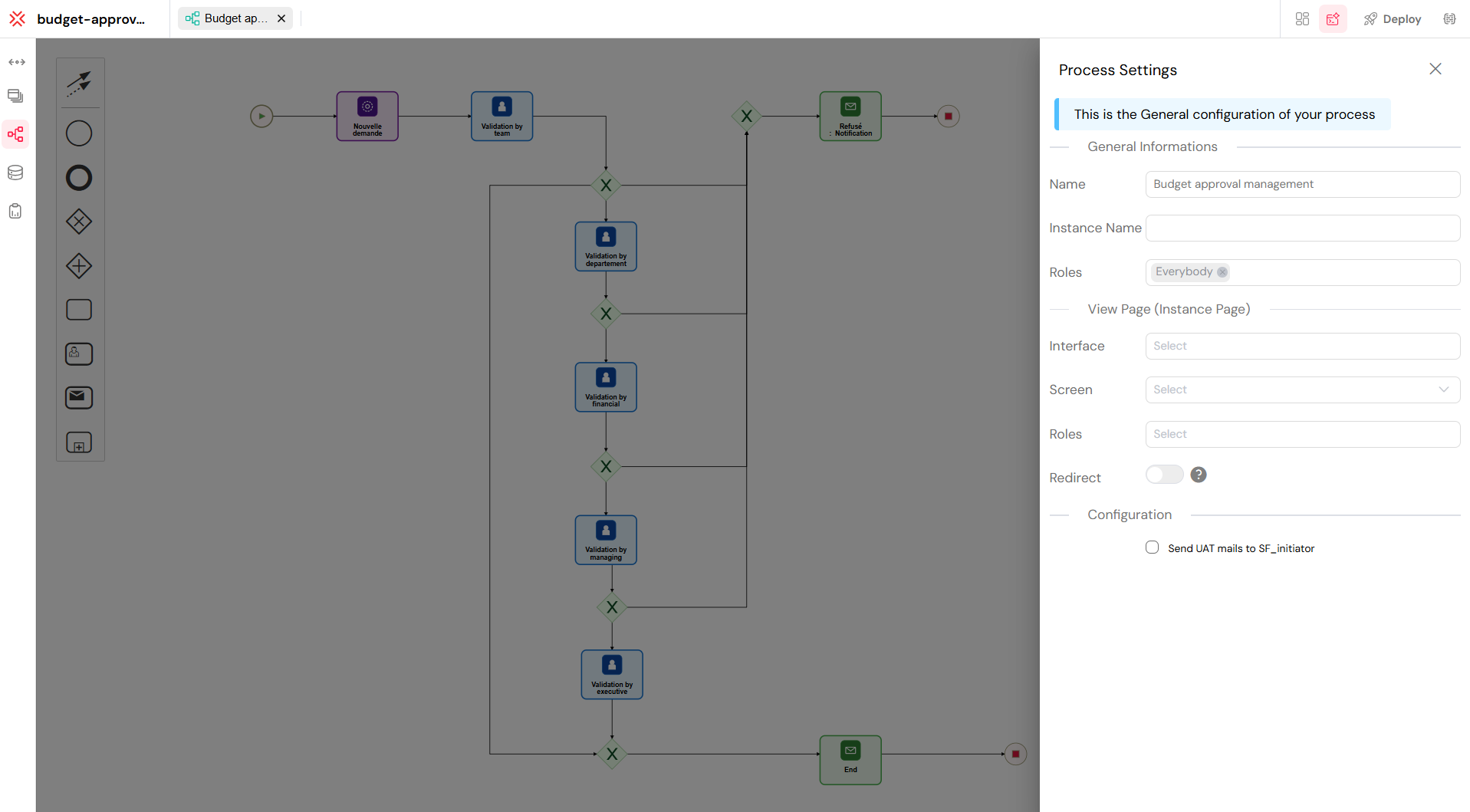
This comprehensive palette shows all available BPMN components in Softyflow's Process Modeler, including tasks, events, Gateways, and flow elements for building complete workflow automation.
1. Task Components
1.1 Empty Task (Normal Task)
Element Type: bpmn:Task
An Empty Task, also called a Normal Task, represents a generic unit of work within the process that doesn’t have a predefined behavior. It can execute custom scripts, perform calculations, or serve as a placeholder for automation logic defined via Input/Output variables.
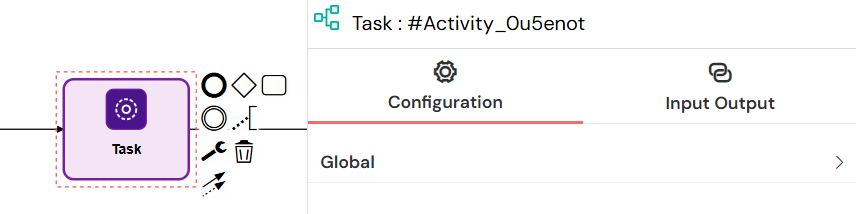
Empty Tasks are frequently used for intermediate processing steps or backend automation, where logic is executed automatically without user interaction.
1.2 User Task (Manual Task)
Element Type: bpmn:UserTask
User Tasks represent manual work that needs to be done by a human user. These tasks appear in user task baskets and can be assigned to specific users or roles.
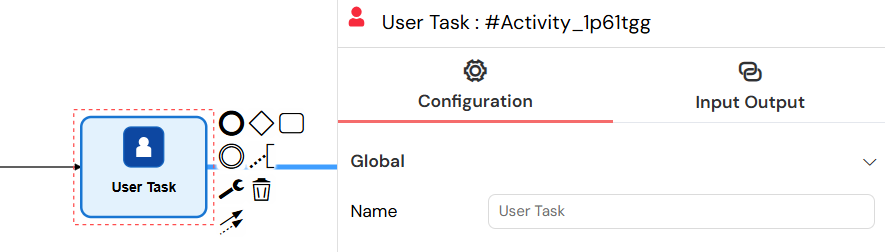
The User Task element represents manual work that requires human interaction, appearing in user task lists for assignment and completion.
