Database Management
Softyflow provides two main approaches for data management: SQL databases via External Data Sources (EDS) and MongoDB Collections. This guide covers both approaches with practical usage examples.
Before diving into database integration, ensure you've completed your project setup and understand how to use databases in your web interfaces and processes.
1. Overview
1.1. SQL via EDS (External Data Sources)
Connect to existing SQL databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, Snowflake) and APIs for enterprise data integration. Learn more about EDS integration.
The External Data Sources (EDS) page in Softyflow serves as the control center for integrating external databases and APIs. It provides a unified view of all configured data sources, whether they are SQL databases like PostgreSQL and MySQL, or APIs.
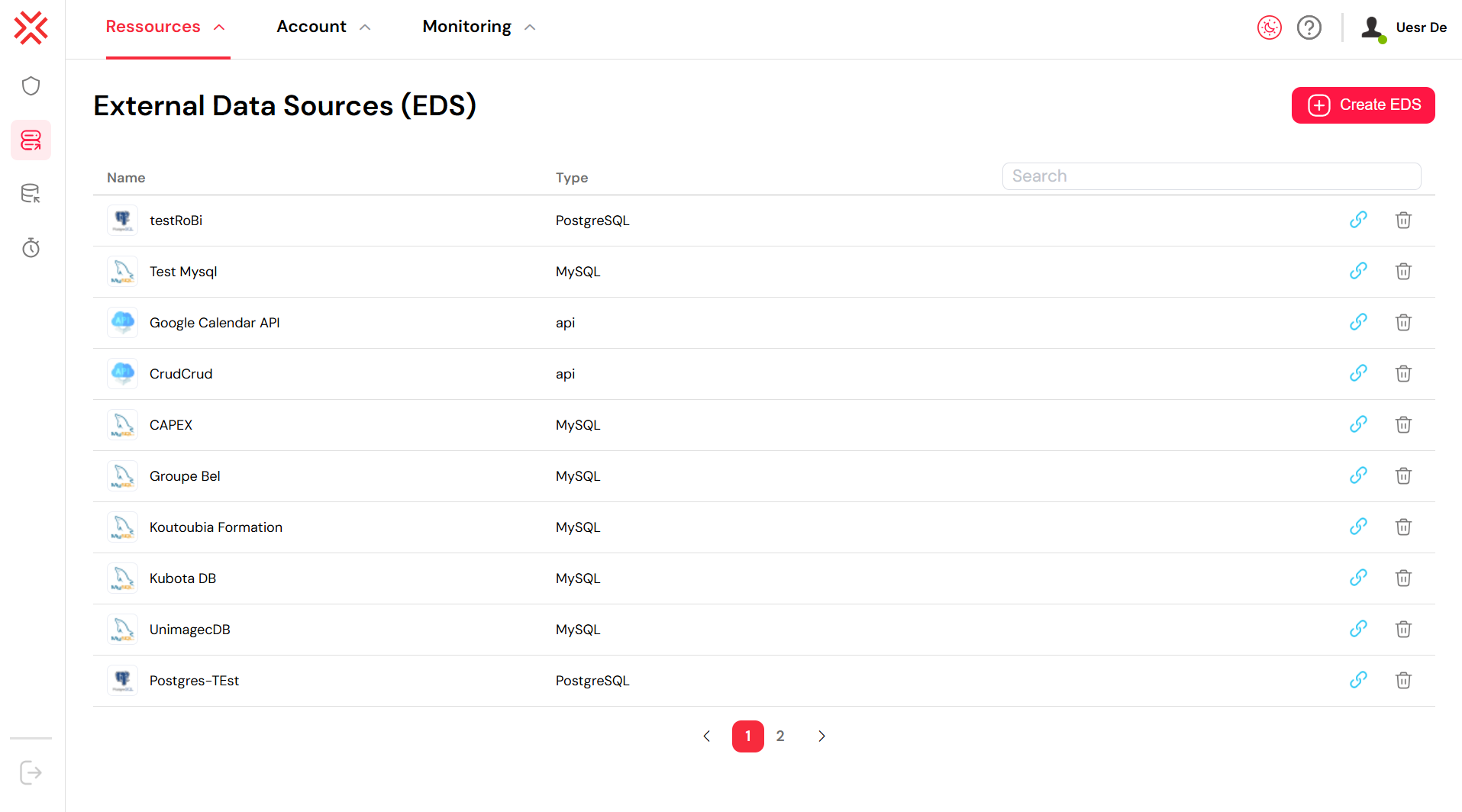
From this interface, you can:
- View all Data Sources: The list shows the Name and Type (e.g., PostgreSQL, MySQL, api) of each configured EDS.
- Create a New EDS: The "+ Create EDS" button allows you to connect to a new external data source.
- Manage Existing EDS: Each item in the list has options to manage the connection.
In the screenshot, you can see several data sources configured. For example, "Test Mysql" is an EDS of type MySQL, and "Google Calendar API" is of type api. This demonstrates the flexibility of Softyflow to connect to both traditional databases and modern web APIs, allowing you to consolidate data from various systems into your applications.
1.2. MongoDB Collections
Use Softyflow's built-in MongoDB for rapid prototyping and application-specific data storage.
The Internal Databases (Collections) page serves as the central interface for managing your project's NoSQL data collections within Softyflow. This screen provides a comprehensive overview of all existing collections, allowing for easy access and management.
