Process & Design
Softyflow's Process Modeler provides a robust and intuitive environment to visually design, build, and test your business workflows using the internationally recognized BPMN 2.0 standard. This comprehensive guide will walk you through all the essential features and components you need to master to create powerful and effective automated process flows.
Before diving into process design, it is crucial to have your project fully set up. Please make sure you have completed the project setup and have already designed the web interfaces that your processes will interact with.
Process design in Softyflow is centered around creating workflows by orchestrating a combination of activities, gateways, and events. These elements work together to automate your business logic. Each process is composed of interconnected process components that define the precise execution path, enforce business rules, and handle data transformations.
Key Components of a Process:
- Activities: These represent the work to be done within the process. This includes tasks performed by users (User Tasks), automated system actions (Normal Tasks), sending emails (Send Tasks), or even invoking other processes (Sub Processes).
- Gateways: These are decision points that control the flow of the process. They allow you to create branches, parallel paths, and conditional logic.
- Events: These act as triggers that start a process, endpoints that terminate it, or intermediate events that react to timers or errors.
- Sequence Flow: These are the connectors that link all the components, defining the order of execution and the path the process will take.
1. Activities & Components
Activities are the fundamental building blocks of any process, representing a unit of work to be performed. Softyflow offers several types of activities to model a wide range of business scenarios.
1.1. User Tasks (Manual Tasks)
User Tasks, also known as Manual Tasks, represent work that must be performed by a human. When a process reaches a User Task, it creates an entry in the assigned user's task basket, where they can open the associated web interface, perform the required action, and complete the task to move the process forward.
Key Configuration Options:
- Assignment: You can assign tasks to specific users, to a group of users by assigning a role, or dynamically assign them based on process variables.
- Interface: Select the UI screen that the user will interact with to complete the task.
- Notifications: Configure email notifications to be sent when a task is assigned, with fully customizable email templates.
- Due Dates: Set deadlines and priority levels for tasks to ensure timely completion.
- Observers: Grant read-only access to the task for specific users or roles who need to monitor progress without taking action.
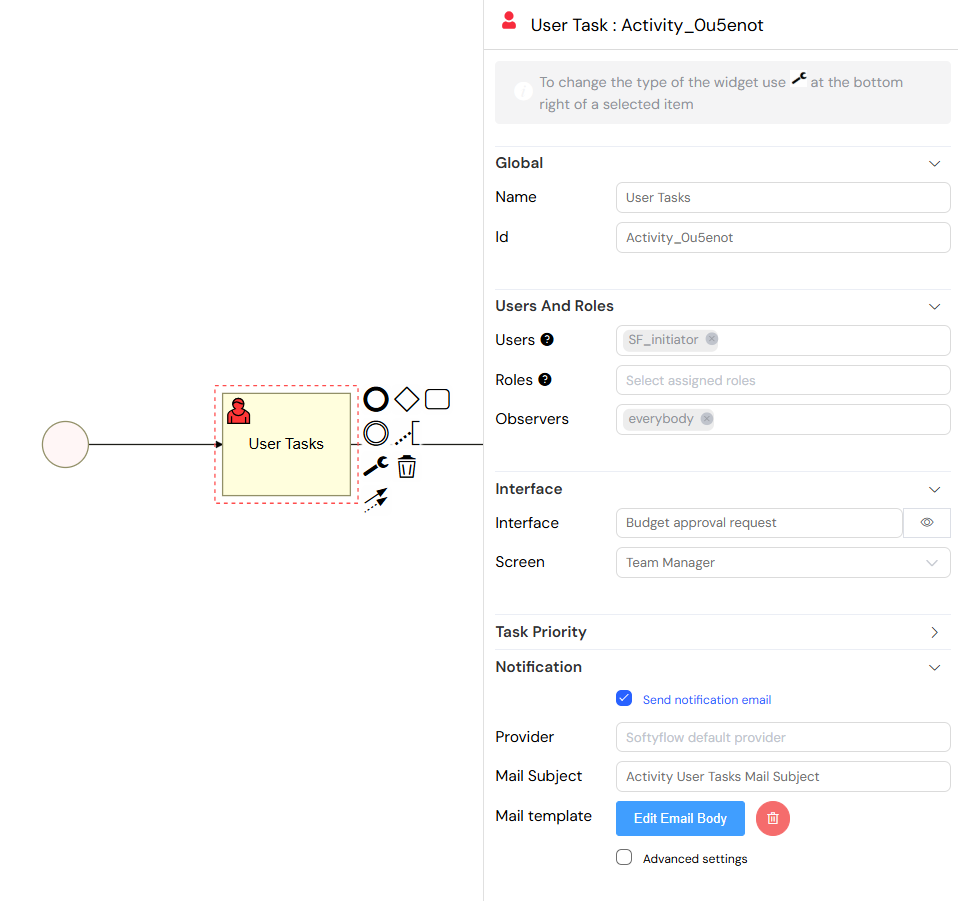
Configuration panel for a User Task, showing assignment, interface, and notification options.
1.2. Send Tasks (Email Tasks)
Send Tasks are used to send automated emails without any human intervention. This is perfect for sending notifications, confirmations, or alerts at specific points in your process.
Key Configuration Options:
- Recipients: Define who receives the email. This can be a static list of users, a role, or dynamically determined from a process variable.
- Templates: Use a rich visual email editor to create beautiful and professional email templates. You can easily include process variables to personalize the content.