Configuration Options
Users and Roles
Users: Assign tasks to specific users by email
- Supports dynamic assignment using variables:
{{ userEmails }} - Can assign to multiple users with comma-separated emails
- Special variables:
{{SF_initiator}},{{SF_latestValidator}}
- Supports dynamic assignment using variables:
Roles: Assign tasks to user groups/roles
- Supports dynamic assignment using variables:
{{ roleId }} - Can assign to multiple roles with comma-separated IDs
- Special role:
public(accessible to all users)
- Supports dynamic assignment using variables:
reCAPTCHA: Enable for public tasks to prevent spam and fraudulent activities
Observers: Users/roles that can view the task in read-only mode
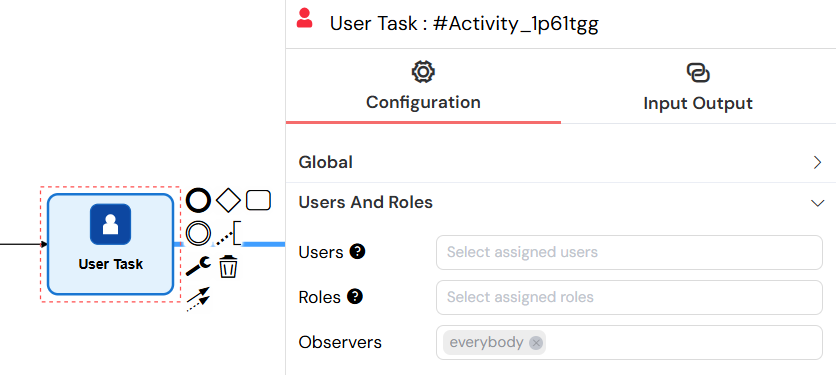
This configuration panel allows you to assign tasks to specific users, roles, or observers, with support for dynamic assignment using process variables.
Interface Configuration
- Interface: Select a web interface (UI) for task execution
- Screen: Choose specific screen within the selected interface
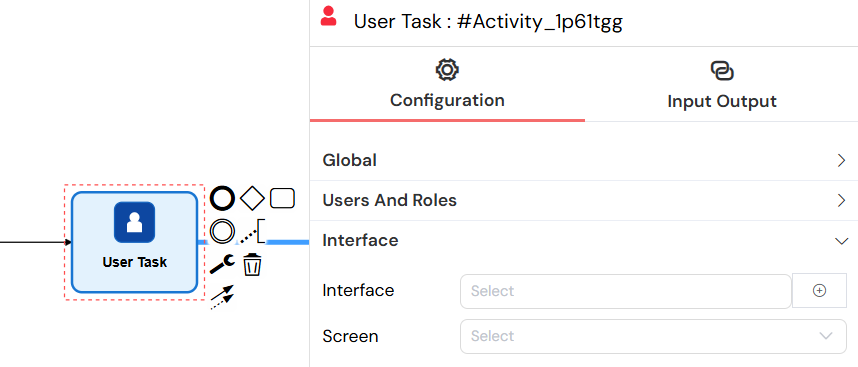
The interface configuration links the task to a specific web interface and screen, determining what form users interact with when completing the task.
Task Priority
- Due in: Set task due date in minutes
- Priority: Set task priority level
- Very Low, Low, Medium, High, Very High
- Description: Task description text
- Hide In Task Basket: Option to hide task from task basket view
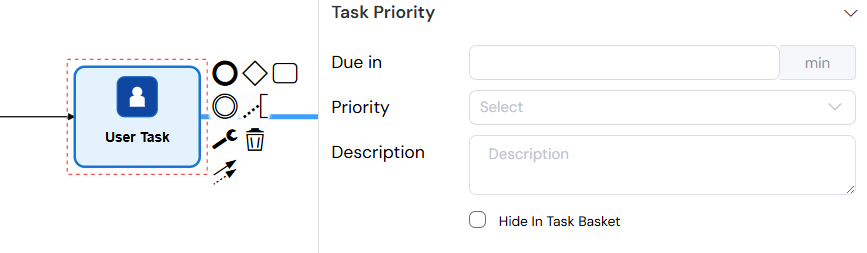
Task priority settings allow you to set due dates, priority levels, descriptions, and visibility options to manage task urgency and organization.
Notification Settings
- Send notification email: Enable/disable email notifications
- Provider: Choose email provider (default: Softyflow provider)
- Mail Subject: Email subject line (supports variables)
- Mail Template: Visual email template editor
- Advanced Settings:
- Send UAT mail to SF_initiator: Send test emails to process initiator
- From: Custom sender email
- Cc: Carbon copy recipients
- Reply to: Reply-to addresses
- Attachments: File attachments from project files
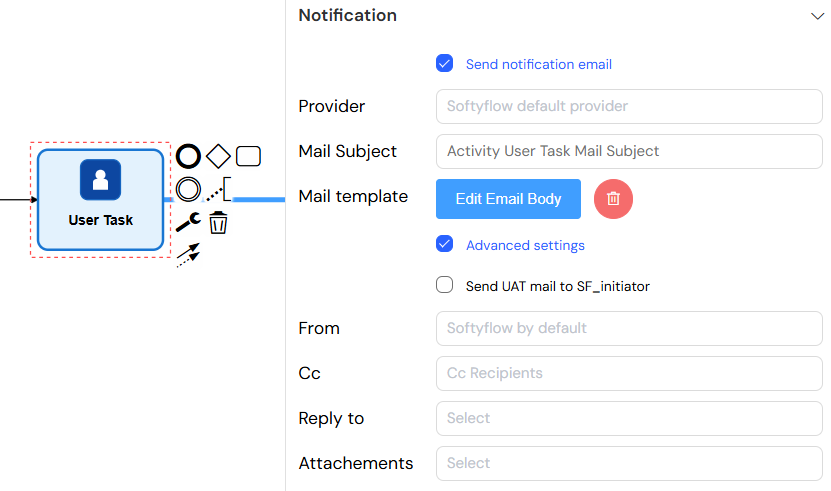
The notification settings enable automatic email alerts for task assignments, with customizable templates, providers, and advanced options for recipients and attachments.