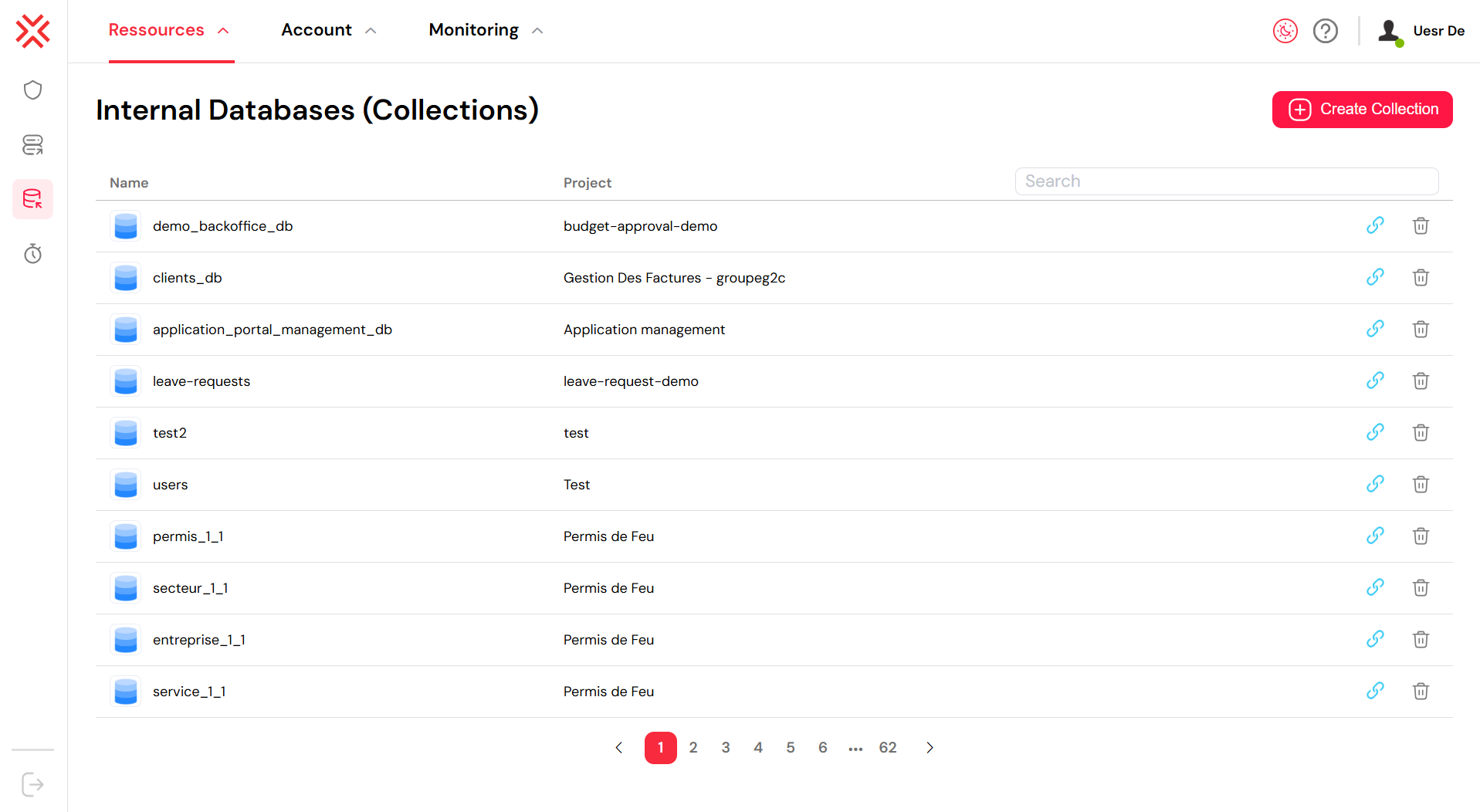
From this page, you can perform several key actions:
- View Collections: The main list displays all available collections with their Name and the Project they are associated with. For example, the image shows a collection named
clients_dbused within the "Gestion Des Factures - groupeg2c" project. - Create a New Collection: By clicking the "+ Create Collection" button in the top-right corner, you can add a new collection to store your application's data.
- Search and Filter: The Search bar enables you to quickly locate a specific collection by name.
- Navigate: Pagination controls at the bottom of the list allow you to browse through multiple pages of collections.
2. SQL via EDS
2.1. Quick Setup
The "Add External Data Sources (EDS)" page is where you configure new connections. This form allows you to define all the necessary parameters for Softyflow to connect to an external database, such as MySQL in this case.
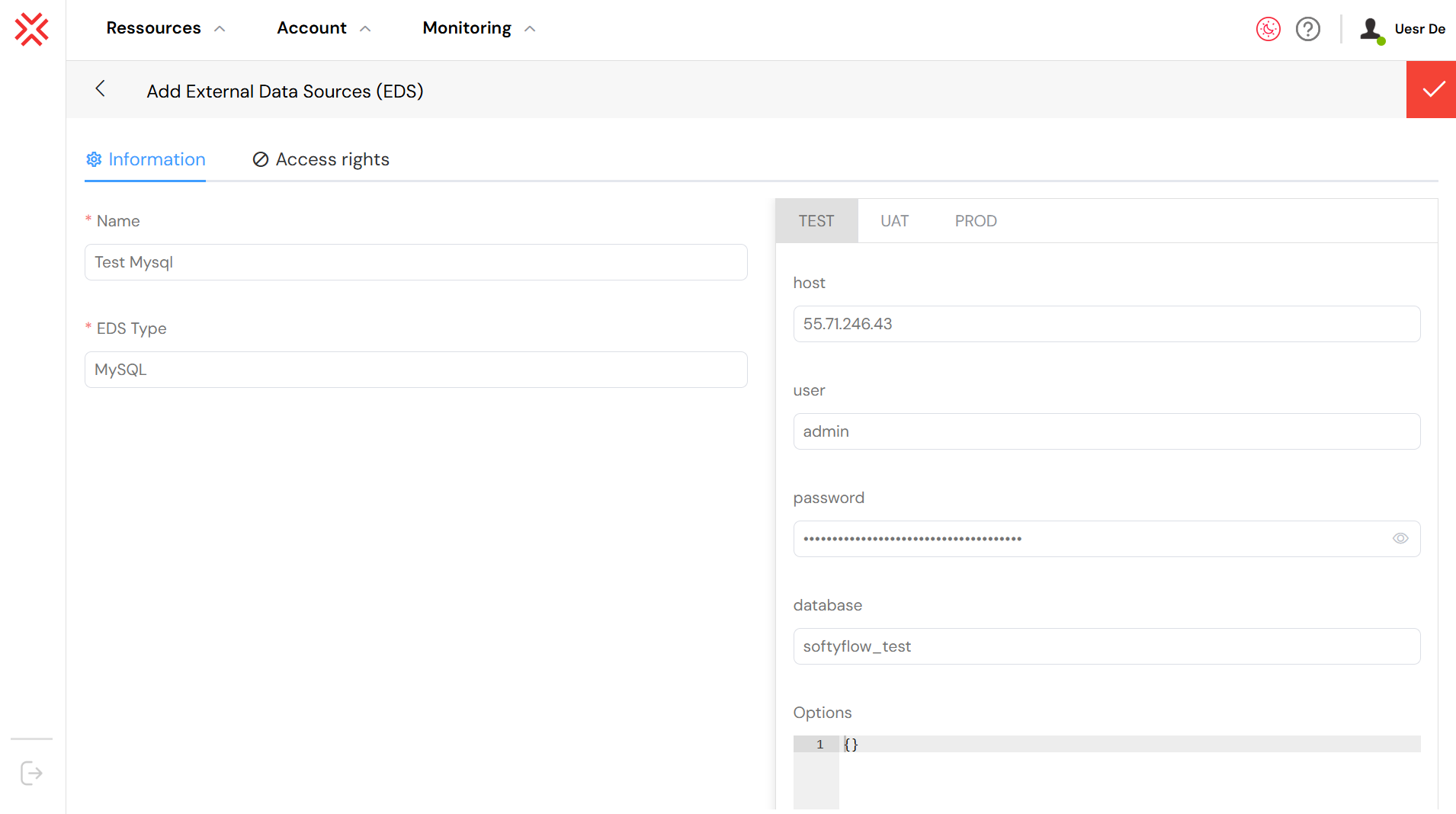
As shown in the image, a new MySQL data source named "Test Mysql" is being configured. The connection details, such as the host (55.71.246.43) and database (softyflow_test), are filled in for the TEST environment. This setup ensures that when the application is running in the test environment, it will connect to the specified test database, isolating it from production data.
Key configuration fields include:
- Name and EDS Type: A user-friendly name for the connection and the type of data source (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL).
- Environment Tabs (TEST, UAT, PROD): Softyflow allows you to specify different connection details for each environment, ensuring that you connect to the correct database (e.g., a test database for development and a production database for live applications).
- Connection Details: This includes the
host,user,password, anddatabasename.
2.2. Common Use Cases
Enterprise Integration: Connect to existing CRM, ERP, or legacy systems using our integration features Data Warehousing: Access analytics data from Snowflake or similar platforms for reporting Cross-System Integration: Sync data between multiple business systems
3. MongoDB Collections
3.1. Quick Setup
Collections are created directly in Softyflow IDE with automatic schema flexibility.