- Providers: Softyflow supports multiple email service providers, allowing you to choose the one that best fits your needs.
- Attachments: Attach files to your emails, sourced from your project's resources.
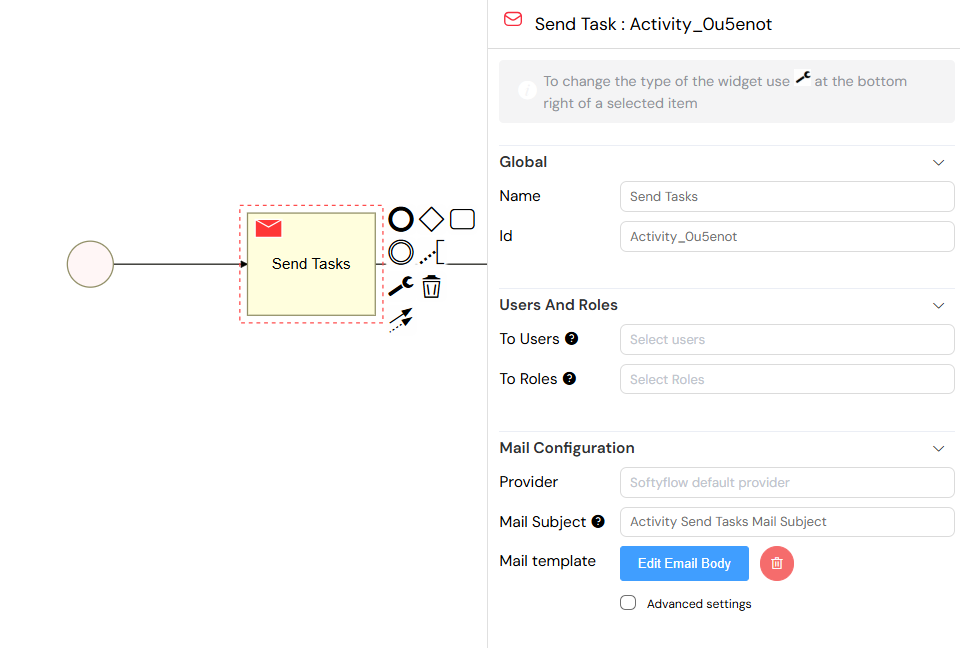
Configuration panel for a Send Task, where you can define recipients, email templates, and attachments.
1.3. Normal Tasks
Normal Tasks are automated system tasks that execute server-side logic without requiring user interaction or sending an email. They are ideal for performing background operations such as data processing, calculations, or calling external services. The logic for a Normal Task is defined using Input/Output parameters, where you can write scripts or use actions to perform the desired operations.
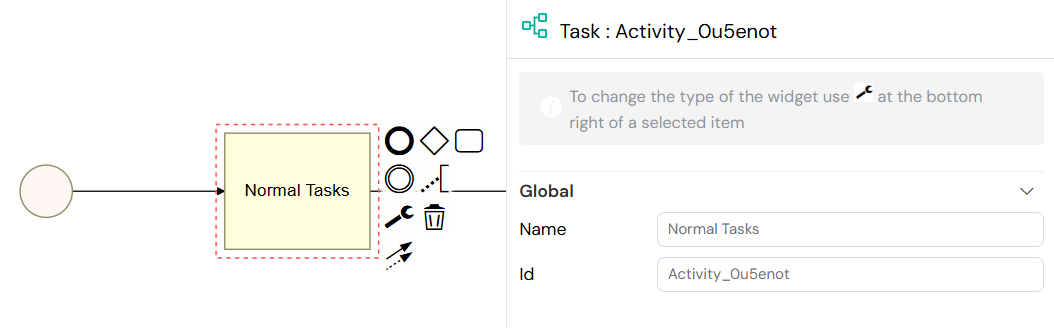
A Normal Task in the process modeler, used for automated background processing.
1.4. Sub Processes
Sub Processes allow you to encapsulate a part of your process and reuse it, or to call another existing process from within your current workflow. This is a powerful feature for creating modular, readable, and maintainable process models.
Key Features:
- Process Selection: Easily choose any other process from your project to be executed as a sub-process.
- Variable Passing: Variables from the parent process are automatically inherited by the sub-process, ensuring a seamless flow of data.
- Parallel Execution: You can run multiple instances of a sub-process in parallel, for example, by iterating over an array of data.
- Result Collection: When running in parallel, the results from all instances can be collected and aggregated for further processing in the parent process.
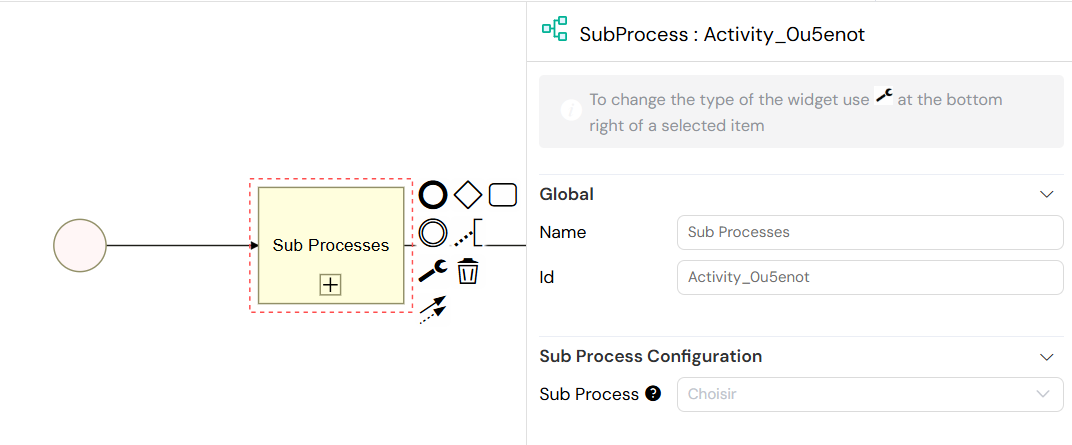
Configuration for a Sub Process, showing process selection and variable mapping.