1.3 Send Task (Mail Task)
Element Type: bpmn:SendTask
The Send Task element automates email delivery during process execution, sending notifications or information without requiring human interaction.
Configuration Options
Recipients
- To Users: Email recipients (users)
- To Roles: Email recipients (roles/groups)
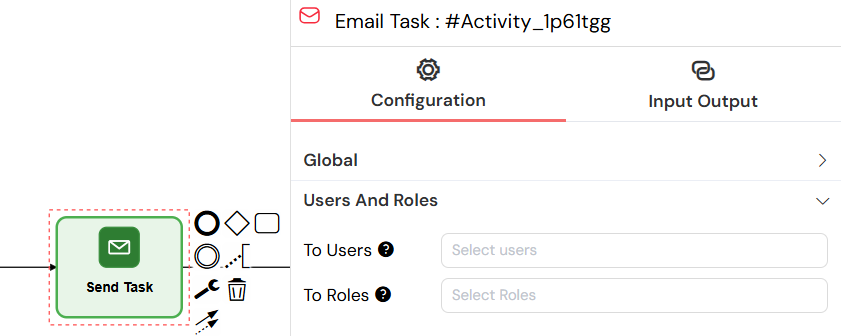
This panel configures email recipients for send tasks, supporting both direct user email addresses and role-based group assignments.
Mail Configuration
- Provider: Email service provider
- Mail Subject: Email subject (supports variables like
{{ taskId }}) - Mail Template: Visual email body editor
- Advanced Settings: Same as User Task notification settings
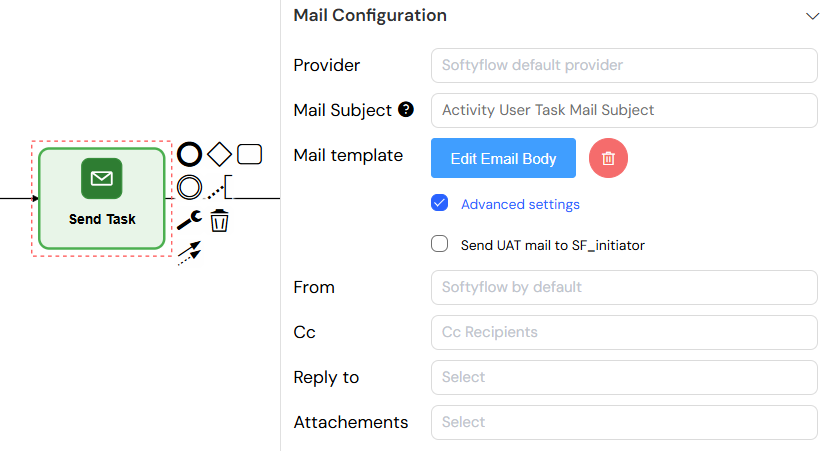
The mail configuration panel allows you to define the email subject and compose the message body using process variables for dynamic content.
Mail Template

The visual email template editor provides a drag-and-drop interface for designing professional email layouts with dynamic content and formatting options.
1.4 Sub Process
Element Type: bpmn:SubProcess
Sub Processes allow embedding and executing other processes within the current process.
The Sub Process element allows you to embed and execute other processes within the current workflow, enabling process modularity and reusability.
Configuration Options
- Sub Process: Select the process to execute
- Parallel Multi-Instance: Enable parallel execution of multiple instances
- Parallel Array: Variable containing array values for multi-instance execution
- Each array value starts a new sub-process instance
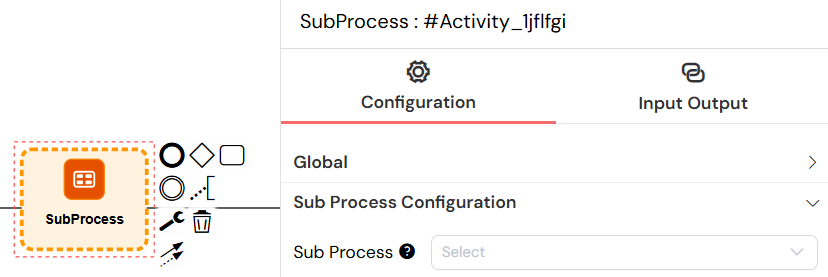
This configuration panel enables you to select which process to execute as a subprocess and configure parallel multi-instance execution for processing arrays of data.
2. Gateway Components
Gateways control the divergence and convergence of process flows based on defined conditions.
2.1 Exclusive Gateway (XOR)
Exclusive Gateways create decision points in the process flow where only one path can be taken based on conditions.
- Used to model decisions based on conditions.
- Only one outgoing path is selected (mutually exclusive).