The management page for a specific MongoDB collection, like "demo_collection" shown in the image, provides tools for managing the collection's data, environment, and access rights.
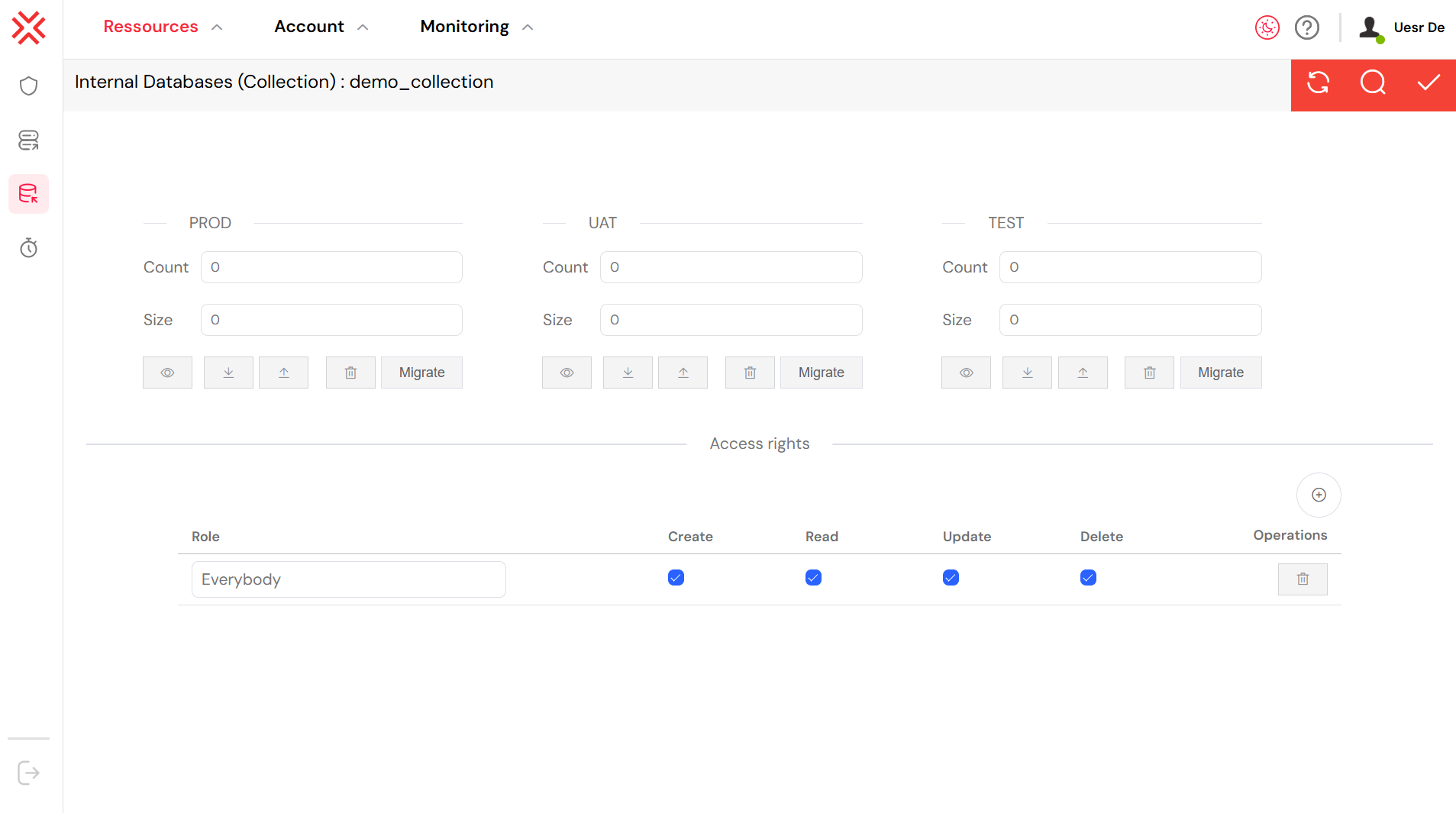
Key features on this page include:
- Environment Management: Separate sections for PROD, UAT, and TEST environments allow you to manage data independently for each stage of your development lifecycle. You can see the
Countof documents and theSizeof the collection for each environment. - Data Operations: Buttons for viewing, downloading, uploading, and deleting data are available for each environment. The Migrate button allows for data migration between environments.
- Access Rights: The lower section is for managing permissions. You can define which Role has
Create,Read,Update, andDelete(CRUD) permissions on the collection. In the example, the "Everybody" role is granted full CRUD permissions, meaning any user with this role can perform all data operations on this collection. This is useful for public or non-sensitive data, but for most applications, you would create more restrictive roles.
3.2. Common Use Cases
- Rapid Prototyping: Quick data storage without database setup
- Application Settings: Store configuration and user preferences
- Temporary Data: Session data, logs, and temporary calculations
- Flexible Schema: Documents with varying structures
4. Usage in Widgets
Integrate your databases with web interface widgets to create dynamic, data-driven interfaces.
You can connect a web interface widget to a data source in the Softyflow UI Designer. The image below shows a "Select" (dropdown) widget being configured to pull its options from an external database.
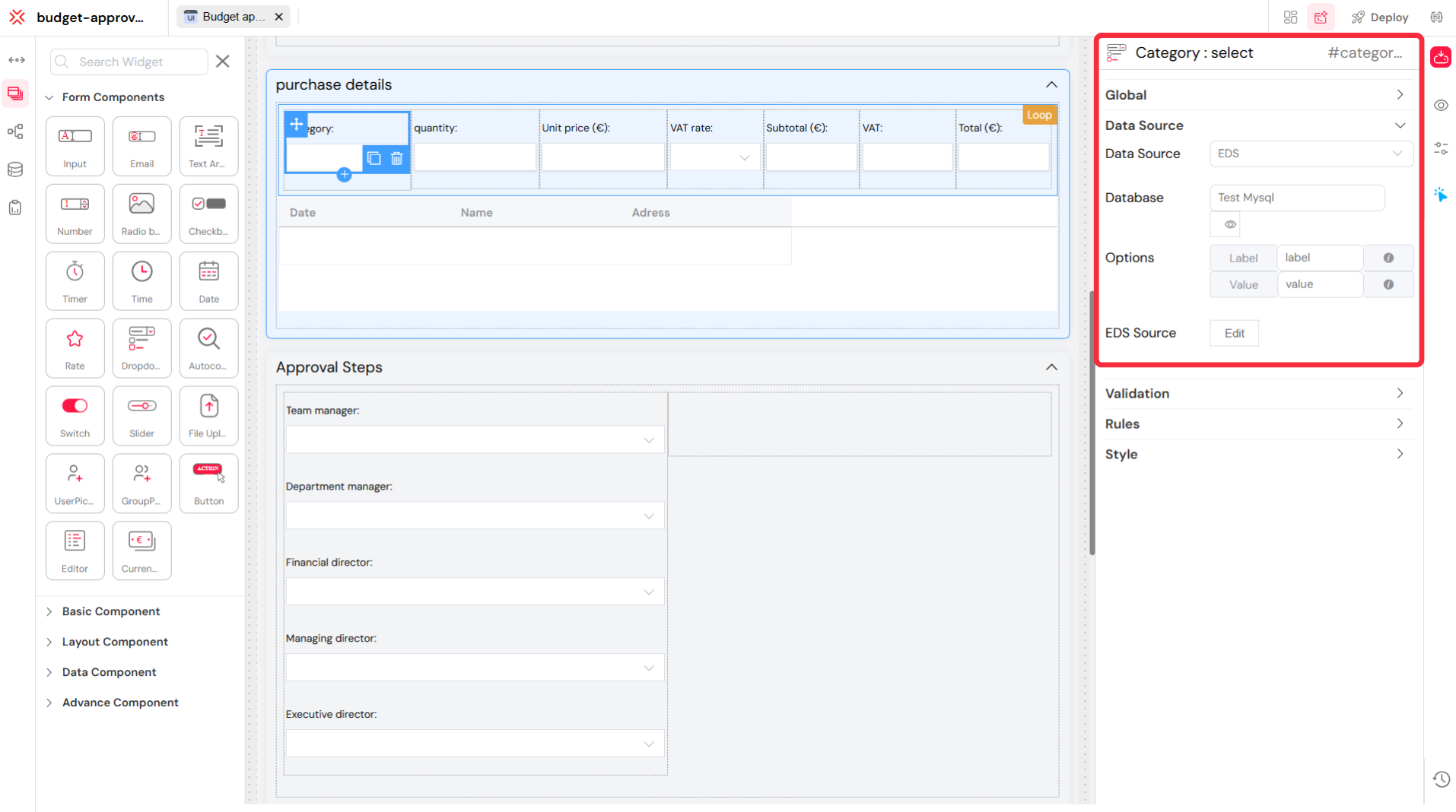
In this example, the "Category" dropdown widget is selected. In the configuration panel on the right, the Data Source is set to "EDS". The specific Database chosen is "Test Mysql". This means the options displayed in the "Category" dropdown on the live form will be populated from the "Test Mysql" external data source. This is a powerful feature for creating dynamic forms where the options change based on data in your databases.