2. Gateways & Flow Control
Gateways are essential for controlling the path of execution in your process. They allow you to implement decision points, create parallel flows, and manage complex business logic.
2.1. Exclusive Gateway (XOR)
The Exclusive Gateway (often called XOR gateway) creates a decision point in your process where only one of the possible outgoing paths can be taken. The choice of path is determined by conditions you define on the sequence flows connected to the gateway. The first condition that evaluates to true will determine the path taken.
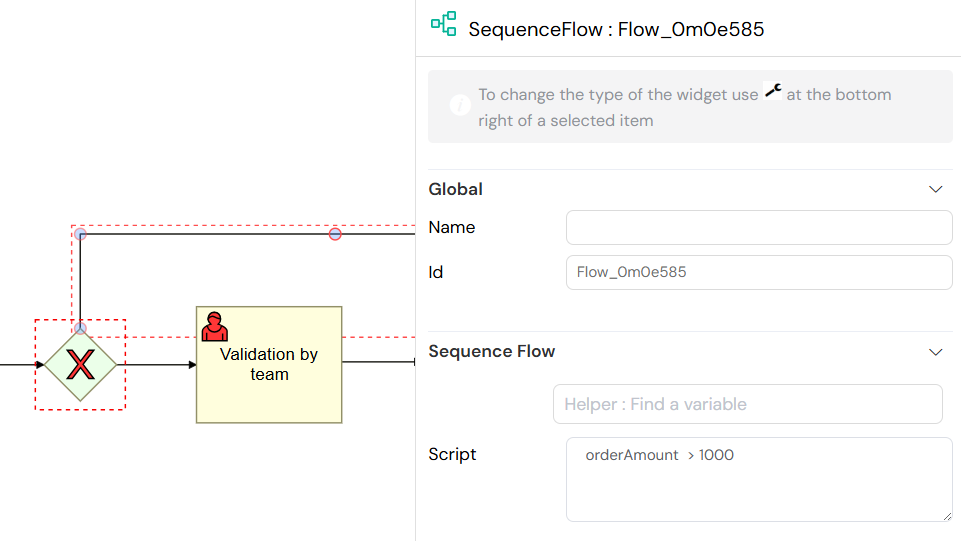
An Exclusive Gateway (XOR) splitting the process flow into multiple conditional paths.
2.2. Parallel Gateway
The Parallel Gateway is used to split the process flow into multiple paths that will execute simultaneously, or to join multiple parallel paths back into one. This is useful when you have several tasks that can be performed at the same time.
Common Use Cases:
- Simultaneous Task Execution: Allow multiple users or systems to work on different tasks at the same time.
- Parallel Approvals: Request approvals from multiple departments simultaneously and wait for all of them to respond.
- Multi-step Processing: Perform several independent data processing steps in parallel to save time.
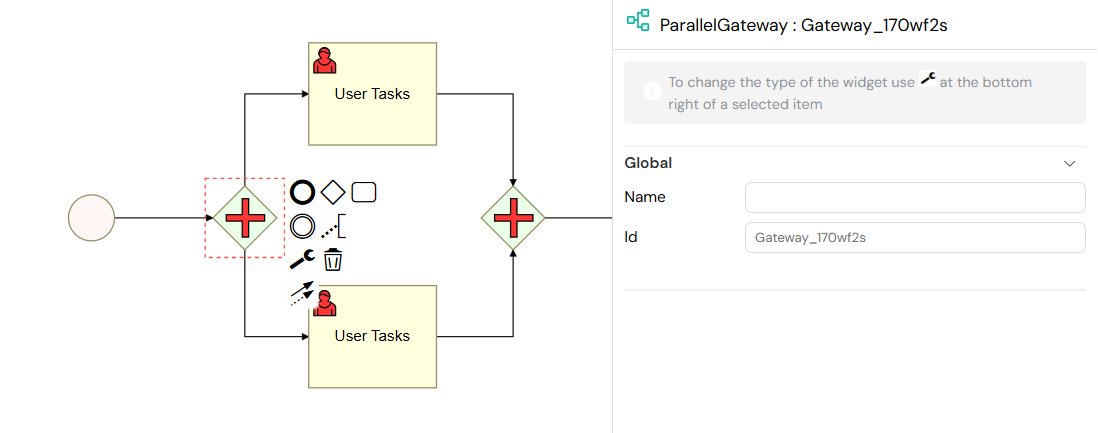
A Parallel Gateway splitting the flow into two concurrent paths.
3. Input/Output Parameters
Input/Output parameters are a powerful feature that allows you to configure data transformations before and after a task is executed. This is where you can define the core logic of your automated tasks. This feature is available for User Tasks, Send Tasks, Normal Tasks, and Sub Processes. For a detailed guide, see our Input/Output Parameters guide.