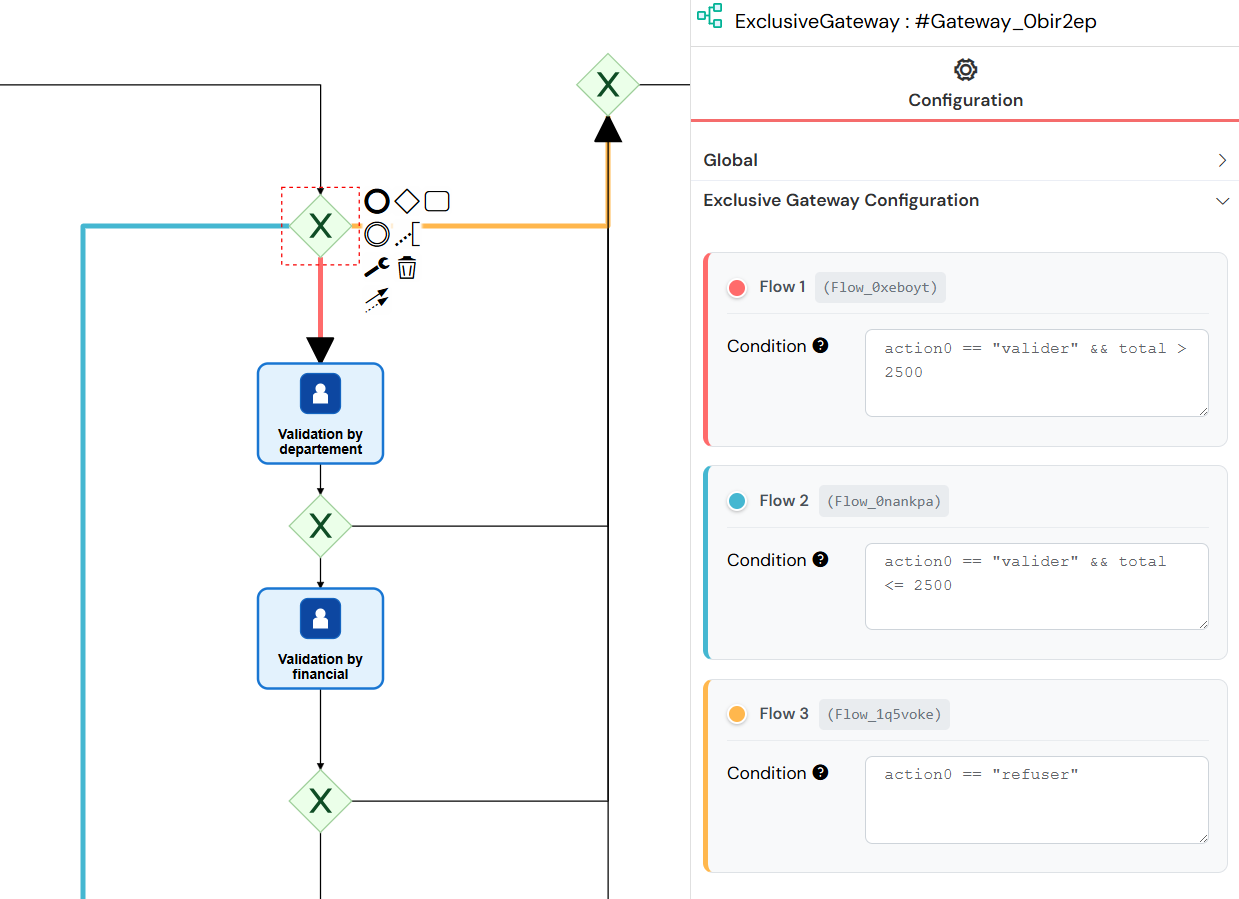
Exclusive Gateways create decision points where only one outgoing path is selected based on conditional expressions, directing workflow to the appropriate branch.
Parallel Gateway
- Used to fork the process into multiple parallel paths.
- Can also join multiple incoming paths into one.
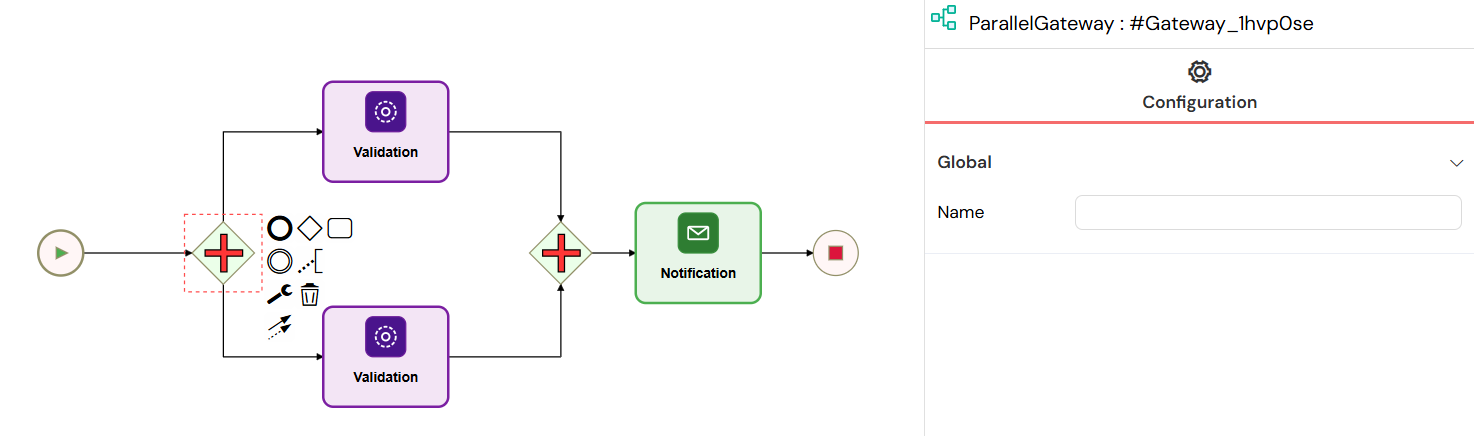
Parallel Gateways enable simultaneous execution of multiple workflow paths, allowing tasks to run concurrently and synchronizing them when all paths complete.
3. Event Components
3.1 Boundary Events
Element Type: bpmn:BoundaryEvent
Boundary Events are attached to activities and can interrupt or run parallel to the main activity.