4.1. Dropdown/Select Widgets
Use Select widgets to display database data as dropdown options.
4.1.1. SQL via EDS
The image below provides a close-up view of the Data Source configuration for a "Select" widget, which is being connected to an External Data Source (EDS).
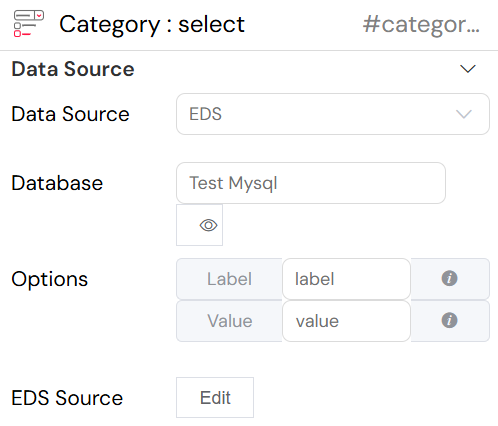
The configuration shown is for a "Category" select widget. By setting the Data Source to EDS and selecting the Test Mysql Database, the developer can then specify a query to retrieve a list of categories. For example, a query like SELECT category_name, category_id FROM categories could be used. The Label would be set to category_name and the Value to category_id, populating the dropdown with category names that correspond to their unique IDs in the database.
Key configuration options are:
- Data Source: Set to
EDS, indicating the widget will fetch its options from an external source. - Database: The specific EDS connection to use, in this case,
Test Mysql. - Options: The
LabelandValuefields determine which columns from the database will be used for the display text and the underlying value of the dropdown options. - EDS Source: Clicking the
Editbutton opens a query editor where you can specify the SQL query or the table to fetch the data from.
The EDS Source query editor allows you to write dynamic SQL queries to fetch data for your widgets. You can embed variables from your application's data model directly into the SQL statement.
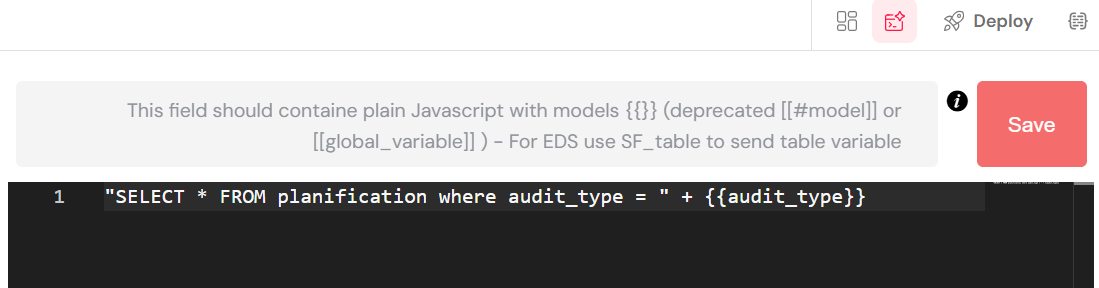
As shown in the image, the SQL query in the editor is:
"SELECT * FROM planification where audit_type = " + {{audit_type}}
This is a dynamic query that selects all records from the planification table where the audit_type column matches the value of the audit_type variable in the application's data model. For example, if a user selects an audit type from another dropdown, its value will be stored in the audit_type variable, and this query will automatically update to filter by that selection. This is a powerful way to create interactive and responsive data-driven applications.
- Query Editor: A text area where you can write plain SQL.
- Dynamic Variables: You can use
{{variable_name}}syntax to insert the value of a variable into the query. This allows the query to change based on user input or other data in the application.
4.1.2. MongoDB Collections
The image below shows the configuration of a "Select" widget that is populated from an internal Softyflow MongoDB collection.
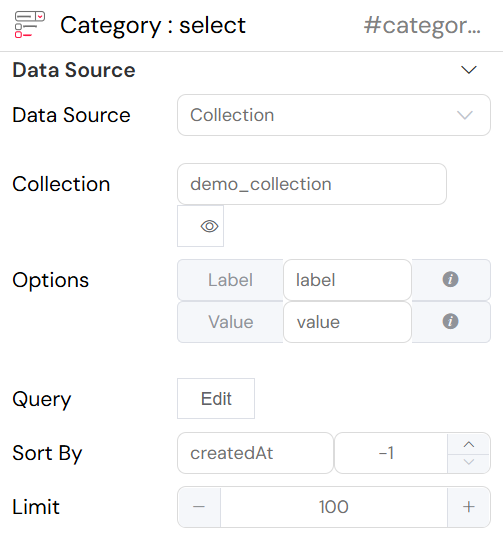
In this example, the "Category" select widget is configured to fetch its options from the demo_collection. The options will be sorted by the createdAt field in descending order, and a maximum of 100 items will be returned. By setting the Label to a field like category_name and Value to _id, the dropdown would display a sorted list of category names from the collection.
Key configuration options are:
- Data Source: Set to
Collection. - Collection: The name of the internal collection to use, here it is
demo_collection. - Options: The
LabelandValuefields specify which fields from the documents in the collection to use for the dropdown's display text and underlying value. - Query: The
Editbutton opens an editor to write a MongoDB query to filter the documents. - Sort By and Limit: These fields allow you to sort the results (e.g., by
createdAtin descending order:-1) and limit the number of options displayed.
The image below displays a code editor within a web interface, likely a part of the Softyflow platform, where a user is defining a MongoDB aggregation pipeline.