 Parameters](/img/02_developpement_guide/02-process-design/input_output.png)
The Input/Output parameter mapping interface.
3.1. Parameter Types
3.1.1. Scripts (JavaScript)
Scripts allow you to write complex server-side logic using JavaScript. You have full access to the Softyflow SDK, which enables you to interact with the platform's core features, manipulate data, and perform advanced calculations.
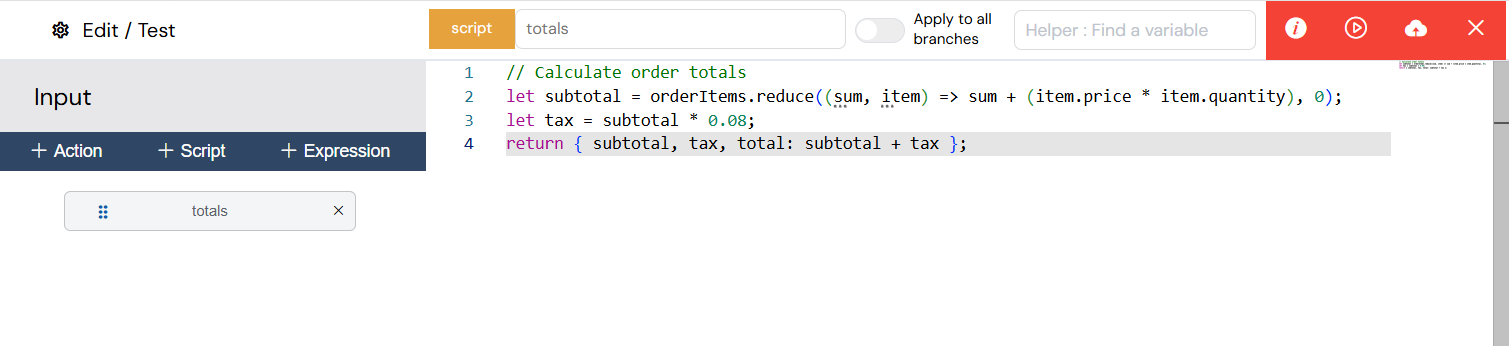
The JavaScript editor for writing custom script logic.
Available SDK Functions:
The SDK provides a rich set of functions to interact with your Softyflow environment.
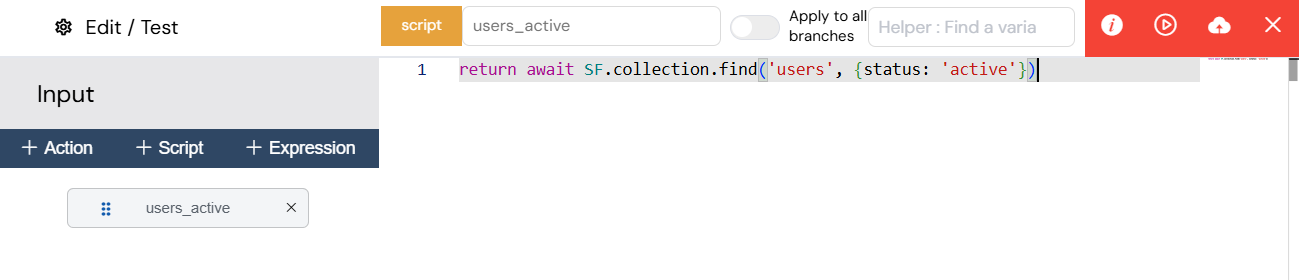
An example of available SDK functions within the script editor.
To learn more about the full capabilities of the SDK, please refer to our Node.js SDK reference.
3.1.2. Expressions
Expressions are used for simple data manipulations, such as assigning values to variables or performing basic string operations. They are a quick and easy way to manage data flow without writing full scripts.
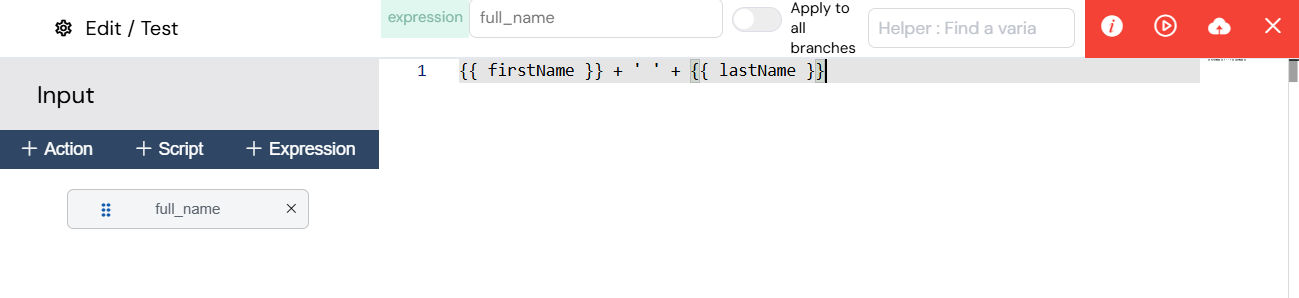
The expression editor for simple variable assignments.
3.1.3. Actions
Actions provide a visual, no-code function builder for performing common operations like UI manipulations and database queries. This allows non-developers to build powerful logic without writing any code.
Available Actions:
- Database Operations: Easily find, insert, update, or delete records from your database.
- Process Management: Launch new processes, validate tasks, or retrieve task information.
- User Management: Find users, update their metadata, and manage roles.