Timer Events
Event Definition: bpmn:TimerEventDefinition
Interrupting Timer (One-time)
- Start in: Time to wait before triggering (in minutes)
- Supports variable-based delays:
{{ delay }} - Interrupts the main activity when triggered
Non-Interrupting Timer (Recurring)
- Every: Recurring interval (in minutes)
- Runs periodically without interrupting the main activity
- Continues until the main activity completes
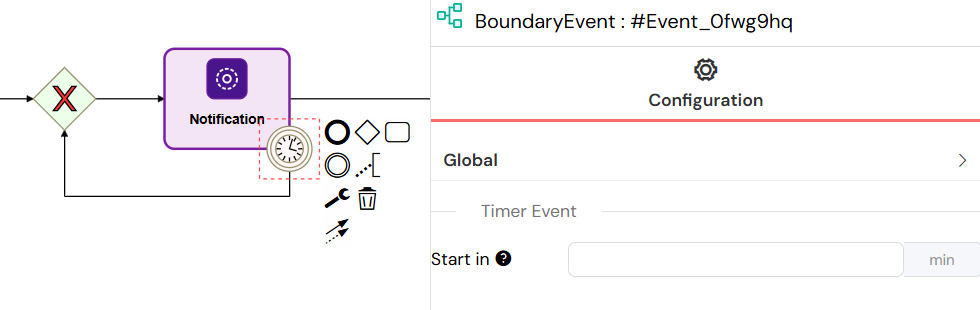
Timer events enable time-based workflow automation, triggering actions after specified delays or at recurring intervals, with support for both interrupting and non-interrupting behavior.
Error Events
Event Definition: bpmn:ErrorEventDefinition
- Catches errors from the attached activity
- Provides error handling and recovery mechanisms
- Can define error-specific handling logic
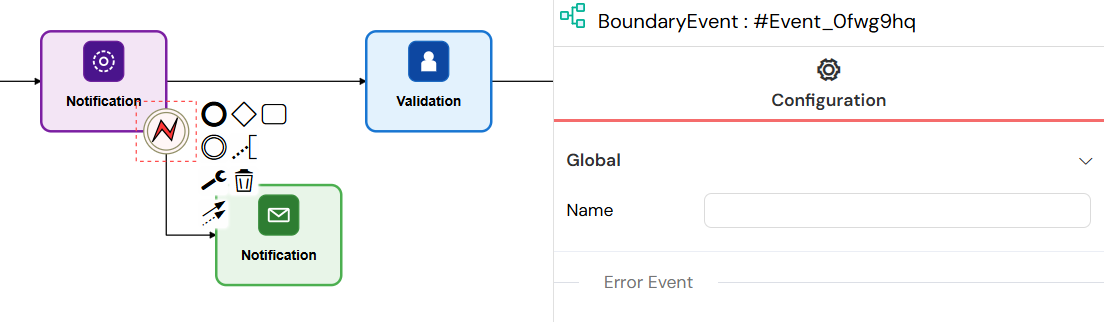
Error events provide error handling mechanisms by catching exceptions from activities and redirecting workflow to error recovery paths.
3.2 Start Events
Element Type: bpmn:StartEvent
Start Events define where process instances begin execution.
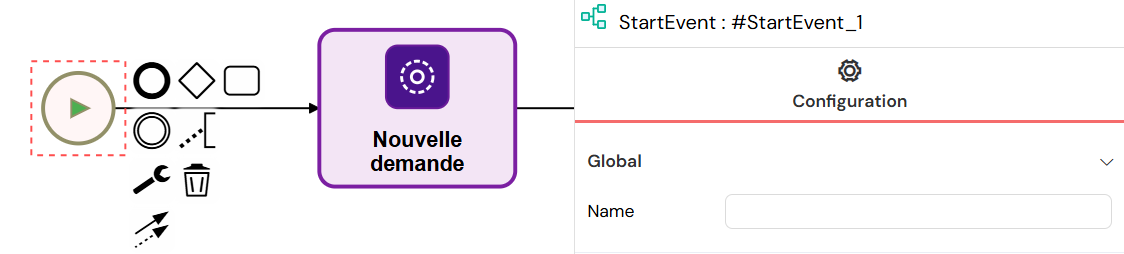
Start Events define the entry points for process instances, marking where workflow execution begins and initializing the process with starting variables. They can only be triggered by a single user who initiates the process execution.
3.3 End Events
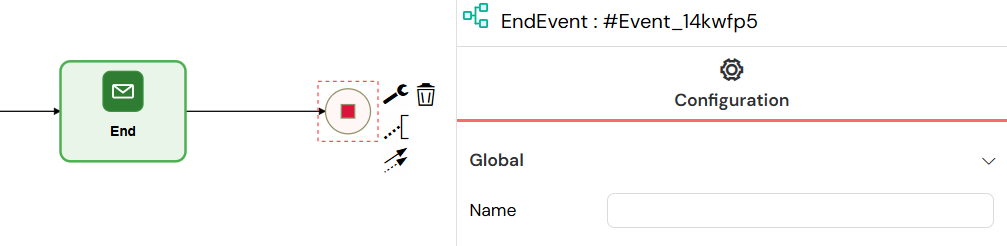
Element Type: bpmn:EndEvent
End Events mark the completion points of process instances, finalizing the workflow execution and storing the final state of process variables.
4. Flow Components
4.1 Sequence Flow
Element Type: bpmn:SequenceFlow
Sequence Flows connect process elements and define the execution order.
Configuration Options
- Conditional Flows: Add JavaScript conditions to control flow
- Default Flows: Fallback paths when no conditions are met
- Variable access for condition evaluation
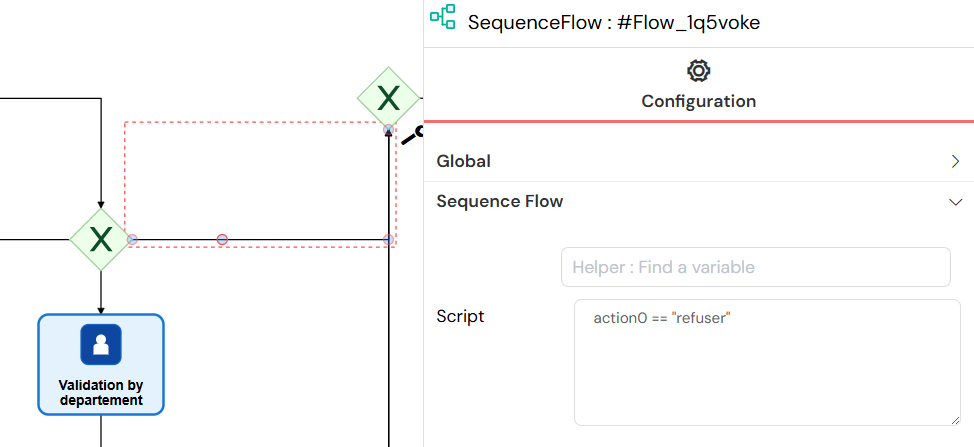
Sequence flows connect process elements and define execution order, with support for conditional expressions to control which paths are taken during workflow execution.