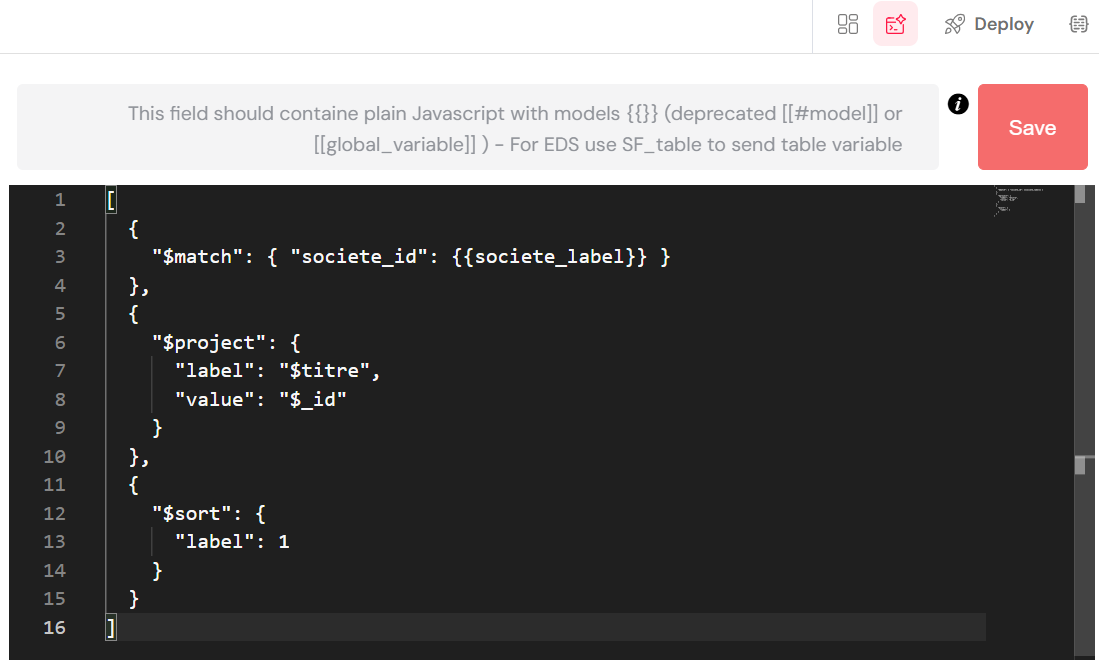
The pipeline consists of three stages: $match, $project, and $sort.
- The
$matchstage filters documents, selecting those wheresociete_idmatches the dynamically inserted value of{{societe_label}}. - The
$projectstage reshapes the output documents to include onlylabel(mapped from the$titrefield) andvalue(mapped from the$_idfield). - The
$sortstage orders the resulting documents in ascending order based on thelabelfield.
4.2. Table Widgets
Display database data in interactive Table widgets for comprehensive data management.
4.2.1. SQL via EDS
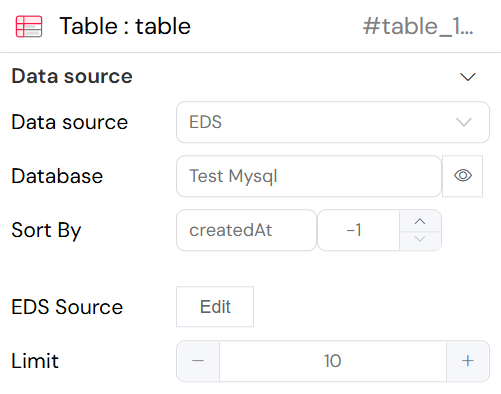
The image below displays the data source configuration for a "Table" widget within the Softyflow interface. The data source is set to "EDS" (Enterprise Data Source), and it is connected to a "Test Mysql" database. The data is configured to be sorted by the "createdAt" field in descending order (-1), and the query is limited to retrieving 10 records. An "Edit" button is available to modify the underlying SQL query of the EDS source, allowing for customized data retrieval to populate the table.
4.2.2. MongoDB Collections
The image below displays the data source configuration for a "Table" widget within the Softyflow interface. The data source is set to "Collection," indicating that the table will be populated with data from an internal database. The configuration specifies that the data should be sorted by the "createdAt" field in descending order (-1) and is limited to 10 records per page. An "Edit" button is available to customize the query, allowing for more advanced filtering and data manipulation to tailor the information displayed in the table.
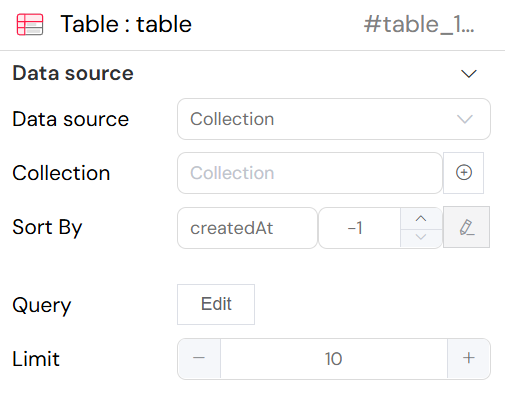
Key configuration fields:
- Data source: This dropdown menu is used to select the origin of your data. In this example, Collection is selected, indicating that the table will be populated with data from a database collection.
- Collection: This field specifies the exact collection you want to display data from.
- Sort By: This allows you to define the order in which the records appear in the table. The configuration
createdAtand-1sorts the items by their creation date in descending order, showing the newest items first. - Query: The Edit button opens a query editor, which allows you to apply specific filters to your data. For instance, you could use it to show only items that meet certain criteria (e.g., status is 'active').
- Limit: This numerical field sets the maximum number of records to be displayed in the table at one time. In the image, it is set to
10.
4.3. Advanced Filtering
4.3.1. Dynamic Filters (SQL)
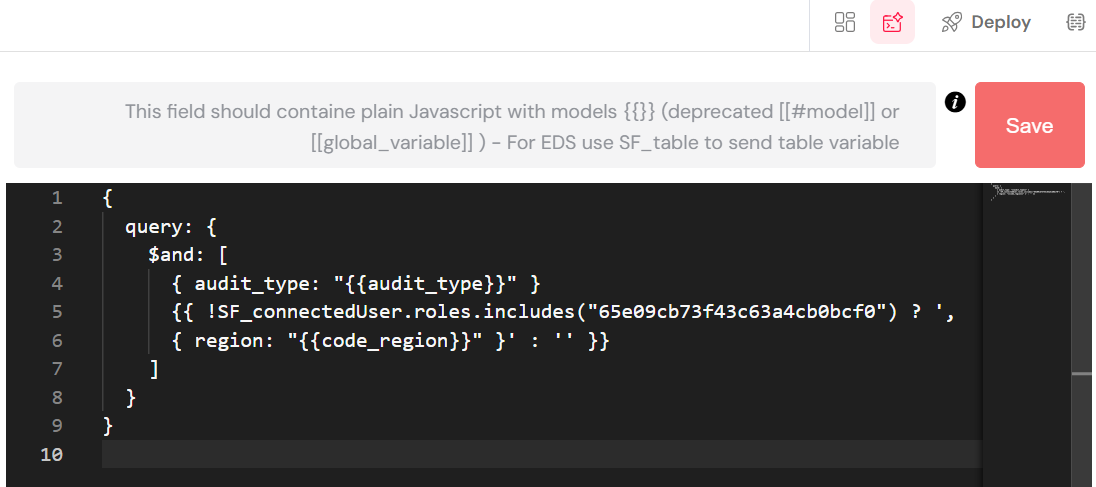
The image below displays a code editor within the Softyflow interface, demonstrating how to construct a dynamic SQL query. The query filters data based on user roles and input variables.