- Utilities: A wide range of utilities are available, such as Generate PDF, Send email, and making API calls.
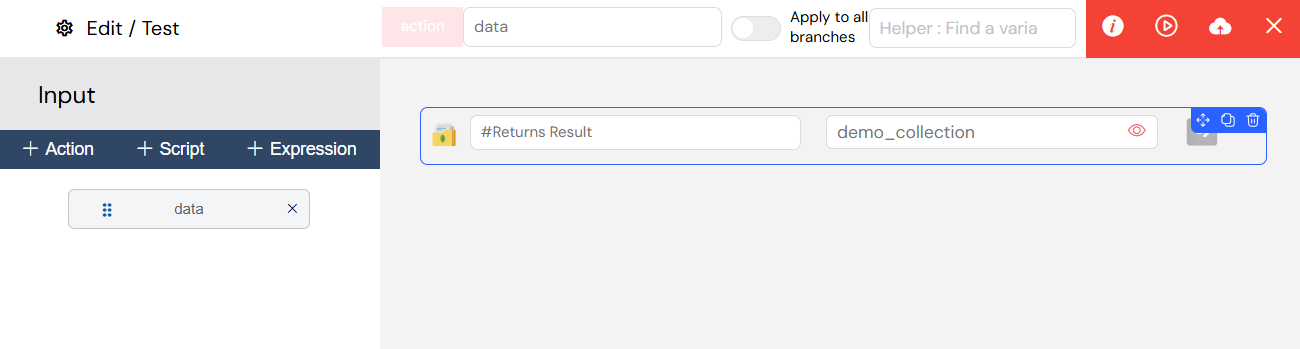
The visual Action builder for creating no-code logic.
For detailed Input/Output configuration, see the Input/Output Parameters guide.
4. Scheduled Tasks & Timers
4.1. Scheduled Tasks
The Scheduled Tasks feature allows you to automate the execution of your processes at regular intervals. You can configure processes to run periodically across different environments: TEST, UAT (Acceptance), and PROD (Production). This is perfect for recurring tasks like generating daily reports or performing nightly data synchronization.
On the Scheduled Tasks page, you will find a table that lists all the scheduled executions you have configured.
4.1.1. Creating a New Scheduled Task
To create a new scheduled task, simply click on the red Create Scheduling Tasks button. This will open the scheduling configuration modal where you can define all the parameters for the execution.
4.1.2. Fields in the Form:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Mode | The environment where the process will run: TEST, ACCEPTANCE, or PRODUCTION. |
| Project | Select the project that contains the process you want to schedule. |
| Process | Choose the specific process to be executed. |
| Start Date and Time | Define the exact date and time when the first execution should start. |
| Delay Between Repetitions | Configure the time interval between executions. You can specify it in days, hours, minutes, or use a cron expression for more complex schedules. |
| Repeat Every | Define the frequency of repetition for the task. |
4.1.3. Delay Options
You can specify how often the process should repeat by selecting one of the following delay types:
DaysHoursMinutesCron(for advanced scheduling patterns, e.g., "0 0 * * MON" to run every Monday at midnight)
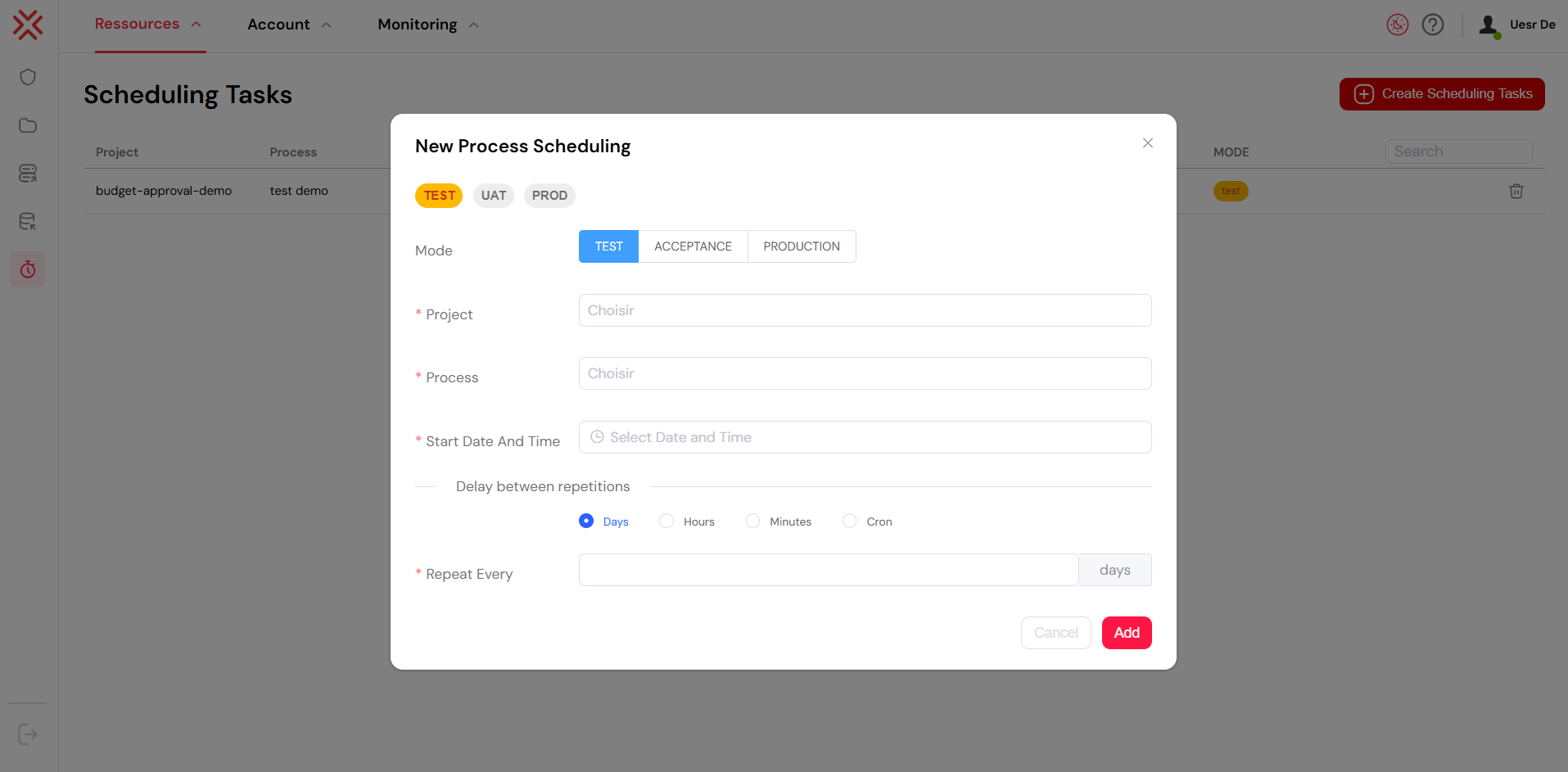
The Scheduled Tasks configuration modal.