5. Input/Output Variables
Available for Empty Task, User Tasks, Send Tasks, and Sub Processes.
I/O Variables define values evaluated before (Input) or after (Output) task execution.
Input Parameters
- Process data before task execution
- Transform external data for task consumption
- Set up task-specific variables
Output Parameters
- Process data after task completion
- Transform task results for process consumption
- Update process variables
Variable Types
Scripts
- Type:
script - Language: JavaScript
- Execution: Server-side execution
- Use Cases: Complex data manipulation, calculations, API calls
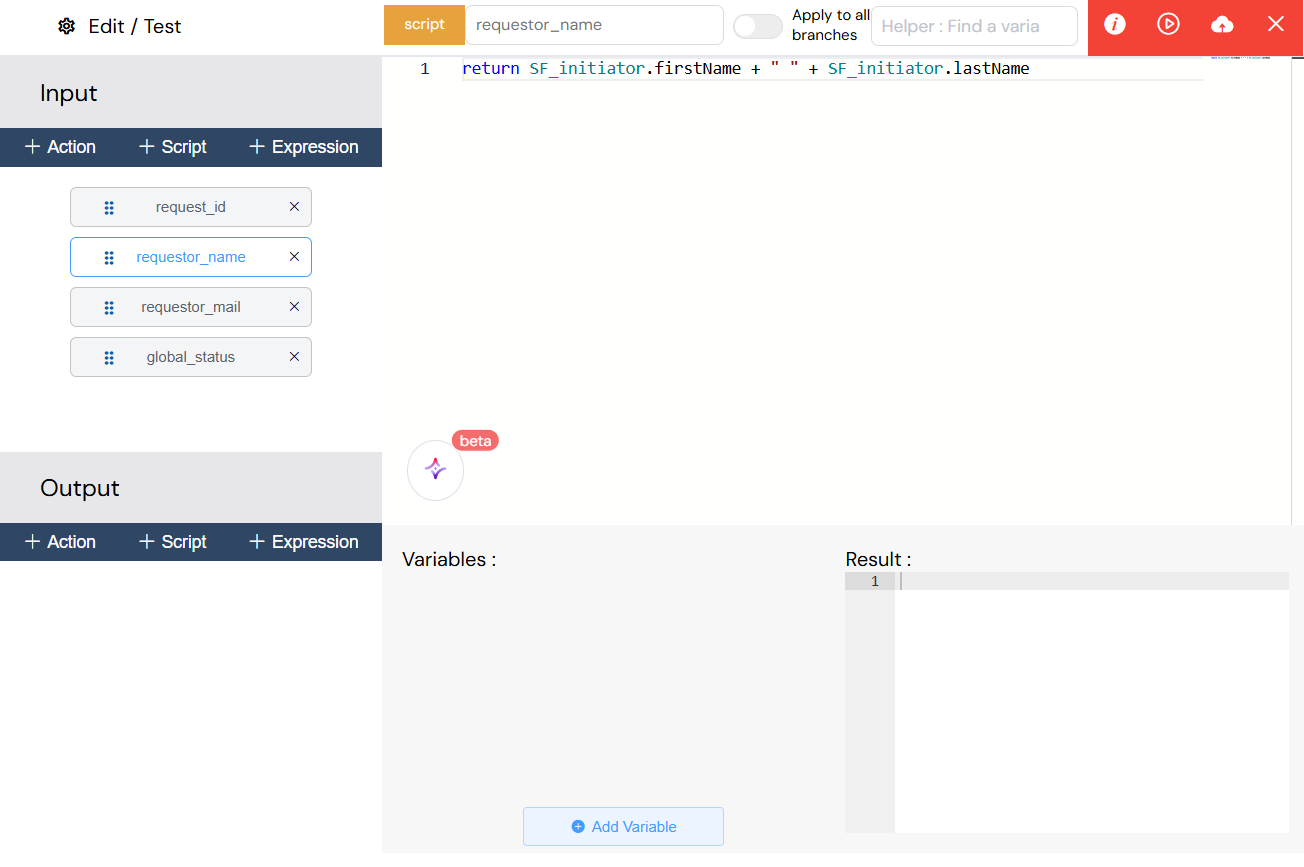
Script-based input/output variables enable complex data manipulation using JavaScript, with server-side execution for calculations, API calls, and business logic processing.