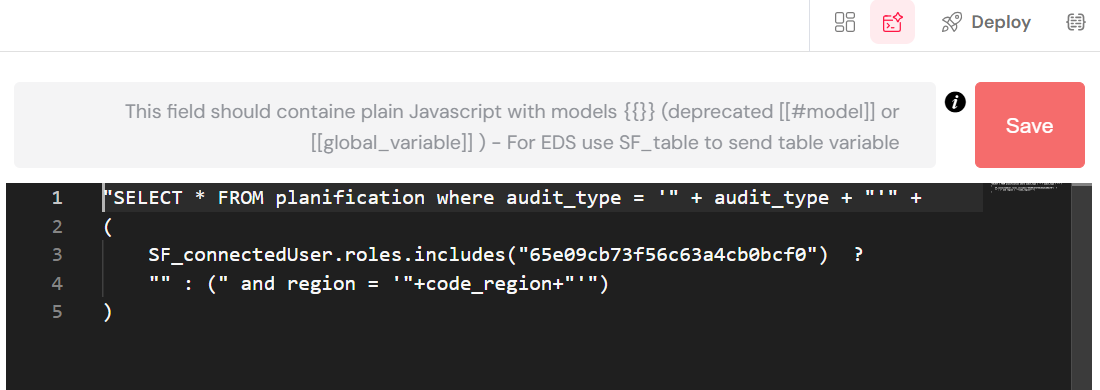
Here's a breakdown of the code:
- Base Query: It starts with a standard SQL
SELECTstatement to retrieve all columns (*) from theplanificationtable, filtering byaudit_type. - Dynamic Filtering:
- A ternary operator (
? :) is used to conditionally add aWHEREclause to the query. - It checks if the connected user's roles (
SF_connectedUser.roles) include a specific role ID. - If the user has the specified role, an additional filter
and region = '"+code_region+"'is appended to the query, further restricting the results based on thecode_regionvariable. - If the user does not have the role, an empty string is added, and the query remains simpler.
- A ternary operator (
This is a powerful feature for creating secure and context-aware applications, where the data presented to users depends on their permissions and selections.
4.3.2. MongoDB Query Filters
The image below shows the MongoDB query editor in Softyflow. It allows you to write JSON-based queries to filter data from a collection. The editor supports dynamic variables using the {{variable}} syntax, enabling you to create filters that respond to user input or other application data.
5. Usage in Actions
Integrate databases with web interface actions and process design for dynamic data handling.
5.1. Form Submission
5.1.1. SQL via EDS
The image below illustrates how to configure a form submission action in Softyflow to save data to an SQL database using an EDS connection.
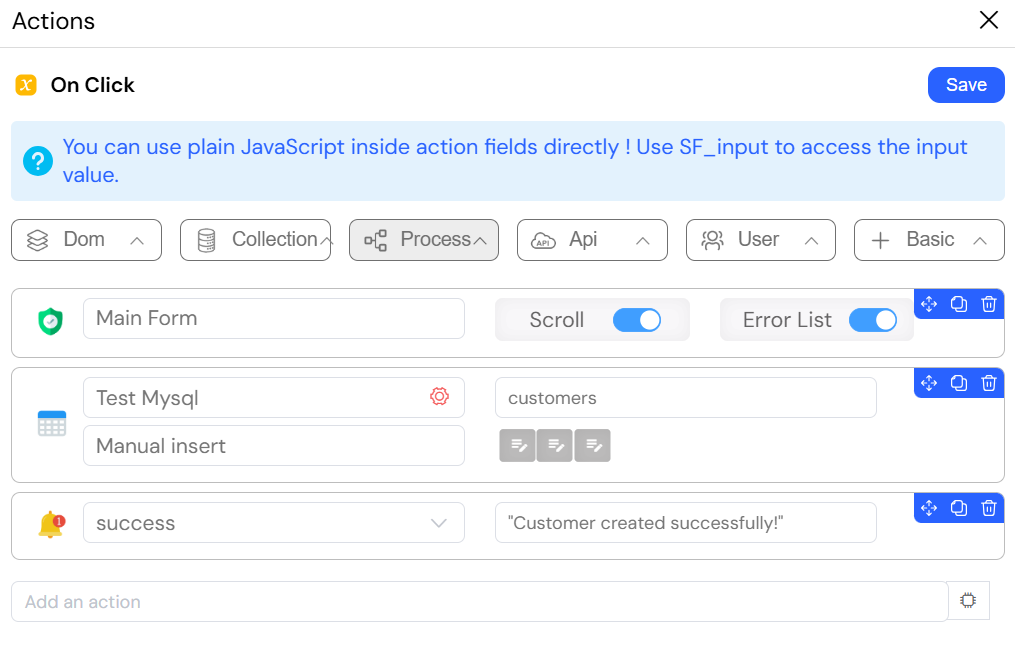
When a user fills out a form on your website and clicks "Submit", Softyflow will:
Validate the data - Ensure all information is properly filled out (valid email, required fields, etc.)
Save to the database - The form information (like
{{variable1}},{{variable2}}) is automatically inserted into a table in your MySQL database called "Test Mysql"Confirm to the user - Display a message to inform the user that their data has been successfully saved
5.1.2. MongoDB Collections
The image below shows how to configure a form submission action in Softyflow to save data to a MongoDB collection. The configuration shows a 'Save in collection' action targeting the demo_collection. The action is set to insert a new document, mapping form fields to the document's fields. This is a common pattern for persisting data entered by users in a web form.
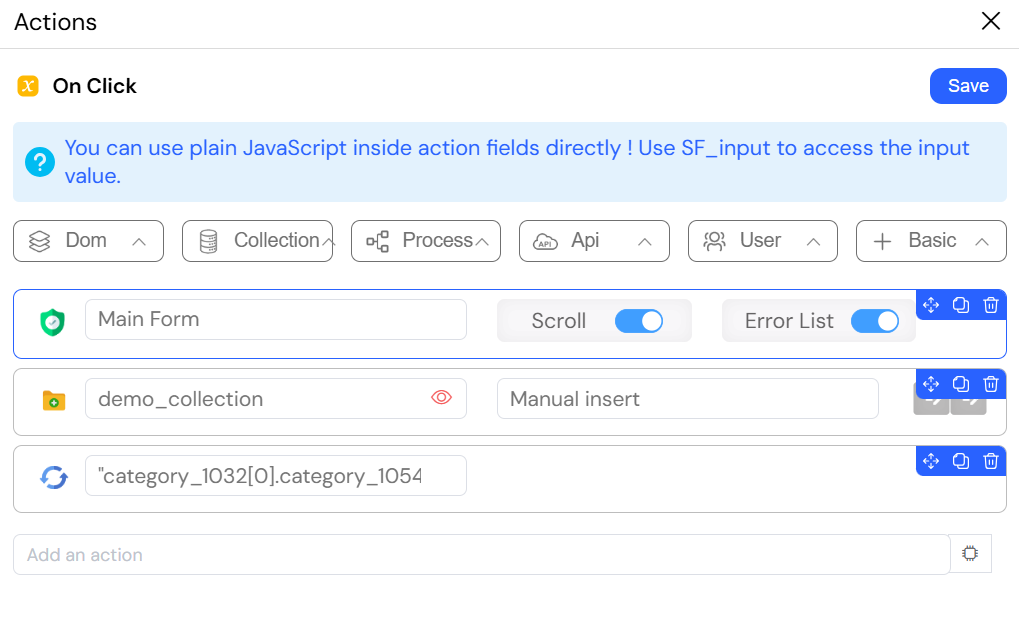
When a user fills out a form on your website and clicks "Submit", Softyflow will:
Validate the data - Check that all form fields meet the validation rules (required fields, correct formats, etc.)