4.2. Timer Events
Timer Events can be attached to activities to handle timeouts. If a task is not completed within a specified time, the timer event will trigger an alternative path in the process. This is crucial for handling escalations or ensuring that processes do not get stuck.
- Start in: The delay before the timer is triggered (in minutes).
- Action: When the timer triggers, it interrupts the main activity and follows the alternative path defined in the process model.
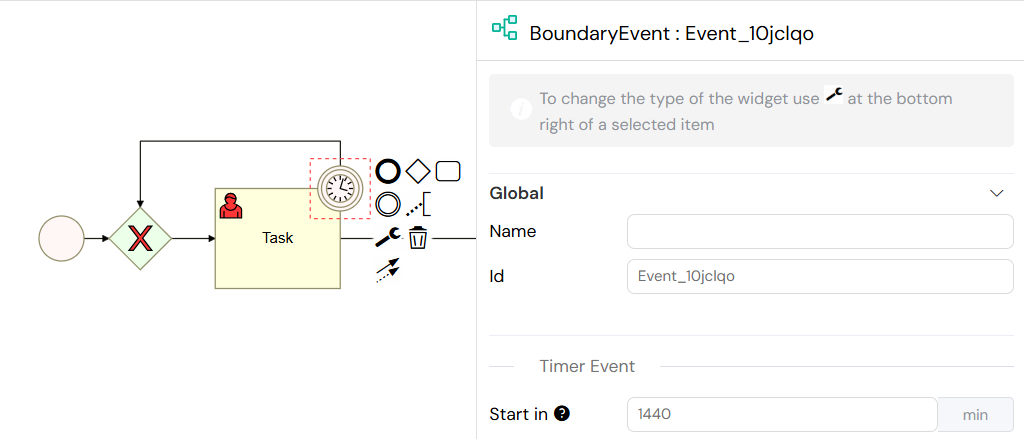
A Timer Event attached to a User Task for timeout handling.
5. Email Notifications
Email notifications are a key part of keeping users and stakeholders informed. They can be configured through Send Tasks for fully automated emails, or as part of a User Task's notification settings.
Key Email Features:
- Variable Integration: Personalize your emails by dynamically inserting process variables into the subject and body.
- Template Editor: Use a visual drag-and-drop editor to design professional and responsive email templates.
- Multi-Provider: Softyflow supports various email service providers, giving you the flexibility to use your preferred service.
- Attachment Support: Attach files from your project's resources to your emails.
5.1. Notification Strategies
- Task Assignment: Notify users as soon as a new task is assigned to them.
- Status Updates: Keep stakeholders informed about the progress of a process.
- Error Alerts: Automatically send notifications to your technical team when an error occurs.
- Escalation: Implement time-based escalation rules to send reminder emails or reassign tasks if they are not completed on time.