Expressions
- Type:
expression - Language: JavaScript expressions
- Execution: Simple value assignments and transformations
- Use Cases: Variable mapping, simple calculations
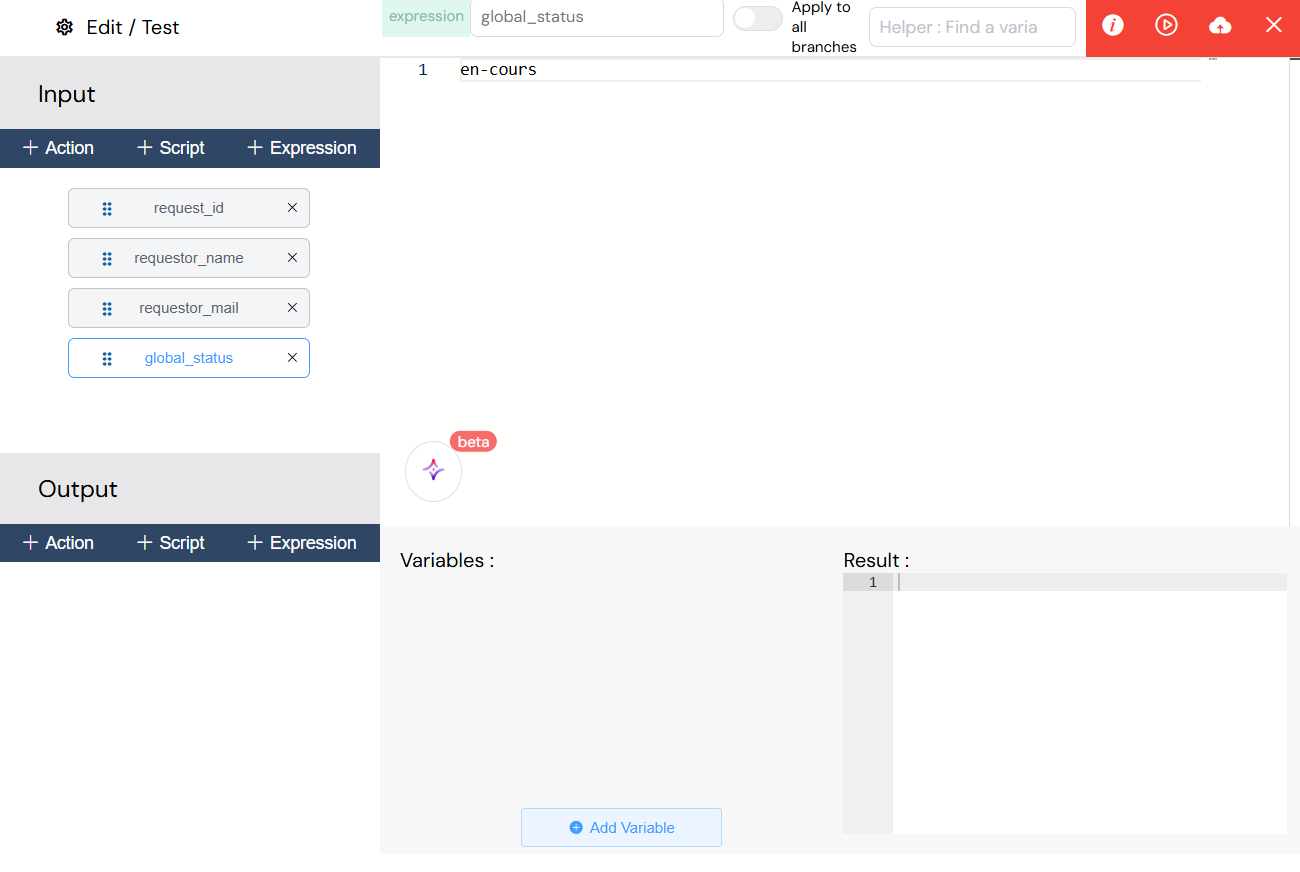
Expression-based variables provide simple value assignments and transformations using JavaScript expressions, ideal for variable mapping and straightforward calculations.
Actions
- Type:
action - UI-Based: Visual function builder
- Capabilities: UI components, database operations, file handling
- Return Value: Configurable return data
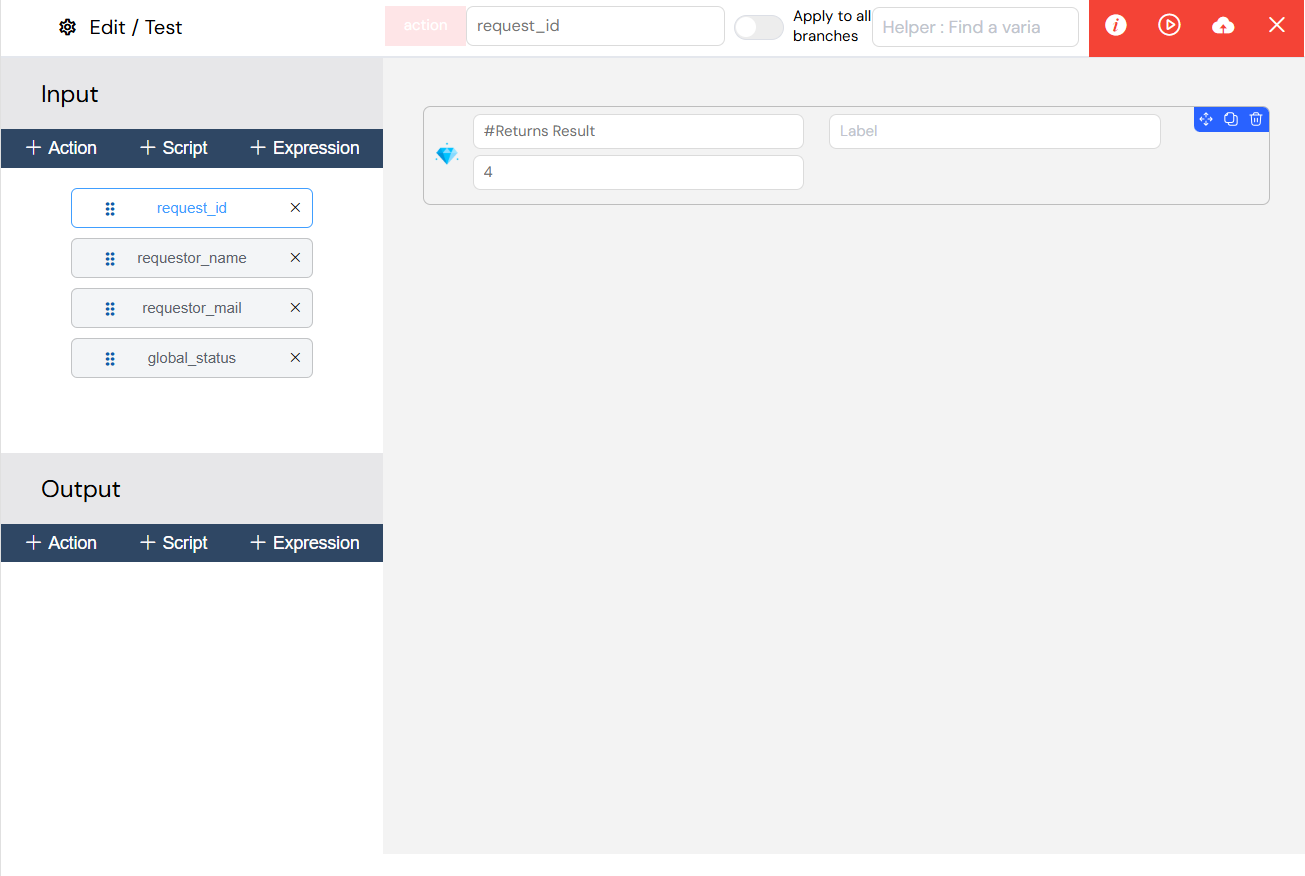
Action-based variables provide a visual function builder for database operations, file handling, and UI components, enabling complex workflows without writing code.