Save to MongoDB - The form information is inserted as a new document into the 'demo_collection'. Form fields are mapped to the document's fields, creating a structured record in your database.
Refresh the display - Automatically reload a widget that shows the updated data (either from a dynamic or static data source)
5.2. Data Loading
5.2.1. MongoDB Aggregation
This image displays the configuration for an "Aggregate collection" action in Softyflow. This action is used to perform advanced data processing on a MongoDB collection using an aggregation pipeline.
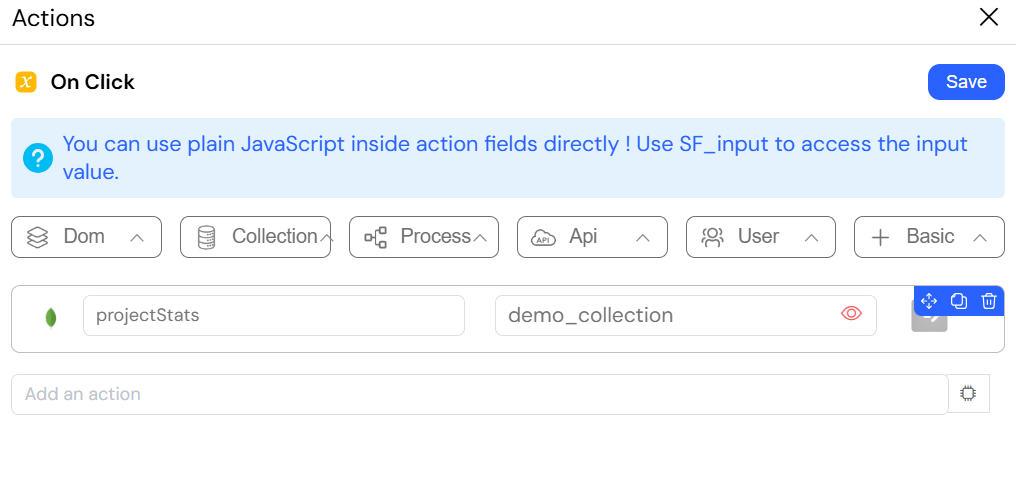
This action is useful for complex data retrieval scenarios, such as filtering, grouping, and transforming data before it is used in a web interface or another process.
5.3. Update Operations
5.3.1. Bulk Update (SQL)
The image shows the configuration of an "Update in EDS" action, designed to modify records in an SQL database. This action is equivalent to an SQL UPDATE statement and is used to change existing data.
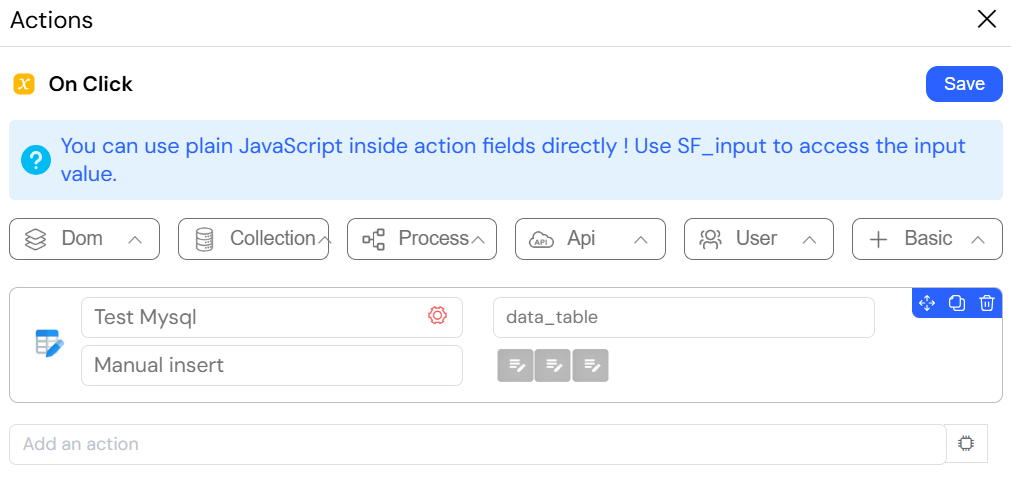
This action is essential for operations like saving changes from an edit form, where a specific record needs to be updated with new information.
5.3.2. MongoDB Update
This image illustrates the "Update in collection" action, which is used to modify a single document in a MongoDB collection.
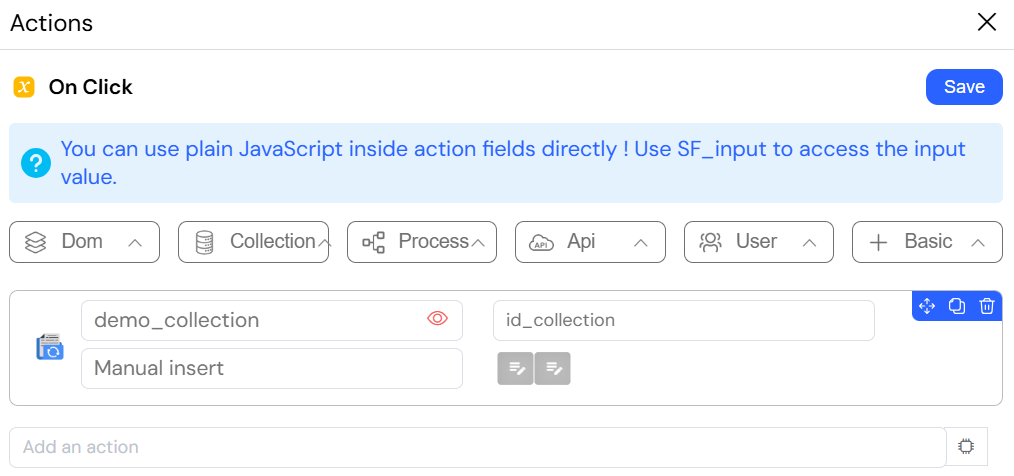
This action is commonly used to save changes to an existing record that is being edited in a form.
6. Forms Integration
6.1. EDS-Based Form
This image shows the configuration of a "Find many in EDS" action. This action is used to retrieve multiple records from an SQL database that match a specific condition.