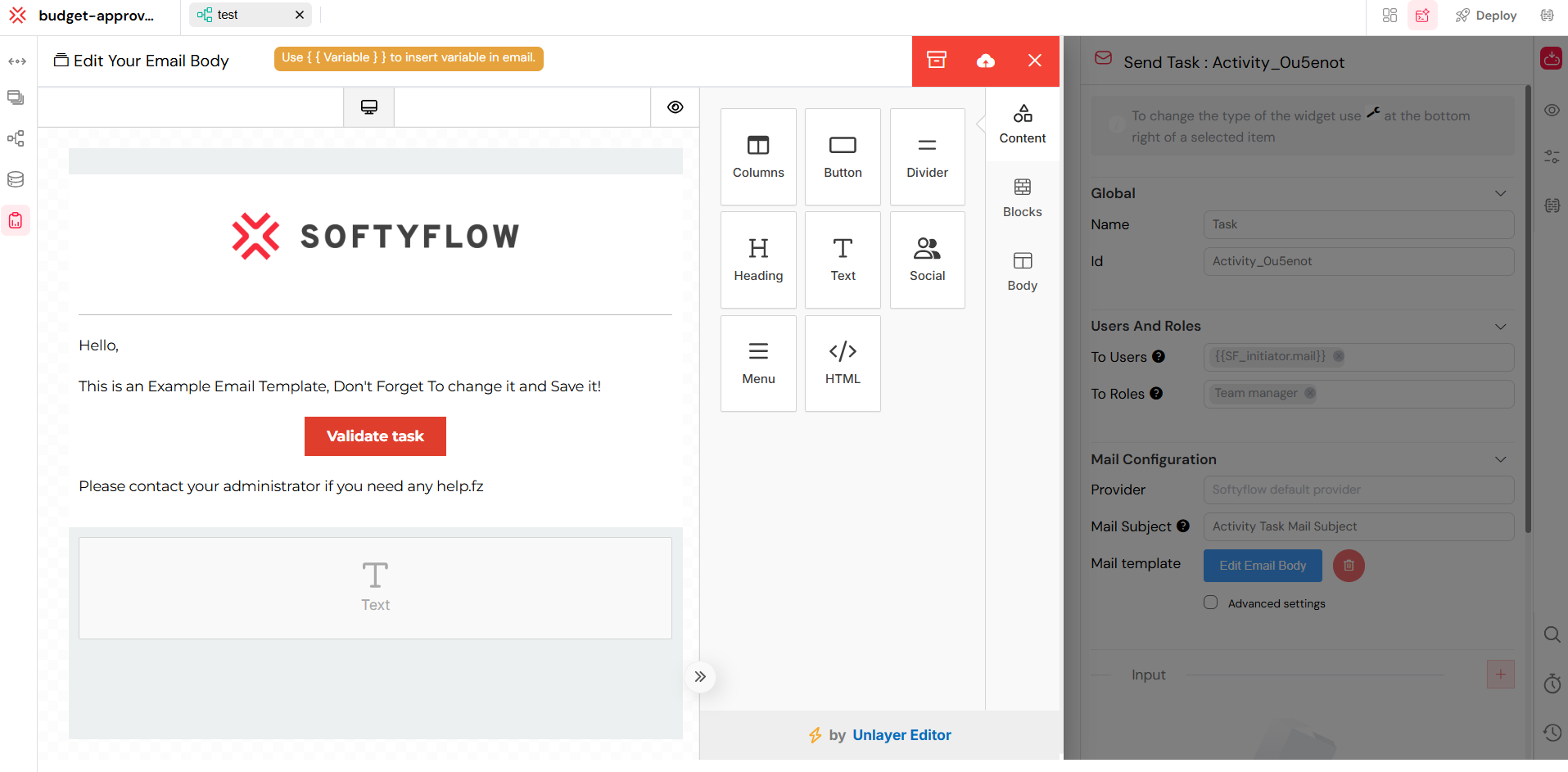
The email template editor for designing custom notifications.
6. Measures & KPIs
Process measures are used to track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in real-time. They allow you to perform calculations during process execution and store the results, which can then be used for creating insightful reports.
6.1. Measure Configuration
Each measure you define requires the following:
- Label: A descriptive name for the measure that will be displayed in reports.
- Type: The data type of the measure (String, Number, Boolean, Date, or Any).
- Field: A JavaScript expression used to calculate the value of the measure.
6.2. Calculation Examples
](/img/02_developpement_guide/02-process-design/measures.png)
The Measures configuration panel for tracking KPIs.
6.3. System Measures
Softyflow automatically provides a set of system measures for every process instance:
SF_last_activity_name: The name of the current activity.SF_involved_users: A list of all users who have participated in the process.SF_status: The current status of the process (e.g., running, completed, aborted).SF_createdAt: The timestamp when the process instance was started.
For more details, see the Measures documentation.
7. Error Handling
Robust error handling is crucial for building reliable applications. Softyflow provides mechanisms to catch and handle errors that may occur during process execution.
7.1. Error Boundary Events
Error Boundary Events can be attached to activities to catch errors that occur within them. When an error is caught, the normal flow is interrupted, and the process follows an alternative path, allowing you to implement recovery logic.
Configuration:
- Attach to Activities: You can attach error events to User Tasks, Normal Tasks, and Sub Processes.
- Error Types: You can configure them to catch specific types of errors or to act as a catch-all for any error.
- Recovery Actions: Define an alternative execution path to handle the error, such as notifying an administrator, retrying the task, or gracefully terminating the process.