6. Advanced Features
6.1 System Variables Reference
The following system variables are automatically available in all process contexts:
| Variable | Type | Description | Available In |
|---|---|---|---|
SF_initiator | Object | Process initiator user information (email, name, id) | All tasks and scripts |
SF_latestValidator | Object | User who completed the most recent task | All tasks and scripts |
SF_mode | String | Execution mode: "test", "uat", or "prod" | All contexts |
SF_version | String | Process version identifier | All contexts |
instanceId | String | Unique process instance identifier | All contexts |
projectId | String | Current project identifier | All contexts |
nextTaskId | String | Identifier of the next task to execute | Process flow |
SF_loop_variables | Any | Current array element in multi-instance execution | Multi-instance subprocesses only |
SF_loop_index | Number | Current iteration index (0-based) | Multi-instance subprocesses only |
SF_sub_process_data | Object | Data returned from subprocess execution | Parent process after subprocess |
SF_sub_process_res | Array | Array of results from parallel subprocess instances | Parent process after multi-instance |
SF_last_activity_name | String | Name of the last executed activity | All contexts |
SF_involved_users | Array | All users who have participated in the process | All contexts |
SF_involved_validators | Array | All users who have validated tasks | All contexts |
SF_involved_roles | Array | All roles assigned to tasks | All contexts |
SF_observer | Array | Observer roles for the process | All contexts |
SF_priority | String | Current process priority level | All contexts |
SF_description | String | Process description text | All contexts |
Usage Examples:
// Access initiator email
let requesterEmail = SF_initiator.email;
// Check execution mode
if (SF_mode === "prod") {
// Production-only logic
}
// Access loop data in multi-instance
let currentItem = SF_loop_variables;
let itemIndex = SF_loop_index;
6.2 Variable Interpolation
- Syntax:
{{ variableName }} - Supported in: Email subjects, templates, assignments, conditions
- Dynamic evaluation during runtime
6.3 Multi-Instance Execution
Parallel Multi-Instance
- Execute multiple instances of sub-processes simultaneously
- Array-based instance creation
- Independent variable scopes per instance
7. Best Practices
This section consolidates best practices from across the process documentation suite.
7.1 Process Design
- Start Simple: Begin with basic flows before adding complexity
- Use Descriptive Names: All elements should have clear, business-friendly names
- Modular Design: Break complex processes into subprocesses
- Plan Error Handling: Define error paths for critical operations
- Document Your Process: Add descriptions and comments for future maintainers
7.2 Variable Management
- Consistent Naming: Use camelCase and descriptive names
- Avoid System Prefixes: Don't start variables with
SF_ - Document Complex Scripts: Add comments explaining business logic
- Test Before Deployment: Validate all scripts in test mode
- Minimize Scope: Keep variable usage as local as possible
7.3 Data Transformation (Input/Output)
- Choose the Right Type:
- Expressions for simple values
- Scripts for complex logic
- Actions for database operations
- Performance: Minimize external API calls in critical paths
- Error Handling: Always use try-catch in complex scripts
- Type Validation: Ensure data types match expectations
7.4 Email Configuration
- Test Templates: Always test in UAT mode first
- Use Variables: Create dynamic, personalized content
- Provider Selection: Configure appropriate providers per environment
- Compliance: Include unsubscribe options where required
7.5 Subprocess Usage
- Clear Interfaces: Document expected input/output variables
- Error Handling: Implement error handling in both parent and subprocess
- Performance: Monitor parallel execution limits
- Testing: Test subprocesses independently before integration
7.6 Measures and Reporting
- Meaningful Names: Use business-friendly measure labels
- Consistent Naming: Follow conventions across all processes
- Appropriate Types: Match measure types to data types
- Handle Null Values: Use conditional logic for missing data
- Test Expressions: Validate with various scenarios
7.7 Security
- Enable reCAPTCHA: For public tasks to prevent spam
- Validate Input: Always validate user input in scripts
- Role-Based Access: Use proper role assignments
- Secure Credentials: Never hardcode API keys or passwords
- Audit Logging: Enable logging for sensitive operations
7.8 Performance Optimization
- Limit Parallel Tasks: Avoid resource exhaustion
- Optimize Queries: Use indexed fields in database queries
- Cache When Possible: Store frequently-accessed data
- Monitor Execution: Track subprocess and task execution times
- Set Appropriate Timeouts: Configure realistic timeout values
7.9 Testing and Deployment
- Test Mode First: Always test in test environment
- Gradual Rollout: Test → UAT → Production
- Version Control: Track process version changes
- Backup Before Changes: Save current version before major updates
- Monitor After Deployment: Watch for errors in production
7.10 Maintenance
- Regular Reviews: Periodically review and optimize processes
- Update Documentation: Keep process descriptions current
- Clean Up Unused: Remove deprecated processes and variables
- Monitor Performance: Track metrics and optimize bottlenecks
- User Feedback: Incorporate user suggestions and issues
This comprehensive guide covers all available BPMN components in Softyflow. Each component can be combined to create sophisticated workflow automation solutions that meet your business requirements.