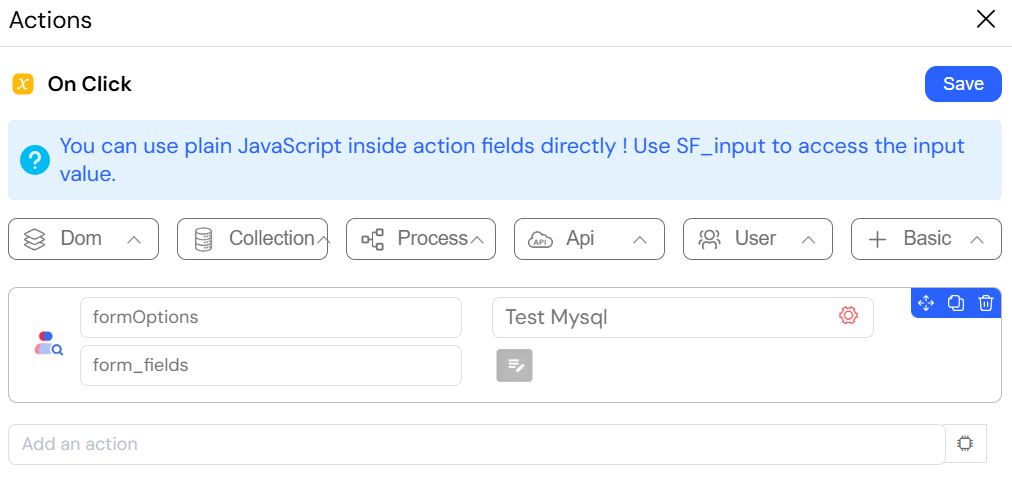
This action is useful for populating tables or lists in a user interface with data that matches user-defined criteria, such as showing all customers from a selected city.
6.2. Collection-Based Form
This image showcases the "Get document" action, which retrieves a single document from a MongoDB collection and populates a form with its data.
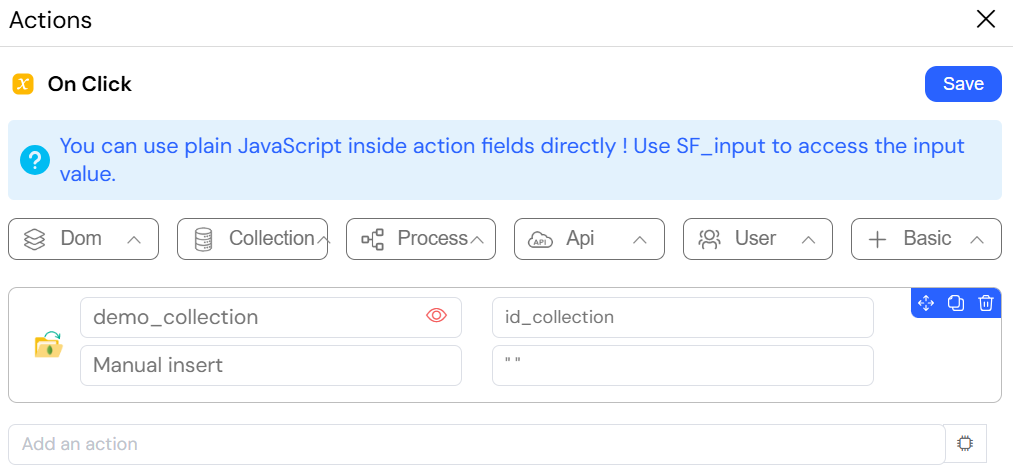
This action is fundamental for creating "edit" forms, where a user selects a record from a list, and the form is pre-filled with the data of that record, ready for modification.
7. Best Practices
7.1. When to Use SQL via EDS
✅ Use for:
- Existing enterprise systems integration
- Complex reporting and analytics
- Large datasets with established relationships
- Multi-system data synchronization
- Regulatory compliance requirements
7.2. When to Use MongoDB Collections
✅ Use for:
- Rapid application development
- Flexible, evolving data structures
- Application-specific configurations
- Temporary or session data
- Small to medium datasets
8. Security Considerations
8.1. SQL Security
- Use parameterized queries to prevent SQL injection
- Implement role-based access control
- Encrypt sensitive data in transit and at rest
- Regular security audits and updates
8.2. MongoDB Security
- Validate input data before insertion
- Use appropriate field-level permissions
- Implement data sanitization
- Regular backup and recovery procedures
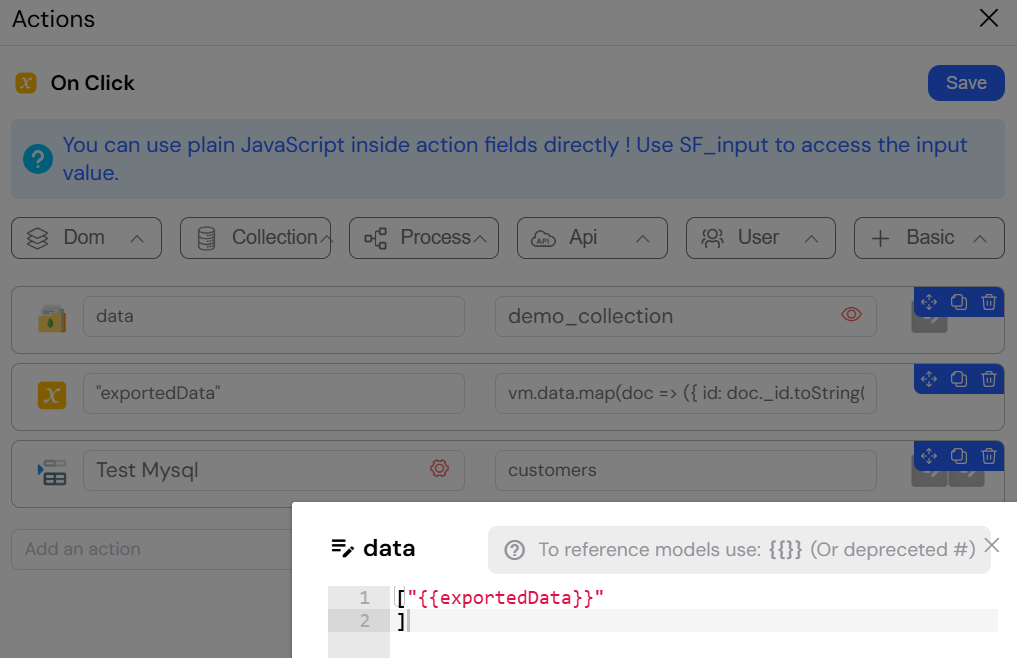
9. Migration Between Systems
9.1. From MongoDB to SQL
This image displays an action sequence in Softyflow that automates a data migration process from a MongoDB collection to an SQL database. The process consists of the following steps:
- Get Collection: The
getCollectionaction retrieves all documents from thedemo_collectionin MongoDB. - Set Variable: The retrieved data is then stored in a variable named
exportedData. This step often involves mapping or transforming the data to a format suitable for the SQL database. - Insert in EDS: The
insert in EDSaction takes the data from theexportedDatavariable and inserts it into thecustomerstable in theTest MysqlSQL database. The fields from the MongoDB documents are mapped to the corresponding columns in the SQL table.
This sequence is a powerful example of how Softyflow can be used to create data pipelines and automate complex workflows involving different database systems.
This documentation provides practical examples for both SQL and MongoDB usage in Softyflow applications. Choose the appropriate data storage method based on your specific requirements and existing infrastructure.
Next Steps
Now that you understand database integration, continue building your application:
- Web Interface Design - Create interfaces that display and interact with your data
- Process Design - Design processes that use your database data
- Integration - Connect with external data sources and APIs
- Reporting - Create reports from your database data
- Test & Deploy - Test your database integrations across environments
- Monitor & Run - Monitor your data-driven processes
For hands-on experience, try our step-by-step tutorials or watch our database video tutorials.
For advanced database features, explore our EDS documentation, MongoDB integration, and learn about using databases in Select widgets and Table widgets.