7.2. Error Handling Strategies
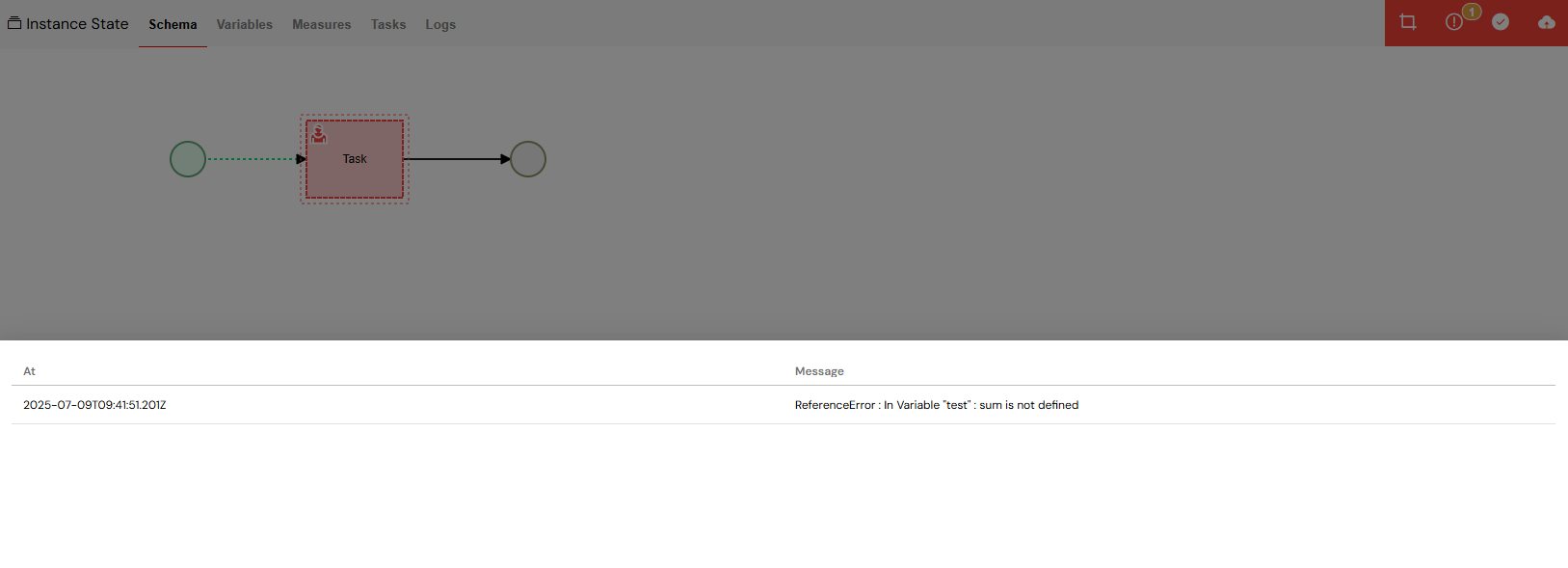
An Error Boundary Event catching an error and redirecting to a handling sub-process.
Best Practices for Error Handling:
- Always provide fallback paths for critical processes to ensure they don't get stuck.
- Log all errors with detailed information for easier debugging and monitoring.
- Implement retry mechanisms for transient failures, such as temporary network issues.
- Use timeout events in conjunction with error handling for long-running operations.
8. Security & Access Control
Security is a top priority, and Softyflow provides granular control over who can do what within your processes.
8.1. Task-Level Security
- User Assignment: Assign tasks directly to a user or a role.
- Observers: Grant read-only access to users who need to monitor a task's progress.
- reCAPTCHA: Protect public-facing tasks from spam and abuse.
- Dynamic Assignment: Use process variables to implement complex, data-driven security rules.
8.2. Process-Level Security
- Role Restrictions: Use role management to control who can start, view, or manage processes.
- View Permissions: Separate the permissions for viewing process instances from the rights to execute tasks.
- Variable Security: Protect sensitive data stored in process variables by controlling who can see or modify it.
8.3. Security Best Practices
- Principle of Least Privilege: Only grant users the permissions they absolutely need to perform their duties.
- Role Hierarchies: Implement a clear and logical role hierarchy that reflects your organizational structure.
- Auditing: Regularly audit process access and modifications to detect any unauthorized activity.
- Secure Credentials: Securely manage all sensitive variables and API credentials.
- Input Validation: Always validate all user inputs in your scripts and expressions to prevent injection attacks.
9. Best Practices
9.1. Process Design
- Modularity: Break down large, complex processes into smaller, reusable sub-processes. This makes your models easier to read, maintain, and test.
- Error Handling: Always design for failure. Provide clear error paths and timeouts for any task that could potentially fail.
- Performance: Be mindful of performance. Avoid running complex calculations or queries in the critical path of your process if they can be done asynchronously.
- Documentation: Use descriptive names for your activities and variables, and add comments to your model to explain complex logic.
9.2. Variable Management
- Naming Conventions: Adopt a consistent and descriptive naming convention for your variables (e.g., camelCase).
- Type Safety: Ensure that your expressions and scripts handle different data types correctly to avoid runtime errors.
- Null Checking: Always check if a variable exists before trying to use it, especially if it comes from an external system.
- Security: Be careful not to expose sensitive data in logs or to users who should not have access to it.
9.3. Testing & Validation
- Unit Testing: Test each component of your process, such as individual scripts or sub-processes, in isolation.
- End-to-End Testing: Validate the entire process flow from start to finish to ensure all integrations work as expected.
- Performance Testing: Monitor the execution times and resource usage of your processes under load to identify any bottlenecks.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Involve your business users in the testing process to ensure the final application meets their needs and expectations.
Next Steps
Now that you have a solid understanding of process design, you can continue building out the rest of your application:
- Web Interface Design - Create the UI screens that will connect to your processes.
- Database Integration - Connect your processes to your data sources.
- Integration - Connect your application with external APIs and services.
- Reporting - Create insightful reports from your process data.
- Test & Deploy - Learn how to test and deploy your processes across different environments.
- Monitor & Run - Find out how to monitor and manage your running process instances.
For a more hands-on experience, we highly recommend trying our step-by-step tutorials or watching our process and reports video tutorials.
For more advanced topics, you can explore our detailed documentation on Process Components, Input/Output Parameters, Measures, and Sub Processes.